Abstract
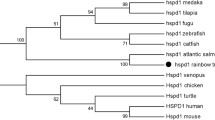
HSP90 plays important roles in multiple cellular stress responses. Here, two cytoplasmic HSP90 isoforms, ScHSP90α and ScHSP90β, were identified from Siniperca chuatsi. Their cDNA and gDNA structures, amino acid sequence features, and sequence identities and phylogenetic analysis with other species were described. Their expression profiles during embryonic development in different tissues and under stressful conditions were analyzed using real-time quantitative PCR. During embryogenesis, transcripts of both genes were detected at low levels during the early developmental stages and were up-regulated from appearance of myomere for ScHSP90a and closure of blastopore for ScHSP90β. ScHSP90α showed a tissue-specific variation with high expression in ovary and brain under non-stressed conditions, while ScHSP90β was ubiquitously highly expressed in different tissues. Acute heat shock resulted in a strong up-regulation of ScHSP90α in heart, liver, and head kidney, while it only weakly induced ScHSP90β in these tissues. ScHSP90α was also markedly induced in liver in a time-dependent manner under hypoxia, while the expression of ScHSP90β was not affected by hypoxia. Additionally, Aeromonas hydrophila infection markedly augmented ScHSP90α in head kidney and spleen and mildly up-regulated ScHSP90β in spleen, while suppressing ScHSP90β in head kidney. These results suggest that ScHSP90α and ScHSP90β are differently involved in embryogenesis and under different environmental conditions including high temperature, hypoxia, and bacterial infection. This study will benefit to further clarify the roles of fish HSP90 isoforms in embryogenesis and under stressful conditions and contribute to further study on enhancing stress tolerance and disease resistance of mandarin fish.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622
Chen CF, Li J (1996) Studies on virulence and isolation of pathogenic bacteria causing bacterial septicemia in mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi basilewsky). J Huazhong Agric Univ 15:370–373
Chen B, Piel WH, Gui LM, Bruford E, Monteiro A (2005) The HSP90 family of genes in the human genome: insights into their divergence and evolution. Genomics 86:627–637
Chen B, Zhong DB, Monteiro A (2006) Comparative genomics and evolution of the HSP90 family of genes across all kingdoms of organisms. BMC Genom 7:156
Chen YM, Kuo CE, Wang TY, Shie PS, Wang WC, Huang SL, Tsai TJ, Chen PP, Chen JC, Chen TY (2010) Cloning of an orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides heat shock protein 90AB (HSP90AB) and characterization of its expression in response to nodavirus. Fish Shellfish Immunol 28:895–904
Chen WX, Liang XF, Fu Y, Ye W (2012) The plankton composition in mandarinfish Siniperca chuatsi ponds and bait fish ponds in hot season. Chin J Fish 25:25–29
Csermely P, Schnaider T, Soti C, Prohaszka Z, Nardai G (1998) The 90-kda molecular chaperone family: structure, function, and clinical applications: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther 79:129–168
Du SJ, Li HQ, Bian YH, Zhong YW (2008) Heat-shock protein 90alpha1 is required for organized myofibril assembly in skeletal muscles of zebrafish embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:554–559
Etard C, Behra M, Fischer N, Hutcheson D, Geisler R, Strahle U (2007) The UCS factor STEIF/UNC-45b interacts with the heat shock protein HSP90a during myofibrillogenesis. Dev Biol 308:133–143
Etard C, Roostalu U, Strahle U (2008) Shuttling of the chaperones UNC45b and HSP90a between the A band and the Z line of the myofibril. J Cell Biol 180:1163–1175
Gornati R, Papis E, Rimoldi S, Chini V, Terova G, Prati M, Saroglia M, Bernardini G (2005) Molecular markers for animal biotechnology: sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.) Hmg-coa reductase mRNA. Gene 344:299–305
Gupta RS (1995) Phylogenetic analysis of the 90 kD heat shock family of protein sequences and an examination of the relationship among animals, plants, and fungi species. Mol Biol Evol 12:1063–1073
Hall BG (2013) Building phylogenetic trees from molecular data with mega. Mol Biol Evol 30:1229–1235
Hermesz E, Abraham M, Nemcsok J (2001) Identification of two HSP90 genes in carp. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 129:397–407
Jackson SE (2013) HSP90: structure and function. Top Curr Chem 328:155–240
Krone PH, Sass JB (1994) HSP90alpha and HSP90beta genes are present in the zebrafish and are differentially regulated in developing embryos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 204:746–752
Langer T, Rosmus S, Fasold H (2003) Intracellular localization of the 90 kDa heat shock protein (HSP90alpha) determined by expression of a EGFP-HSP90alpha-fusion protein in unstressed and heat stressed 3T3 cells. Cell Biol Int 27:47–52
Lao HH, Sun YN, Yin ZX, Wang J, Chen C, Weng SP, He W, Guo CJ, Huang XD, Yu XQ, He JG (2008) Molecular cloning of two c1q-like cDNAs in mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 125:37–46
Lele Z, Hartson SD, Martin CC, Whitesell L, Matts RL, Krone PH (1999) Disruption of zebrafish somite development by pharmacologic inhibition of HSP90. Dev Biol 210:56–70
Li FH, Luan W, Zhang CS, Zhang JQ, Wang B, Xie YS, Li SH, Xiang JH (2009) Cloning of cytoplasmic heat shock protein 90 (FcHSP90) from Fenneropenaeus chinensis and its expression response to heat shock and hypoxia. Cell Stress Chaperones 14:161–172
Lin TS, Xue LY, Sun AF, Zhu YF (2012) Effect of temperature and pathogen on HSP90 expression in Larimichthys crocea. Chi J Cell Biol 34:555–564
Montero D, Terova G, Rimoldi S, Tort L, Negrin D, Zamorano MJ, Izquierdo M (2015) Modulation of adrenocorticotrophin hormone (ACTH)-induced expression of stress-related genes by PUFA in inter-renal cells from european sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). J Nutr Sci. doi:10.1017/jns.2015.6
Ni M, Wen HS, Li JF , Chi ML, Ren YY, Song ZF , Ding HM (2014) Two HSPs gene from juvenile Amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii): cloning, characterization and expression pattern to crowding and hypoxia stress. Fish Physiol Biochem 40:1801–1816
Pan F, Zarate JM, Tremblay GC, Bradley TM (2000) Cloning and characterization of salmon HSP90 cDNA: upregulation by thermal and hyperosmotic stress. J Exp Zool 287:199–212
Roberts RJ, Agius C, Saliba C, Bossier P, Sung YY (2010) Heat shock proteins (chaperones) in fish and shellfish and their potential role in relation to fish health: a review. J Fish Dis 33:789–801
Rupik W, Jasik K, Bembenek J, Widlak W (2011) The expression patterns of heat shock genes and proteins and their role during vertebrate’s development. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 159:349–366
Sarkar S, Singh MD, Yadav R, Arunkumar KP, Pittman GW (2011) Heat shock proteins: molecules with assorted functions. Front Biol 6:312–327
Sass JB, Weinberg ES, Krone PH (1996) Specific localization of zebrafish HSP90alpha mRNA to myoD–expressing cells suggests a role for HSP90alpha during normal muscle development. Mech Dev 54:195–204
Sreedhar AS, Csermely P (2004) Heat shock proteins in the regulation of apoptosis—new strategies in tumor therapy: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther 101:227–257
Stenslokken KO, Ellefsen S, Larsen HK, Vaage J, Nilsson GE (2010) Expression of heat shock proteins in anoxic crucian carp (Carassius carassius): support for cold as a preparatory cue for anoxia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298:R1499–R1508
Tokyol C, Karaorman G, Bastug M (2005) Effects of acute and adaptive hypoxia on heat shock protein expression in hepatic tissue. High Alt Med Biol 6:247–255
Wang TT, Chen SL, Meng L, Liu Y (2010) Molecular cloning and expression of heat shock protein 90 gene cDNA from turbot Psetta maxima. Prog Fish Sci 31:51–59
Wang PF, Zeng S, Xu P, Zhou L, Zeng L, Lu X, Wang HF, Li GF (2014) Identification and expression analysis of two HSP70 isoforms in mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi. Fish Sci 80:803–817
Wang PF, Xu P, Zeng S, Zhou L, Zeng L, Li GF (2015) Comparative analysis of sequence feature and expression of two heat shock cognate 70 genes in mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi. Gene 560:226–236
Yamashita M, Yabu T, Ojima N (2010) Stress protein HSP70 in fish. Aquat BioSci Monogr 3:111–141
Young JC, Obermann WM, Hartl FU (1998) Specific binding of tetratricopeptide repeat proteins to the c-terminal 12-kDa domain of HSP90. J Biol Chem 273:18007–18010
Zhou CP, Lin HZ, Huang Z, Wang J, Wang Y, Yu W (2015) Effects of dietary soybean isoflavones on non-specific immune responses and hepatic antioxidant abilities and mRNA expression of two heat shock proteins (HSPs) in juvenile golden pompano Trachinotus ovatus under pH stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol 47:1043–1053
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by Foshan Innovative and Entepreneurial Research Team Program (No. 2014IT100122), The Science and Technology Projects of Guangdong Oceanic and Fisheries (No. A201401A02), The Science and Technology Planning Projects of Guangdong Province (Nos. 2014A020208022, 2015A030310253), the Special Scientific Research Funds for Central Non-profit Institutes, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (No. 2014TS26) and Special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest, China (No. 201303048).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, PF., Zeng, S., Xu, P. et al. Two HSP90 genes in mandarin fish Siniperca chuatsi: identification, characterization and their specific expression profiles during embryogenesis and under stresses. Fish Physiol Biochem 42, 1123–1136 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0202-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10695-016-0202-x