Abstract
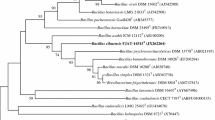
A novel facultatively aerobic bacterium designated SY8 was isolated from a peanut rhizosphere soil sample collected in Jiangsu Province, China. Cells are Gram-stain-positive, rod-shaped, and agar colonies are creamy, opaque, and usually rhizoidal. Strain growth occurs at 30 – 45 °C (optimum 30 °C), pH 4.0 – 10.0 (optimum pH 6.0) and 0 – 4% (w/v) NaCl (optimum 2%) in Luria–Bertani medium. Phylogenetic analysis of the 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that strain SY8 forms a distinct lineage in the clade of genus Bacillus and is related to Bacillus pseudomycoides DSM 12442 T (99.9%). Phylogenetic analysis of the concatenated gene sequences of 16S rRNA, gryB and rpoD also indicated that strain SY8 forms a distinct lineage in Bacillus. Calculation of the average nucleotide identities and the digital DNA–DNA hybridization values between strain SY8 and the related type Bacillus strains further revealed that strain SY8 represents a distinct species. The predominant cellular fatty acids are iso C15:0 (28.7%) and summed feature 3 (C16:1ω7c and/or C16:1ω6c) (10.3%). The major polar lipids consisted of diphosphatidyl glycerol, phosphatidyl glycerol, phosphatidyl ethanolamine, phosphatidylinositol, and three unidentified phospholipids. The major menaquinone of SY8 was MK-7. Based on phenotypic, phylogenetic, chemotaxonomic, and genomic features, strain SY8 represents a novel species of the genus Bacillus. The name Bacillus arachidis sp. nov. is proposed with strain SY8T (= CCTCC AB 2021100 T=LMG 32409 T) designated as the type strain.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Strain SY8T = CCTCC AB 2021100 T = LMG 32409 T. The GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene and the whole-genome sequences of strain SY8T are OM062591 and JAGDQJ000000000, respectively.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Bérdy J (2005) Bioactive microbial metabolites. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 58:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2005.1
Goodfellow M, Fiedler HP (2010) A guide to successful bioprospecting: informed by actinobacterial systematics. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 98:119–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9460-2
Méndez Acevedo M, Carroll LM, Mukherjee M, Mills E, Xiaoli L, Dudley EG, Kovac J (2020) Novel effective Bacillus cereus group species “Bacillus clarus” is represented by antibiotic-producing strain ATCC 21929 isolated from soil. mSphere 5:e00882-e920. https://doi.org/10.1128/mSphere.00882-20
Guinebretière MH, Thompson FL, Sorokin A, Normand P, Dawyndt P, Ehling-Schulz M, Svensson B, Sanchis V, Nguyen-The C, Heyndrickx M, De Vos P (2008) Ecological diversification in the Bacillus cereus group. Environ Microbiol 10:851–865. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2007.01495.x
Jensen MP, Ardö Y, Vogensen FK (2009) Isolation of cultivable thermophilic lactic acid bacteria from cheeses made with mesophilic starter and molecular comparison with dairy-related Lactobacillus helveticus strains. Lett Appl Microbiol 49:396–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2009.02673.x
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001755
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.64483-0
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
Guinebretière MH, Velge P, Couvert O, Carlin F, Debuyser ML, Nguyen-The C (2010) Ability of Bacillus cereus group strains to cause food poisoning varies according to phylogenetic affiliation (groups I to VII) rather than species affiliation. J Clin Microbiol 48:3388–3391. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.00921-10
Bauer AW, Kirby WM, Sherris JC, Turck M (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol 45:493–496
Denner EB, Paukner S, Kämpfer P, Moore ER, Abraham WR, Busse HJ, Wanner G, Lubitz W (2001) Sphingomonas pituitosa sp. nov., an exopolysaccharide-producing bacterium that secretes an unusual type of sphingan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:827–841. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-51-3-827
Liu Y, Zhai L, Yao S, Cao Y, Cao Y, Zhang X, Su J, Ge Y, Zhao R, Cheng C (2015) Brachyb acterium hainanense sp. nov., isolated from noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) branch. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:4196–4201. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000559
Yi L, Luo L, Lü X (2018) Efficient exploitation of multiple novel bacteriocins by combination of complete genome and peptidome. Front Microbiol 9:1567. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.0156
Logan NA (2009) Bacillus. In: De Vos P, Garrity G, Jones D, Krieg NR, Ludwig W (eds) In Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology (The Firmicutes), 3, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, NY, USA, pp 21–128
Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:19126–19131. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0906412106
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Trüper HG (1987) Report of the Ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 37:463–464. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-37-4-463
Liu Y, Du J, Lai Q, Zeng R, Ye D, Xu J, Shao Z (2017) Proposal of nine novel species of the Bacillus cereus group. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2499–2508. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001821
Liu X, Wang L, Han M, Xue QH, Zhang GS, Gao J, Sun X (2020) Bacillus fungorum sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from spent mushroom substrate. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 70:1457–1462. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.003673
Collins MD, Jones D (1981) Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implication. Microbiol rev 45:316–354. https://doi.org/10.1128/mr.45.2.316-354.1981
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31771946).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Z. Xiao. Performed the experiments: Y. Li, J. Shen, Q. Liu, Y. Liu, Y. Chu. Analyzed the data: Y. Chen, Z. Xiao. Contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools: Z. Xiao. Wrote the paper: Y. Chen, Z. Xiao.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Li, Y., Shen, J. et al. Bacillus arachidis sp. nov., Isolated from Peanut Rhizosphere Soil. Curr Microbiol 79, 231 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02925-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02925-2