Abstract
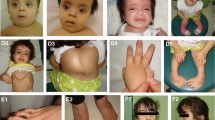
Generalized lentiginosis (GL) is characterized by widespread lentigines without associated noncutaneous abnormalities. In this study we performed a genome-wide linkage search in a Chinese family with GL and localized the familial GL locus to chromosome 4q21.1–q22.3, with a maximum two-point LOD score of 3.01 for D4S395 and D4S423 at a recombination fraction of 0. Multipoint analysis (maximum LOD score of 5.08 between markers D4S395 and D4S1563) and haplotype construction showed strong evidence of linkage in a region of 20 Mb flanked by markers D4S2915 and D4S1560 on chromosome 4q21.1–q22.3. This is the first report of linkage for GL, and it will provide further insight into the controversy of whether GL is an entity distinct from LEOPARD syndrome.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelmalek NF, Gerber TL, Menter A (2002) Cardiocutaneous syndromes and associations. J Am Acad Dermatol 46:161–183
Arnsmeier SL, Paller AS (1996) Pigmentary anomalies in the multiple lentigines syndrome: is it distinct from LEOPARD syndrome? Pediatr Dermatol 13:100–104
Barsh GS (1995) Pigmentation, pleiotropy, and genetic pathways in humans and mice. Am J Hum Genet 57:743–747
Bastiaens M, ter Huurne J, Gruis N, Bergman W, Westendorp R, Vermeer BJ, Bouwes Bavinck JN (2001) The melanocortin-1-receptor gene is the major freckle gene. Hum Mol Genet 10:1701–1708
Ber Rahman S, Bhawan J (1996) Lentigo. Int J Dermatol 35:229–239
Betti R, Pozzi M, Inselvini E, Pazzini C, Crosti C (1998) Sporadic generalized lentiginosis without systemic involvement. Eur J Dermatol 8:183–185
Broman KW, Murray JC, Sheffield VC, White RL, Weber JL (1998) Comprehensive human genetic maps: individual and sex-specific variation in recombination. Am J Hum Genet 63:861–689
Chong WS, Klanwarin W, Giam YC (2004) Generalized lentiginosis in two children lacking systemic associations: case report and review of the literature. Pediatr Dermatol 21:139–145
Chrousos GP, Stratakis CA (1998) Carney complex and the familial lentiginosis syndromes: link to inherited neoplasias and developmental disorders, and genetic loci. J Intern Med 243:573–579
Coppin BD, Temple IK (1997) Multiple lentigines syndrome (LEOPARD syndrome or progressive cardiomyopathic lentiginosis). J Med Genet 34:582–586
Curtis D, Gurling H (1993) A procedure for combining two-point LOD scores into a summary multipoint map. Hum Hered 43:173–185
Dib C, Faure S, Fizames C, Samson D, Drouot N, Vignal A, Millasseau P, Marc S, Hazan J, Seboun E, Lathrop M, Gyapay G, Morissette J, Weissenbach J (1996) A comprehensive genetic map of the human genome based on 5,264 microsatellites. Nature 380:152–154
Digilio MC, Conti E, Sarkozy A, Mingarelli R, Dottorini T, Marino B, Pizzuti A, Dallapiccola B (2002) Grouping of multiple-lentigines/LEOPARD and Noonan syndromes on the PTPN11 gene. Am J Hum Genet 71:389–394
Gyapay G, Morissette J, Vignal A, Dib C, Fizames C, Millasseau P, Marc S, Bernardi G, Lathrop M, Weissenbach J (1994) The 1993-94 Gènèthon human genetic linkage map. Nat Genet 7:246–339
Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM, Julier C, Ott J (1984) Strategies for multilocus linkage analysis in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:3443–3446
Salama NR, Yeung T, Schekman RW (1993) The Sec13p complex and reconstitution of vesicle budding from the ER with purified cytosolic proteins. EMBO J 12:4073–4082
Soragna D, Vettori A, Carraro G, Marchioni E, Vazza G, Bellini S, Tupler R, Savoldi F, Mostacciuolo ML (2003) A locus for migraine without aura maps on chromosome 14q21.2–q22.3. Am J Hum Genet 72:161–167
Stratakis CA, Carney JA, Lin JP, Papanicolaou DA, Karl M, Kastner DL, Pras E, Chrousos GP(1996) Carney complex, a familial multiple neoplasia and lentiginosis syndrome. Analysis of 11 kindreds and linkage to the short arm of chromosome 2. J Clin Invest 97:699–705
Sturm RA, Teasdale RD, Box NF (2001) Human pigmentation genes: identification, structure and consequences of polymorphic variation. Gene 277:49–62
Tang BL, Peter F, Krijnse-Locker J, Low SH, Griffiths G, Hong W (1997) The mammalian homolog of yeast Sec13p is enriched in the intermediate compartment and is essential for protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi apparatus. Mol Cell Biol 17:256–266
Tang BL, Zhang T, Low DY, Wong ET, Horstmann H, Hong W (2000) Mammalian homologues of yeast sec31p. An ubiquitously expressed form is localized to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) exit sites and is essential for ER-Golgi transport. J Biol Chem 275:13597–13604
Uhle P, Norvell SS Jr (1988) Generalized lentiginosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 18:444–447
Voron DA, Hatfield HH, Kalkhoff RK (1976) Multiple lentigines syndrome. Case report and review of the literature. Am J Med 60:447–456
Zahorcsek Z, Schneider I (1996) Generalized lentiginosis manifesting through three generations. Int J Dermatol 35:357–359
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the national 973 and 863 Programs, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Shanghai Municipal Commission for Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qinghe Xing and Xiangdong Chen contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, Q., Chen, X., Wang, M. et al. A locus for familial generalized lentiginosis without systemic involvement maps to chromosome 4q21.1–q22.3. Hum Genet 117, 154–159 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-1284-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-1284-1