Summary
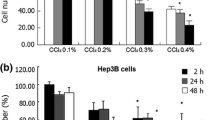
This study was performed to evaluate the isomer-specific cytotoxic effects of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on rat hepatoma dRLh-84 cells in vitro. A 10trans,12cis (10t,12c)-CLA showed a strong cytotoxic effect on dRLh-84 cells in culture, whereas no such effect was observed with 9cis,11trans (9c,11t)-CLA or linoleic acid. The optimum concentration for induction of cytotoxity by 10t,12c-CLA was 5 to 10 μM, but the effect was alleviated at higher concentrations. Coincubation with oleic or palmitoleic acid and 10t,12c-CLA cancelled the cytotoxic effect, but other major saturated or polyunsaturated fatty acids and eraidic acid did not interfere with 10t,12c-CLA-induced cytotoxity. The cytotoxic effect was also alleviated by α-tocopherol (α-toc) and α-tocotrienol but not by any other antioxidant regent examined. Significant cytotoxity of 10t,12c-CLA was detected after only a 15-min incubation, and the most noticeable effect was seen after 3 h. After incubation with 10t,12c-CLA at 10 μM, an additional 90 μM, an additional 90 μM of 10t,12c-CLA or 100 μM of α-toc was also able to alleviate the cytotoxity. When cells were treated with 10 μM 10t,12c-CLA for more than 48 h, treatment with additional CLA or α-toc could not prevent cell death.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzi, A.; Boscoboinik, D.; Marilley, D.; Ozer N. K.; Stauble, B.; Tasinato, A. Vitamin E: a sensor and an information transducer of the cell oxidation state. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 62:1337S-1346S; 1995.
Basu, S.; Smedman, A.; Vessby, B. Conjugated linoleic acid induces lipid peroxidation in humans. FEBS Lett. 468:33–36; 2000.
Belury, M. A.; Nickel, K. P.; Bird, C. E.; Wu, Y. M. Dietary conjugated linoleic acid modulation of phorbol ester skin tumor promotion. Nutr. Cancer 26:149–157; 1996.
Boscoboinik, D. O.; Chatelain, E.; Bartoli, G. M.; Stauble, B.; Azzi, A. Inhibition of protein kinase C activity and vascular smooth muscle cell growth by d-alpha-tocopherol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1224:418–426; 1994.
Choi, Y.; Kim, Y. C.; Han, Y. B.; Park, Y.; Pariza, M. W.; Ntambi, J. M. The trans-10, cis-12 isomer of conjugated linoleic acid downregulates stearoyl-CoA desaturese 1 gene expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes J. Nutr. 130:1920–1924; 2000.
Chujo, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Nou, S.; Koyanagi, N.; Tachibana, H.; Yamada, K. Effect of conjugated linoleic acid isomers on growth factor-induced proliferation of human breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 202:81–87; 2003.
Desbordes, C.; Lea, M. A. Effects of C18 fatty acids on DNA synthesis in hepatoma and breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 15:2017–2021; 1995.
Igarashi, M.; Miyazawa, T. The growth inhibitory effect of conjugated linoleic acid on a human hepatoma cell line, HepG2, is induced by a change in fatty acid metabolism, but not the facilitation of lipid peroxidation in the cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1530:162–171; 2001.
Ip, C.; Chin, S. F.; Scimeca, J. A.; Pariza, M. W. Mammary cancer prevention by conjugated dienoic derivative of linoleic acid. Cancer Res. 51:6118–6124; 1991.
Ip, C.; Singh, M.; Thompson, H. J.; Scimeca, J. A. Conjugated linoleic acid suppresses mammary carcinogenesis and proliferative activity of the mammary gland in the rats. Cancer Res. 54:1212–1215; 1994.
Kamp, F.; Zakim, D.; Zhang, F.; Noy, N.; Hamilton, J. A. Fatty acid flip-flop in phospholipid bilayers is extremely fast. Biochemistry 34:11928–11937; 1995.
Khanna, S.; Roy, S.; Ryu, H.; Bahadduri, P.; Swaan, P. W.; Ratan, R. R.; Sen, C. K. Molecular basis of vitamin E action: tocotrienol modulates 12-lipoxygenase, a key mediator of glutamate-induced neurodegeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 278:43508–43515; 2003.
Kleinfeld, A. M.; Storms S.; Watts, M. Transport of long-chain native fatty acids across human erythrocyte ghost membranes. Biochemistry 37:8011–8019; 1998.
Listenberger, L. L.; Han, X.; Lewis, S. E.; Cases, S.; Farese, R. V., Jr.; Ory, D. S.; Schaffer, J. E. Triglyceride accumulation protects against fatty acidinduced lipotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:3077–3082; 2003.
Ntambi, J. M.; Miyazaki, M. Recent insights into stearoly-CoA desaturase. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 14:255–261; 2003.
O'Shea, M.; Stanton, C.; Devery, R. C. Antioxidant enzyme defence responses of human MCF-7 and SW480 cancer cells to conjugated linoleic acid. Anticancer Res. 19:1953–1959; 1999.
Palacios, A.; Piergiacomi, V.; Catala, A. Antioxidant effect of conjugated linoleic acid and vitamin A during non enzymatic lipid peroxidation of rat liver microsomes and mitochondria. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 250:107–113; 2003.
Park, Y.; Storkson, J. M.; Ntambi, J. M.; Cook, M. E.; Sih, C. J.; Pariza, M. W. Inhibition of hepatic stearoyl-CoA desaturase activity by trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid and its derivatives. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1486:285–292; 2000.
Riserus U.; Basu, S.; Jovinge, S.; Fredrikson, G. N.; Arnlov, J.; Vessby, B. Supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid causes isomer-dependent oxidative stress and elevated C-reactive protein: a potential link to fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. Circulation 106:1925–1929; 2002.
Schonberg, S.; Krokan, H. E. The inhibitory effect of conjugated dienoic derivatives (CLA) of linoleic acid on the growth of human tumor cell lines is in part due to increased lipid peroxidation. Anticancer Res. 15:1241–1246; 1995.
Sen, C. K.; Khanna, S.; Roy, S.; Packer, L. Molecular basis of vitamin E action. Tocotrienol potently inhibits glutamate-induced pp60(c-Src) kinase activation and death of HT4 neuronal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 275:13049–13055; 2000.
Shulz, T. D.; Chew, B. P.; Seaman, W. R.; Luedecke, L. O. Inhibitory effect of conjugated dienoic derivatives of linoleic acid and beta-carotene on the in vitro growth of human cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 63:125–133; 1992.
Suzuki, Y. J.; Tsuchiya, M.; Wassall, S. R.; Choo, Y. M.; Govil, G.; Kagan, V. E.; Packer, L. Structural and dynamic membrane properties of alpha-tocopherol and alpha-tocotrienol: implication to the molecular mechanism of their antioxidant potency. Biochemistry 32:10692–10699; 1993.
Tan, J.; Hallahan, D. E. Growth factor-independent activation of protein kinase B contributes to the inherent resistance of vascular endothelium to radiation-induced apoptotic response. Cancer Res. 63:7663–7667; 2003.
Yamasaki, M.; Chujo, H.; Koga, Y.; Rikimaru, T.; Shimada, M.; Sugimachi, K.; Tachibana, H.; Yamada, K. Potent cytotoxic effect of trans-10, cis12 isomer of conjugated linoleic acid on rat hepatoma dRLh-84 cells. Cancer Lett. 188:171–180; 2002a.
Yamasaki, M.; Chujo, H.; Nou, S.; Tachibana, H.; Yamada, K. Alleviation of the cytotoxic activity induced by trans10, cis12-conjugated linoleic acid in rat hepatoma dRLh-84 cells by oleic or palmitoleic acid. Cancer Lett. 196:187–196; 2003.
Yamasaki, M.; Ikeda, A.; Hirao, A.; et al. Effect of dietary conjugated linoleic acid on the growth of rat hepatoma dRLh-84. Nutr. Cancer. 40:140–148; 2001.
Yamasaki, M.; Ikeda, A.; Hirao, A.; et al. Dose dependent effect of dietary conjugated linoleic acid on the growth of rat hepatoma dRLh-84 cells in vivo. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 48:505–511; 2002b.
Yamasaki, M.; Kishihara, K.; Mansho, K.; Ogino, Y.; Kasai, M.; Sugano, M.; Tachibana, H.; Yamada, K. Dieetary conjugated linoleic acid increases immunoglobulin productivity of Sprague-Dawley rat spleen lymphocytes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 64:2159–2164; 2000.
Yoon, C. S.; Ha, T. Y.; Rho, J. H.; Sung, K. S.; Cho, I. J. Inhibitory effect of conjugated linoleic acid in vitro growth of human hepatoma. FASEB J. 11:A578; 1997.
Yu, L.; Adams, D.; Gabel, M. Conjugated linoleic acid isomers differ in their free radical scavenging properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50:4135–4140; 2001.
Zhong, M.; Lu, Z.; Foster, D. A. Downregulating PKC delta provides a PI3K/Akt-independent survival signal that overcomes apoptotic signals generated by c-Src overexpression. Oncogene 21:1071–1078; 2002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamasaki, M., Nou, S., Tachibana, H. et al. Cytotoxity of the trans10,cis12 isomer of conjugated linoleic acid on rat hepatoma and its modulation by other fatty acids, tocopherol, and tocotrienol. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 41, 239–244 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1290/0402008.1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/0402008.1