Abstract
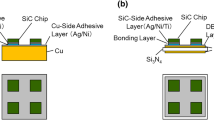
The effect of the diameter of Bi–Sn alloy particles on the bonding strength of hybrid joints formed between SiC chips and direct-bonded copper (DBC) plates using a Cu nanoparticles/Bi–Sn solder was studied. The bonding strength was the highest at 40 MPa for a Bi–Sn alloy particle diameter of 10 µm. Further, the bonding strength was dependent on the area of the bonding layer adhering to the SiC-side fracture surface, as determined by the die-shear test. Ni, which was deposited on the SiC chips and DBC plates before the bonding process, remained near the interfacial area of the bonding layer in the joints formed using the 5 µm particles. In contrast, Ni diffused all over the bonding area, with the exception of the interfacial area where Cu–Sn compounds were formed, in the joints produced using the larger alloy particles. The distribution of Sn in the bonding layer became more uniform and the segregation of Bi at the interface became more pronounced as the particle size was reduced. Further, with an increase in the particle size, the Ag layers deposited on the surfaces of the SiC chips and DBC plates diffused into the bonding layer after the first firing step at 473 K, which was performed before the secondary firing step at 623 K. These results imply that the diameter of the Bi–Sn solder particles in hybrid joints affects the interfacial structure, as it governs the wetting behavior of the Bi–Sn solder and hence has a determining effect on the bonding strength.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.G. Neudeck, R.S. Okojie, L.Y. Chen, Proc. IEEE. 90, 1065 (2002)
G. Liu, B.R. Tuttle, S. Dhar, Appl. Phys. Rev. 2, 021307 (2015)
T. Kimoto, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 040103 (2015)
H.S. Chin, K.Y. Cheong, A.B. Ismail, Metall. Mater. Trans B 41, 824 (2010)
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, J.K. Kivilahti, Mater. Sci. Eng. R. 49, 1 (2005)
H. Ma, J.C. Suhling, J. Mater. Sci. 44, 1141 (2009)
L. Zhang, C. He, Y. Guo, J. Han, Y. Zhang, X. Wang, Microelectron. Reliab. 52, 559 (2012)
E. Ide, S. Angata, A. Hirose, K.F. Kobayashi, Acta Mater. 53, 2385 (2005)
K.S. Siow, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 947 (2014)
T. Ishizaki, R. Watanabe, J. Mater Chem. 22, 25198 (2012)
T. Ishizaki, T. Satoh, A. Kuno, A. Tane, M. Yanase, F. Osawa, Y. Yamada, Microelectron. Reliab. 53, 1543 (2013)
T. Yamakawa, T. Takemoto, M. Shimoda., H. Nishikawa, K. Shiokawa, N. Terada, J. Electron. Mater. 42, 1260 (2013)
Y. Kobayashi, T. Shirochi, Y. Yasuda, T. Morita, Int. J. Adhes Adhes. 33, 50 (2012)
J. Liu, H. Chen, H. Ji, M. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 33289 (2016)
J. Li, C.M. Johnson, C. Buttay, W. Sabbah, S. Azzopardi, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 215, 299 (2015)
Ph Buffat, J.P. Borel, Phys. Rev. A. 13, 2287 (1976)
T. Ishizaki, K. Akedo, T. Satoh, R. Watanabe, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 774 (2014)
T. Satoh, T. Ishizaki, K. Akedo, J. Electron. Mater. 46, 1279 (2017)
T. Satoh, T. Ishizaki, M. Usui, Mater. Des. 124, 203 (2017)
S. Tajima, T. Satoh, T. Ishizaki, M. Usui, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 1764 (2017)
B. Predel, Phase equilibria, crystallographic and thermodynamic data of binary alloys B-Ba-C-Zr, in Landolt-Börnstein - Group IV Physical Chemistry, ed. by O. Madelung, vol 5B (Springer, Berlin, 1992). http://materials.springer.com/bp/docs/978-3-540-46733-5. Accessed 14 July 2015
P. Franke, D. Neuschütz, Binary systems. Part 3: Binary Systems from Cs-K to Mg-Zr Cu-Sn, in Landolt-Börnstein - Group IV Physical Chemistry, ed. by P. Franke, D. Neuschütz, vol 19B3 (Springer, Berlin, 2005). http://materials.springer.com/lb/docs/sm_lbs_978-3-540-31688-6_17. Accessed 14 July 2015
G.P. Vassilev, K.I. Lilova, J.-C. Gachonc, J. Alloy. Compd. 469, 264 (2009)
W.H. Tao, C. Chen, C.E. Ho, W.T. Chen, C.R. Kao, Chem. Mater. 13, 1051 (2001)
I. Karakaya, W.T. Thompson, J. Phase Equilibria. 14, 525 (1993)
M.S. Lee, C. Chen, C.R. Kao, Chem. Mater. 11, 292 (1999)
M.S. Lee, C.M. Liu, C.R. Kao, J. Electron. Mater. 28, 57 (1999)
S.W. Chen, Y.W. Yen, J. Electron. Mater. 28, 1203 (1999)
A. Hayashi, C.R. Cao, Y.A. Chang, Scr. Mater. 37, 393 (1997)
A. Paul, C. Ghosh, W.J. Boettinger, Metall. Mater. Trans. A. 42A, 952 (2011)
Y. Yuan, Y. Guan, D. Li, N. Moelans, J. Alloys Compd. 661, 282 (2016)
S. Bader, W. Gust, H. Hiever, Acta Metall. Mater. 43, 329 (1995)
S.-W. Yoon, M.D. Glover, K. Shiozaki, IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 28, 2448 (2013)
J. Shen, Y.C. Chan, S.Y. Liu, Acta Mater. 57, 5196 (2004)
B. Predel, Phase equilibria, crystallographic and thermodynamic data of binary alloys Cr-Cs-Cu-Zr, in Landolt-Börnstein - Group IV Physical Chemistry, ed. by O. Madelung, vol 5D (Springer, Berlin, 1994). http://materials.springer.com/lb/docs/sm_lbs_978-3-540-47417-3_1119. Accessed 25 Dec 2017
B. Predel, Phase equilibria, crystallographic and thermodynamic data of binary alloys Cr-Cs-Cu-Zr, in Landolt-Börnstein - Group IV Physical Chemistry, ed. by O. Madelung, vol 5I (Springer, Berlin, 1998), http://materials.springer.com/lb/docs/sm_lbs_978-3-540-70692-2_2265. Accessed 25 Dec 2017
M. Nakayama, M. Kajihara, Mater. Trans. 55, 1266 (2014)
A. Wierzbicka-Miernik, J. Wojewoda-Budka, K. Miernik, L. Litynska-Dobrzynsk, N. Schell, J. Alloys Compd. 693, 1102 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Satoh, T., Ishizaki, T. & Usui, M. Effect of bismuth–tin alloy particle diameter on bonding strength of copper nanoparticles/bismuth–tin solder hybrid joints. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 29, 7161–7176 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8704-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8704-1



