Abstract
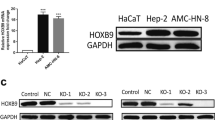
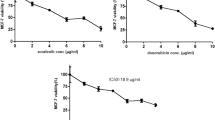
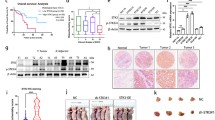
Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1) is involved in tumorigenesis, tumor growth and metastasis, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in many digestive tract tumors. It is reportedly highly expressed in Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma, but its effects on the occurrence and progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) remain unclear. In this study, real-time PCR and western blot analysis confirmed significant upregulation of DCLK1 expression in human ESCC tissues and cell lines. CCK-8 assay showed that transfection with siRNA against DCLK1 (si-DCLK1) markedly inhibited cell proliferation and colony formation in the ESCC cell lines Eca109 and TE1. Transwell assay revealed that si-DCLK1 transfection inhibited the migratory and invasive capacities of Eca109 and TE1 cells. Moreover, si-DCLK1 increased the chemosensitivity of these cells to cisplatin, as indicated by inhibited cell viability and colony formation, and increased ROS and apoptosis in cisplatin-treated cells. Western blot assay revealed that expression of nuclear β-catenin and c-Myc was significantly increased in ESCC tissues and that si-DCLK1 markedly downregulated nuclear β-catenin and c-Myc in Eca109 cells. Treatment with lithium chloride, an activator of β-catenin signaling, partially abolished the si-DCLK1-induced inhibition of proliferation, migration, invasion, and chemoresistance of ESCC cells. These findings suggest that knockdown of DCLK1 may inhibit the progression of ESCC by regulating proliferation, migration, invasion, and chemosensitivity via suppressing the β-catenin/c-Myc pathway, supporting a promising therapeutic target against ESCC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandrakesan P, Weygant N, May R, Qu D, Chinthalapally HR, Sureban SM, Ali N, Lightfoot SA, Umar S, Houchen CW (2014) DCLK1 facilitates intestinal tumor growth via enhancing pluripotency and epithelial mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 5:9269–9280. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2393
Chandrakesan P, Yao J, Qu D, May R, Weygant N, Ge Y, Ali N, Sureban SM, Gude M, Vega K, Bannerman-Menson E, Xia L, Bronze M, An G, Houchen CW (2017) Dclk1, a tumor stem cell marker, regulates pro-survival signaling and self-renewal of intestinal tumor cells. Mol Cancer 16:30. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0594-y
Christman EM, Chandrakesan P, Weygant N, Maple JT, Tierney WM, Vega KJ, Houchen CW (2019) Elevated doublecortin-like kinase 1 serum levels revert to baseline after therapy in early stage esophageal adenocarcinoma. Biomark Res 7:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40364-019-0157-z
Deng H, Qianqian G, Ting J, Aimin Y (2018) miR-539 enhances chemosensitivity to cisplatin in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting DCLK1. Biomed Pharmacother 106:1072–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.024
Gao T, Wang M, Xu L, Wen T, Liu J, An G (2016) DCLK1 is up-regulated and associated with metastasis and prognosis in colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 142:2131–2140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-016-2218-0
Ge Y, Weygant N, Qu D, May R, Berry WL, Yao J, Chandrakesan P, Zheng W, Zhao L, Zhao KL, Drake M, Vega KJ, Bronze MS, Tomasek JJ, An G, Houchen CW (2018) Alternative splice variants of DCLK1 mark cancer stem cells, promote self-renewal and drug-resistance, and can be targeted to inhibit tumorigenesis in kidney cancer. Int J Cancer 143:1162–1175. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31400
Global Burden of Disease Cancer C, Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, Dicker DJ, Chimed-Orchir O, Dandona R, Dandona L, Fleming T, Forouzanfar MH, Hancock J, Hay RJ, Hunter-Merrill R, Huynh C, Hosgood HD, Johnson CO, Jonas JB, Khubchandani J, Kumar GA, Kutz M, Lan Q, Larson HJ, Liang X, Lim SS, Lopez AD, MF MI, Marczak L, Marquez N, Mokdad AH, Pinho C, Pourmalek F, Salomon JA, Sanabria JR, Sandar L, Sartorius B, Schwartz SM, Shackelford KA, Shibuya K, Stanaway J, Steiner C, Sun J, Takahashi K, Vollset SE, Vos T, Wagner JA, Wang H, Westerman R, Zeeb H, Zoeckler L, Abd-Allah F, Ahmed MB, Alabed S, Alam NK, Aldhahri SF, Alem G, Alemayohu MA, Ali R, Al-Raddadi R, Amare A, Amoako Y, Artaman A, Asayesh H, Atnafu N, Awasthi A, Saleem HB, Barac A, Bedi N, Bensenor I, Berhane A, Bernabe E, Betsu B, Binagwaho A, Boneya D, Campos-Nonato I, Castaneda-Orjuela C, Catala-Lopez F, Chiang P, Chibueze C, Chitheer A, Choi JY, Cowie B, Damtew S, das Neves J, Dey S, Dharmaratne S, Dhillon P, Ding E, Driscoll T, Ekwueme D, Endries AY, Farvid M, Farzadfar F, Fernandes J, Fischer F, GH TT, Gebru A, Gopalani S, Hailu A, Horino M, Horita N, Husseini A, Huybrechts I, Inoue M, Islami F, Jakovljevic M, James S, Javanbakht M, Jee SH, Kasaeian A, Kedir MS, Khader YS, Khang YH, Kim D, Leigh J, Linn S, Lunevicius R, HMA ER, Malekzadeh R, Malta DC, Marcenes W, Markos D, Melaku YA, Meles KG, Mendoza W, Mengiste DT, Meretoja TJ, Miller TR, Mohammad KA, Mohammadi A, Mohammed S, Moradi-Lakeh M, Nagel G, Nand D, Le Nguyen Q, Nolte S, Ogbo FA, Oladimeji KE, Oren E, Pa M, Park EK, Pereira DM, Plass D, Qorbani M, Radfar A, Rafay A, Rahman M, Rana SM, Soreide K, Satpathy M, Sawhney M, Sepanlou SG, Shaikh MA, She J, Shiue I, Shore HR, Shrime MG, So S, Soneji S, Stathopoulou V, Stroumpoulis K, Sufiyan MB, Sykes BL, Tabares-Seisdedos R, Tadese F, Tedla BA, Tessema GA, Thakur JS, Tran BX, Ukwaja KN, BSC U, Vlassov VV, Weiderpass E, Wubshet Terefe M, Yebyo HG, Yimam HH, Yonemoto N, Younis MZ, Yu C, Zaidi Z, MES Z, Zenebe ZM, CJL M, Naghavi M (2017) Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol 3:524–548. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688
Huang XP, Li X, Situ MY, Huang LY, Wang JY, He TC, Yan QH, Xie XY, Zhang YJ, Gao YH, Li YH, Rong TH, Wang MR, Cai QQ, Fu JH (2018) Entinostat reverses cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via down-regulation of multidrug resistance gene 1. Cancer Lett 414:294–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.10.023
Ji D, Zhan T, Li M, Yao Y, Jia J, Yi H, Qiao M, Xia J, Zhang Z, Ding H, Song C, Han Y, Gu J (2018) Enhancement of sensitivity to chemo/radiation therapy by using miR-15b against DCLK1 in colorectal cancer. Stem Cell Rep 11:1506–1522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.10.015
Kauppila JH, Mattsson F, Brusselaers N, Lagergren J (2018) Prognosis of oesophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma following surgery and no surgery in a nationwide Swedish cohort study. BMJ Open 8:e021495. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-021495
Lee KB, Ye S, Park MH, Park BH, Lee JS, Kim SM (2014) p63-mediated activation of the beta-catenin/c-Myc signaling pathway stimulates esophageal squamous carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Cancer Lett 353:124–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.016
Li J, Wang Y, Ge J, Li W, Yin L, Zhao Z, Liu S, Qin H, Yang J, Wang L, Ni B, Liu Y, Wang H (2018) Doublecortin-like kinase 1 (DCLK1) regulates B cell-specific moloney murine leukemia virus insertion site 1 (Bmi-1) and is associated with metastasis and prognosis in pancreatic Cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 51:262–277. https://doi.org/10.1159/000495228
Liu R, Li Y, Tian L, Shi H, Wang J, Liang Y, Sun B, Wang S, Zhou M, Wu L, Nie J, Lin B, Tang S, Zhang Y, Wang G, Zhang C, Han J, Xu B, Liu L, Gong K, Zheng T (2018) Gankyrin drives metabolic reprogramming to promote tumorigenesis, metastasis and drug resistance through activating beta-catenin/c-Myc signaling in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 443:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2018.11.030
Liu W, Wang S, Sun Q, Yang Z, Liu M, Tang H (2018) DCLK1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB pathway in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 142:2068–2079. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31232
May R, Riehl TE, Hunt C, Sureban SM, Anant S, Houchen CW (2008) Identification of a novel putative gastrointestinal stem cell and adenoma stem cell marker, doublecortin and CaM kinase-like-1, following radiation injury and in adenomatous polyposis coli/multiple intestinal neoplasia mice. Stem Cells 26:630–637. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2007-0621
Sarkar S, Kantara C, Ortiz I, Swiercz R, Kuo J, Davey R, Escobar K, Ullrich R, Singh P (2012) Progastrin overexpression imparts tumorigenic/metastatic potential to embryonic epithelial cells: phenotypic differences between transformed and nontransformed stem cells. Int J Cancer 131:E1088–E1099. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.27615
Schellnegger R, Quante A, Rospleszcz S, Schernhammer M, Hohl B, Tobiasch M, Pastula A, Brandtner A, Abrams JA, Strauch K, Schmid RM, Vieth M, Wang TC, Quante M (2017) Goblet cell ratio in combination with differentiation and stem cell markers in Barrett esophagus allow distinction of patients with and without esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Prev Res 10:55–66. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-16-0117
Smyth EC, Lagergren J, Fitzgerald RC, Lordick F, Shah MA, Lagergren P, Cunningham D (2017) Oesophageal cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17048. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.48
Song W, Ma J, Lei B, Yuan X, Cheng B, Yang H, Wang M, Feng Z, Wang L (2018) Six1 promotes proliferation and migration of human colorectal cancer cells through activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cancer Sci 110:608–616. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13905
Vega KJ, May R, Sureban SM, Lightfoot SA, Qu D, Reed A, Weygant N, Ramanujam R, Souza R, Madhoun M, Whorton J, Anant S, Meltzer SJ, Houchen CW (2012) Identification of the putative intestinal stem cell marker doublecortin and CaM kinase-like-1 in Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27:773–780. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06928.x
Wang X, Yang Y, Huycke MM (2017) Commensal-infected macrophages induce dedifferentiation and reprogramming of epithelial cells during colorectal carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 8:102176–102190. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22250
Westphalen CB, Takemoto Y, Tanaka T, Macchini M, Jiang Z, Renz BW, Chen X, Ormanns S, Nagar K, Tailor Y, May R, Cho Y, Asfaha S, Worthley DL, Hayakawa Y, Urbanska AM, Quante M, Reichert M, Broyde J, Subramaniam PS, Remotti H, Su GH, Rustgi AK, Friedman RA, Honig B, Califano A, Houchen CW, Olive KP, Wang TC (2016) Dclk1 defines quiescent pancreatic progenitors that promote injury-induced regeneration and tumorigenesis. Cell Stem Cell 18:441–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2016.03.016
Weygant N, Qu D, May R, Tierney RM, Berry WL, Zhao L, Agarwal S, Chandrakesan P, Chinthalapally HR, Murphy NT, Li JD, Sureban SM, Schlosser MJ, Tomasek JJ, Houchen CW (2015) DCLK1 is a broadly dysregulated target against epithelial-mesenchymal transition, focal adhesion, and stemness in clear cell renal carcinoma. Oncotarget 6:2193–2205. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3059
Whorton J, Sureban SM, May R, Qu D, Lightfoot SA, Madhoun M, Johnson M, Tierney WM, Maple JT, Vega KJ, Houchen CW (2015) DCLK1 is detectable in plasma of patients with Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 60:509–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3347-4
Wu X, Ruan Y, Jiang H, Xu C (2017) MicroRNA-424 inhibits cell migration, invasion, and epithelial mesenchymal transition by downregulating doublecortin-like kinase 1 in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 85:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2017.01.020
Yuan H, Zhou W, Yang Y, Xue L, Liu L, Song Y (2018) ISG15 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis via c-MET/Fyn/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 367:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.03.017
Zhao YL, Li JB, Li YJ, Li SJ, Zhou SH, Xia H (2018) Capn4 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis by regulating ZEB1 through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Thorac Cancer 10:24–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/1759-7714.12893
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the American Journal Experts for helpful suggestion and highly qualified English language edit.
Funding
Doctoral Research Initiation Fund of Henan Provincial people’s Hospital Post-doctoral Research Initiation Fund of Henan Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The ethics committee of Henan Provincial People’s Hospital approved the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• DCLK1 is upregulated in ESCC tissues and cells.
• DCLK1 knockdown reduces the proliferation, migration, and invasion of ESCC cells.
• DCLK1 knockdown sensitizes ESCC cells to cisplatin.
• DCLK1 affects ESCC progression via the β-catenin/c-Myc pathway.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Zhou, S., Guo, E. et al. DCLK1 inhibition attenuates tumorigenesis and improves chemosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting β-catenin/c-Myc signaling. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 472, 1041–1049 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02415-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02415-z