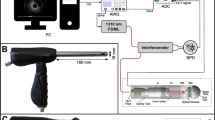
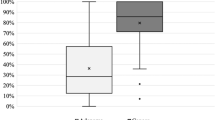
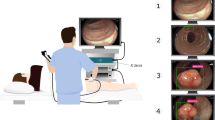
Abstract
Gastrointestinal endoscopy is undergoing major improvements, which are driven by new available technologies and substantial refinements of optical features. In this Review, we summarize available and evolving imaging technologies that could influence the clinical algorithm of endoscopic diagnosis. Detection, characterization and confirmation are essential steps required for proper endoscopic diagnosis. Optical and nonoptical methods can help to improve each step; these improvements are likely to increase the detection rate of neoplasias and reduce unnecessary endoscopic treatments. Furthermore, functional and molecular imaging are emerging as new diagnostic tools that could provide an opportunity for personalized medicine, in which endoscopy will define disease outcome or predict the response to targeted therapy.
Key Points
-
Technological developments of gastrointestinal endoscopy improve endoscopic diagnosis
-
High-definition, virtual and conventional chromoendoscopy facilitate detection and characterization of mucosal lesions
-
Endomicroscopy is able to provide in vivo histology during ongoing endoscopy
-
Nonoptical spectroscopic methods can be used to identify neoplastic areas or to determine the field effect of cancer
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laiyemo, A. O. et al. Likelihood of missed and recurrent adenomas in the proximal versus the distal colon. Gastrointest. Endosc. 74, 253–261 (2011).
Kahi, C. J., Hewett, D. G., Norton, D. L., Eckert, G. J. & Rex, D. K. Prevalence and variable detection of proximal colon serrated polyps during screening colonoscopy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 9, 42–46 (2011).
Singh, H., Nugent, Z., Demers, A. A. & Bernstein, C. N. Rate and predictors of early/missed colorectal cancers after colonoscopy in Manitoba: a population-based study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 105, 2588–2596 (2010).
ASGE Technology Committee et al. High-resolution and high-magnification endoscopes. Gastrointest. Endosc. 69, 399–407 (2009).
Subramanian, V., Mannath, J., Hawkey, C. J. & Ragunath, K. High definition colonoscopy vs. standard video endoscopy for the detection of colonic polyps: a meta-analysis. Endoscopy 43, 499–505 (2011).
Sauk, J., Hoffman, A., Anandasabapathy, S. & Kiesslich, R. High-definition and filter-aided colonoscopy. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 39, 859–881 (2010).
Waye, J. D. Wide view and retroview during colonoscopy. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 39, 883–900 (2010).
Leufkens, A. M. et al. Effect of a retrograde-viewing device on adenoma detection rate during colonoscopy: the TERRACE study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 73, 480–489 (2011).
DeMarco, D. C. et al. Impact of experience with a retrograde-viewing device on adenoma detection rates and withdrawal times during colonoscopy: the Third Eye Retroscope study group. Gastrointest. Endosc. 71, 542–550 (2010).
Waye, J. D. et al. A retrograde-viewing device improves detection of adenomas in the colon: a prospective efficacy evaluation. Gastrointest. Endosc. 71, 551–556 (2010).
Wallace, M. B. & Kiesslich, R. Advances in endoscopic imaging of colorectal neoplasia. Gastroenterology 138, 2140–2150 (2010).
Kiesslich, R. & Neurath, M. F. Chromoendoscopy and other novel imaging techniques. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 35, 605–619 (2006).
Brown, S. R. & Baraza, W. Chromoscopy versus conventional endoscopy for the detection of polyps in the colon and rectum. Cochrane Database of Syst. Rev. Issue 10. Art. No.: CD006439. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006439.pub3 (2010).
Subramanian, V., Mannath, J., Ragunath, K. & Hawkey, C. J. Meta-analysis: the diagnostic yield of chromoendoscopy for detecting dysplasia in patients with colonic inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 33, 304–312 (2011).
Ngamruengphong, S., Sharma, V. K. & Das, A. Diagnostic yield of methylene blue chromoendoscopy for detecting specialized intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus: a meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 69, 1021–1028 (2009).
Goetz, M. & Kiesslich, R. Advanced imaging of the gastrointestinal tract: research vs. clinical tools? Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 25, 412–421 (2009).
Kiesslich, R. et al. Endoflag: a new software based filter technology significantly increases the diagnostic yield of colorectal neoplasia during screening colonoscopy. A prospective randomized controlled trial. Gastrointest. Endosc. 71, AB185 (2010).
Kuiper, T. & Dekker, E. Imaging: NBI—detection and differentiation of colonic lesions. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 7, 128–130 (2010).
Mannath, J., Subramanian, V., Hawkey, C. J. & Ragunath, K. Narrow band imaging for characterization of high grade dysplasia and specialized intestinal metaplasia in Barrett's esophagus: a meta-analysis. Endoscopy 42, 351–359 (2010).
Herrero, L. A., Weusten, B. L. & Bergman, J. J. Autofluorescence and narrow band imaging in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 39, 747–758 (2010).
Uedo, N. et al. Role of narrow band imaging for diagnosis of early-stage esophagogastric cancer: current consensus of experienced endoscopists in Asia-Pacific region. Dig. Endosc. 23 (Suppl. 1), 58–71 (2011).
Kato, M. et al. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging achieves superior accuracy in the differential diagnosis of superficial gastric lesions identified with white-light endoscopy: a prospective study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 72, 523–529 (2010).
Wallace, M. B., Wax, A., Roberts, D. N. & Graf, R. N. Reflectance spectroscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 19, 233–242 (2009).
Boustany, N. N., Boppart, S. A. & Backman, V. Microscopic imaging and spectroscopy with scattered light. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 15, 285–314 (2010).
Backman, V. & Roy, H. K. Light-scattering technologies for field carcinogenesis detection: a modality for endoscopic prescreening. Gastroenterology 140, 35–41 (2011).
Roy, H. K., Goldberg, M. J., Bajaj, S. & Backman, V. Colonoscopy and optical biopsy: bridging technological advances to clinical practice. Gastroenterology 140, 1863–1867 (2011).
Matousek, P. & Stone, N. Emerging concepts in deep Raman spectroscopy of biological tissue. Analyst 134, 1058–1066 (2009).
Stallmach, A., Schmidt, C., Watson, A. & Kiesslich, R. An unmet medical need: advances in endoscopic imaging of colorectal neoplasia. J. Biophotonics 4, 482–489 (2011).
Bergholt, M. S. et al. Characterizing variability in in vivo Raman spectra of different anatomical locations in the upper gastrointestinal tract toward cancer detection. J. Biomed. Opt. 16, 037003 (2011).
Kendall, C. Evaluation of Raman probe for oesophageal cancer diagnostics. Analyst 135, 3038–3041 (2010).
Huang, Z. et al. In vivo detection of epithelial neoplasia in the stomach using image-guided Raman endoscopy. Biosens. Bioelectron 26, 383–389 (2010).
Curvers, W. L., Kiesslich, R. & Bergman, J. J. Novel imaging modalities in the detection of oesophageal neoplasia. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 22, 687–720 (2008).
Curvers, W. L. et al. Endoscopic tri-modal imaging is more effective than standard endoscopy in identifying early-stage neoplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology 139, 1106–1114 (2010).
Curvers, W. L. Endoscopic tri-modal imaging for detection of early neoplasia in Barrett's oesophagus: a multi-centre feasibility study using high-resolution endoscopy, autofluorescence imaging and narrow band imaging incorporated in one endoscopy system. Gut 57, 167–172 (2008).
Kuiper, T. et al. Endoscopic trimodal imaging detects colonic neoplasia as well as standard video endoscopy. Gastroenterology 140, 1887–1894 (2011).
Testoni, P. A. Optical coherence tomography. ScientificWorldJournal 7, 87–108 (2007).
Kang, W. et al. Endoscopically guided spectral-domain OCT with double-balloon catheters. Opt. Express 18, 17364–17372 (2010).
Hatta, W. et al. Optical coherence tomography for the staging of tumor infiltration in superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gastrointest. Endosc. 71, 899–906 (2010).
Testoni, P. A. & Mangiavillano, B. Optical coherence tomography for bile and pancreatic duct imaging. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 19, 637–653 (2009).
Cobb, M. J. et al. Imaging of subsquamous Barrett's epithelium with ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography: a histologic correlation study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 71, 223–230 (2010).
Arvanitakis, M. et al. Intraductal optical coherence tomography during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography for investigation of biliary strictures. Endoscopy 41, 696–701 (2009).
Neumann, H. Review article: in vivo imaging by endocytoscopy. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 33, 1183–1193 (2011).
ASGE Technology Committee et al. Endocytoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 70, 610–613 (2009).
Singh, R., Chen Yi Mei, S. L., Tam, W., Raju, D. & Ruszkiewicz, A. Real-time histology with the endocytoscope. World J. Gastroenterol. 16, 5016–5019 (2010).
Rotondano, G. et al. Endocytoscopic classification of preneoplastic lesions in the colorectum. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 25, 1111–1116 (2010).
Matysiak-Budnik, T. et al. In vivo real-time imaging of human duodenal mucosal structures in celiac disease using endocytoscopy. Endoscopy 42, 191–196 (2010).
Pohl, H. et al. Endocytoscopy for the detection of microstructural features in adult patients with celiac sprue: a prospective, blinded endocytoscopy-conventional histology correlation study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 70, 933–941 (2009).
Goetz, M., Watson, A. & Kiesslich, R. Confocal laser endomicroscopy in gastrointestinal diseases. Biophotonics 4, 498–508 (2011).
Kiesslich, R., Goetz, M. & Neurath, M. F. Virtual histology. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 22, 883–897 (2008).
Kiesslich, R. et al. Confocal laser endoscopy for diagnosing intraepithelial neoplasias and colorectal cancer in vivo. Gastroenterology 127, 706–713 (2004).
Wallace, M. B. & Fockens, P. Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Gastroenterology 136, 1509–1513 (2009).
Wallace, M. B. et al. The safety of intravenous fluorescein for confocal laser endomicroscopy in the gastrointestinal tract. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 31, 548–552 (2010).
Sanduleanu, S. et al. In vivo diagnosis and classification of colorectal neoplasia by chromoendoscopy-guided confocal laser endomicroscopy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 8, 371–378 (2010).
Li, C. Q. & Li, Y. Q. Endomicroscopy of intestinal metaplasia and gastric cancer. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 39, 785–796 (2010).
Canto, M. I. Endomicroscopy of Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 3 9, 759–769 (2010).
Neumann, H., Kiesslich, R., Wallace, M. B. & Neurath, M. F. Confocal laser endomicroscopy: technical advances and clinical applications. Gastroenterology 139, 388–392 (2010).
Kiesslich, R. et al. Chromoscopy-guided endomicroscopy increases the diagnostic yield of intraepithelial neoplasia in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 132, 874–882 (2007).
Goetz, M. & Wang, T. D. Molecular imaging in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastroenterology 138, 828–833e1 (2010).
Fottner, C. et al. In vivo molecular imaging of somatostatin receptors in pancreatic islet cells and neuroendocrine tumors by miniaturized confocal laser-scanning fluorescence microscopy. Endocrinology 151, 2179–2188 (2010).
Goetz, M. et al. In vivo molecular imaging of colorectal cancer with confocal endomicroscopy by targeting epidermal growth factor receptor. Gastroenterology 138, 435–446 (2010).
Hsiung, P. L. et al. Detection of colonic dysplasia in vivo using a targeted heptapeptide and confocal microendoscopy. Nat. Med. 14, 454–458 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally to researching, discussing, writing, reviewing and editing this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors declare an association with Pentax. R. Kiesslich has acted as a consultant, been a member of a speakers bureau and received grant or research support. P. R. Galle has been a member of a speakers bureau and received grant or research support. Both M. Goetz and A. Hoffman have been a member of a speakers bureau.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiesslich, R., Goetz, M., Hoffman, A. et al. New imaging techniques and opportunities in endoscopy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8, 547–553 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2011.152
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2011.152
This article is cited by
-
Single multimode fibre for in vivo light-field-encoded endoscopic imaging
Nature Photonics (2023)
-
Novel endoscopic optical diagnostic technologies in medical trial research: recent advancements and future prospects
BioMedical Engineering OnLine (2021)
-
Simultaneous Detection of EGFR and VEGF in Colorectal Cancer using Fluorescence-Raman Endoscopy
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Detection of colorectal polyps in humans using an intravenously administered fluorescent peptide targeted against c-Met
Nature Medicine (2015)
-
Diagnostic fiber-based optical imaging catheters
Biomedical Engineering Letters (2014)