Abstract
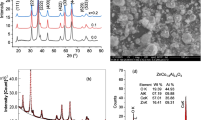
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have garnered substantial interest as nanofillers for improving the properties of polymer composites due to their exceptional mechanical, electrical, and thermal characteristics. As nanofillers, carbon nanotubes can be incorporated into various materials to enhance their performance and functionality. In the present work, polymer blends of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP)/polyethylene oxide (PEO) doped with different concentrations of carbon nanotubes (CNTS 1%, 3%, and 5%) were fabricated by solution casting technique. X-ray diffraction studies reveal that the prepared polymer blend nanocomposites exhibit the semicrystalline nature. The intensity of the XRD peaks obtained for PVP/PEO blend at 19.3˚ is found to be reduced with an increase of CNTs concentration from 1 to 5%. The DSC thermograms show the glass transition temperatures (Tg) of PVP/PEO films doped with different concentrations of CNTs appeared in the region between 51–60 °C. The decrease in the degree of crystallinity for PVP/PEO doped with CNTs is noticed. The surface morphology and chemical composition of pure and CNTs doped PVP/PEO blends were examined by FESEM with EDS. The direct and indirect optical bandgap values for pure PVP/PEO blend are found to be 4.90 eV and 4.66 eV. With the increase of concentration of CNTs from 1 to 5%, the direct band gap ranges from 4.30 to 3.40 eV, while the indirect band gap decreases from 4.20 to 3.67 eV. The obtained results confirm that PVP/PEO doped with CNTs had promising applications in the optoelectronic and photonic devices.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
References
S. Choudhary, Structural, optical, dielectric and electrical properties of (PEO–PVP)–ZnO nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 121, 196–209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.05.017
Y. Pavani, S. Bhavani, A.K. Sharma, V.V.R. NarasimhaRao, Investigations on PEO/PVP/NaBr complexed polymer blend electrolytes for electrochemical cell applications. J. Member. Sci. 454, 200–211 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3643635
M. Atta, M. Abdelhamied, A.M. Abdelreheem, M.R. Berber, Flexible methyl cellulose/polyaniline/silver composite films with enhanced linear and nonlinear optical properties. Polymers 13, 1225 (2021). https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-270302/v1
M. Tommalieh, Gamma radiation assisted modification on electrical properties of Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone/Polyethylene Oxide blend doped by copper oxide nanoparticles. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 179, 109236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2020.109236
M.A. Hillmyer, F.S. Bates, Synthesis and characterization of model polyalkane-poly (ethylene oxide) block copolymers. Macromolecules 29, 6994–7002 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma960774t
E.M. Abdelrazek, A.M. Abdelghany, A.E. Tarabiah, H.M. Zidan, AC conductivity and dielectric characteristics of PVA/PVP nanocomposite filled with MWCNTs. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 15521–15533 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01929-2
F. Gami, N. Algethami, H.M. Ragab, A. Rajah, A.E. Tarabiah, Structural, optical and electrical studies of chitosan/polyacrylamide blend filled with synthesized selenium nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 1257, 132631 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2022.132631
Z. Spitalsky, D. Tasis, K. Papagelis, C. Galiotis, Carbon nanotube-polymer composites: chemistry, processing, mechanical and electrical properties. Prog. Polym. Sci. 35, 357–401 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2009.09.003
X.-D. Qi, J.-h Yang, N. Zhang, T. Huang, Z.-W. Zhou, I. Kühnert, P. Pötschke, Y. Wang, Selective localization of carbon nanotubes and its effect on the structure and properties of polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 123, 101471 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2021.101471
A. Iqbal, A. Saeed, A. Ul-Hamid, A review featuring the fundamentals and advancements of polymer/CNT nanocomposite application in aerospace industry. Polym. Bull. 78, 539–557 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-03096-0
H.F. Kayiran, Numerical analysis of composite disks based on carbon/aramid–epoxy materials. J Emerg Mater Res 11, 155–159 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1680/jemmr.21.00052
H.M. Zidan, E.M. Abdelrazek, A.M. Abdelghany, A.E. Tarabiah, Characterization and some physical studies of PVA/PVP filled with MWCNTs. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8(1), 904–913 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.04.023
S. Bortel, R. Hodorowicz, Lamot, Relation between crystallinity degree and stability in solid state of high molecular weight poly(ethylene oxide)s. Die Micromole. Chem. 180, 2491–2498 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.1979.021801023
K. Chrissopoulou, K.S. Andrikopoulos, S. Fotiadou, S. Bollas, C. Karageorgaki, D.C. Los, G.A. Voyiatzis, S.H. Anastasiadis, Crystallinity and chain conformation in PEO/layered silicate nanocomposites. Macromolecules 44, 9710–9722 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/ma201711r
Sharanappa Chapi, H. Devendrappa. Raghu, Enhanced electrochemical, structural, optical, thermal stability and ionic conductivity of (PEO/PVP) polymer blend electrolyte for electrochemical applications. Ionics 22, 803–814 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1600-2
P. Dhatarwal, R.J. Sengwa, Nanofiller controllable optical parameters and improved thermal properties of (PVP/PEO)/Al2O3 and (PVP/PEO)/SiO2 nanocomposites. Optik 233, 166594 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.166594
B. Chana, R. Kumar, Optical, electrical and acoustical properties of CuSO4 doped PVP based polymer solution. Adv. Appl. Res. 9(2), 69–75 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5958/2349-2104.2017.00014.6
S. Saber, S. El-Sayed, A.M. El Sayed, Influence of Eu3+ on the structural, optical and electrical properties of PEO–PVA: dual bandgap materials for optoelectronic applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 34, 406 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09841-6
M.M. Atta, A.M.A. Henaish, A.M. Elbasiony, Eman O. Taha, A.M.: Dorgham, Structural, optical, and thermal properties of PEO/PVP blend reinforced biochar. 127, 112268/1–8 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2022.112268
R. Ahmed, M. Atta, E. Taha, Optical spectroscopy, thermal analysis, and dynamic mechanical properties of graphene nano-platelets reinforced polyvinylchloride. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 22699–22717 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06756-y
R.J. Sengwa, S. Choudhary, P. Dhatarwal, Nonlinear optical and dielectric properties of TiO2 nanoparticles incorporated PEO/PVP blend matrix based multifunctional polymer nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 12275–12294 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01587-4
H.E. Ali, I. Yahia, H. Algarni, Y. Khairy, Enhancing the optical absorption, conductivity, and nonlinear parameters of PVOH films by Bi-doping. New J. Phys. 23, 043001 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1367-2630/abe614
K.K. Kumar, M. Ravi, Y. Pavani, S. Bhavani, A. Sharma, V.N. Rao, Investigations on the effect of complexation of NaF salt with polymer blend (PEO/PVP) electrolytes on ionic conductivity and optical energy band gaps. Phys. B Condens. Matter 406, 1706–1712 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2011.02.010
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to convey their sincere gratitude to DST-FIST, India for providing infrastructural equipments Spectroscopic Ellipsometer and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) through the grant No. SR/FST/PSI-194/2014 dated July 21, 2015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. R.: investigation, conceptualization, writing-review and editing. B. P.: advising on conceptualization, review. R. K.: methodology, formal analysis, original draft, review, editing and corrections. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ravulapalli, S., Padal, K.T.B. & Kumar, B.R. Structural and optical properties of PVP/PEO blends doped with CNTs. emergent mater. 6, 1923–1933 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-023-00580-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-023-00580-2