Abstract
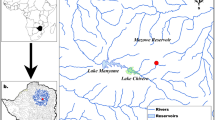
Regular annual flooding of the Amazonian rivers changes the aquatic environment affecting fish feeding strategies. The Rio Madeira has been greatly impacted by deforestation for agricultural projects, damming for a hydroelectric power plant, and alluvial gold extraction. We studied fish-Hg concentrations within defined weight ranges of representative species at the top of the food web, comparing high and low water seasons. Selected piscivorous species (Cichla spp, Hoplias malabaricus, Pinirampus pirinampu, Serrasalmus spp) showed a large variation of Hg concentrations but only “traíra” (Hoplias malabaricus) showed a statistically significant difference between seasons. However, the bioaccumulation trends during high and low waters were similar for “tucunaré” (Cichla spp) and “traíra” (Hoplias malabaricus) but different for “piranhas” (Serrasalmus spp), “barba chata” (Pinirampus pirinampu) and the detritivorous Prochilodus nigricans. Fish-Hg bioaccumulation is species specific; changes in feeding strategies brought by flooding seasons can change the bioaccumulation pattern without systematically affecting the overall accrual of methylmercury in tertiary consumer species. It appears that naturally occurring Hg and the high sediment load of the Rio Madeira are secondary factors in the Hg bioaccumulation pattern of fish species at the top of the food chain.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida MD, Lacerda LD, Bastos WR, Herrmann JC (2005) Mercury loss from soils following conversion from forest to pasture in Rondonia, Western Amazon, Brazil. Environ Pollut 137:179–186
Barbosa AC, Souza JR, Dórea JG, Jardim W, Fadini P (2003) Mercury biomagnification in tropical black water, the Rio Negro, Brazil. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:235–246
Bastos WR, Malm Olaf, Pfeiffer WC, Cleary D (1998) Establishment and analytical quality control of laboratories for Hg determination in biological and geological samples in the Amazon, Brasil. Ciênc Cult 50:255–260
Bastos WR, Gomes JP, Oliveira RC, Almeida R, Nascimento EL, Bernardi JVE, Lacerda LD, Silveira EG, Pfeiffer WC (2006) Mercury in the environment and riverside population in the Madeira River Basin, Amazon, Brazil. Sci Total Environ 368:344–351
CPRM (2002) Companhia de Pesquisa de Recursos Minerais. Serviço Geológico do Brasil—Perspectivas do Meio Ambiente do Brasil; Rio de Janeiro, Brasil, pp 27
Dorea JG (2003) Fish are central in the diet of Amazonian riparians: should we worry about their mercury concentrations? Environ Res 92:232–244
Dorea JG, Barbosa AC, Silva GS (2006) Fish-mercury bioaccumulation as a function of feeding behavior and hydrological cycles of the Rio Negro, Amazon. Comp Biochem Physiol 142:275–283
Dorea JG, Barbosa AC (2007) Anthropogenic impact of mercury accumulation in fish from the Rio Madeira and Rio Negro Rivers (Amazonia). Biol Tr El Res (in press)
Goulding M, Carvalho ML, Ferreira EG (1988) Rio Negro: rich life in poor water: Amazonian diversity and floodplain ecology as seen through fish communities. SPB Academic Publishing The Hague, p 200
Gragson TL (1992) Fishing the waters of Amazônia: Native subsistence economies in a tropical rain forest. Am Anthrop 94:428–440
Guimaraes JR, Roulet M, Lucotte M, Mergler D (2000) Mercury methylation along a lake-forest transect in the Tapajós river floodplain, Brazilian Amazon: seasonal and vertical variations. Sci Total Environ 261:91–98
Junk WJ (1985) Temporary fat storage, an adaptation of some fish species to the water level fluctuations and related environmental changes of the Amazon River. Amazoniana 9:315–351
Latrubesse EM, Stevaux JC, Sinha R (2005) Tropical rivers. Geomorphology 70:187–206
Lechler PJ, Miller JR, Lacerda LD, Vinson D, Bonzongo JC, Lyons WB, Warwick JJ (2000) Elevated mercury concentrations in soils, sediments, water, and fish of the Madeira River Basin, Brazilian Amazon: a function of natural enrichment? Sci Total Environ 260:87–96
Mailman M, Stepnuk L, Cicek N, Bodaly RA (2006) Strategies to lower methyl mercury concentrations in hydroelectric reservoirs and lakes: A review. Sci Total Environ 368:224–235
Malm O, Pfeiffer WC, Bastos WR, Souza CMM (1989) Utilização do Acessório de Geração de Vapor Frio para Análise de Mercúrio em Investigações Ambientais por Espectrofotometria de Absorção Atômica. Ciênc Cult 41:88–92
Malm O, Guimarães JRD, Castro MB, Bastos WR, Viana JP, Branches FJP, Silveira EG, Pfeiffer WC (1997) Follow-up of mercury levels in fish, human hair and urine in the Madeira and Tapajós basins, Amazon, Brazil. Water Air Soil Pollut 97:45–51
Maurice-Bourgoin L, Quiroga I, Chincheros J, Courau P (2000) Mercury distribution in waters and fishes of the upper Madeira rivers and mercury exposure in riparian Amazonian populations. Sci Total Environ 260:73–86
Sampaio da Silva D, Lucotte M, Roulet M, Poirier H, Mergler D, Oliveira Santos E, Crossa M (2005) Trophic structure and bioaccumulation of mercury in fish of three natural lakes of the Brazilian Amazon. Water Air Soil Pollut 165:77–94
Santos GM, Ferreira EJG, Jegu M (1991) Catálogo dos Peixes do Rio Jamari, Rondônia. Instituto Nacional de Pesquisas da Amazônia/INPA. Manaus, Amazonas, 123
Valle CM, Santana GP, Augusti R, Egreja Filho FB, Windmoller CC (2005) Speciation and quantification of mercury in Oxisol, Ultisol, and Spodosol from Amazon (Manaus, Brazil). Chemosphere 58:779–792
Acknowledgements
This work was partly supported by the National Research Council of Brazil-CNPq (PPG7, project-556985/2005-2).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bastos, W.R., de Almeida, R., Dórea, J.G. et al. Annual flooding and fish-mercury bioaccumulation in the environmentally impacted Rio Madeira (Amazon). Ecotoxicology 16, 341–346 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0138-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-007-0138-0