Abstract
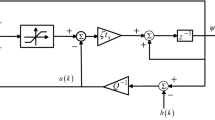
In this paper, a new approach based on Projection Recurrent Neural Network (PRNN) and Discrete-time Sliding Mode Control (DTSMC) has been proposed to stabilize Fractional-order Chaotic Systems with uncertain fractional-order. The main idea is to describe the FOLS as a linear regression where the unknown parameters vector includes the terms dependent on the fractional order. Constrained Quadratic Programming (CQP) has been introduced to minimize the difference between the FOLS and its regression description, in which the fractional orders are considered as optimization variables. According to the optimality conditions for the CQP, the PRNN as a numerical optimizer has been extended. The exponential reaching laws are used to obtain the control signals of DTSMC. The estimated fractional order is simultaneously applied to the controller. The asymptotic stability of the optimizer, as well as the robustness of the proposed algorithm against the uncertainty in the fractional order, have been evaluated.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Layek GC (2015) An introduction to dynamical systems and chaos. Springer, New Delhi, pp 1–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-2556-0
Ye G (2010) Image scrambling encryption algorithm of pixel bit based on chaos map. Pattern Recogn Lett 31(5):347–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2009.11.008
Njitacke ZT, Fotsin HB, Negou AN, Tchiotsop D (2016) Coexistence of multiple attractors and crisis route to chaos in a novel memristive diode bidge-based Jerk circuit. Chaos Solitons Fractals 91:180–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2016.05.011
Petráš I (2010) A note on the fractional-order Volta’s system. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 15(2):384–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2009.04.009
Balootaki MA, Rahmani H, Moeinkhah H, Mohammadzadeh A (2020) On the synchronization and stabilization of fractional-order chaotic systems: recent advances and future perspectives. Physica A: Stat Mech Appl 551:124203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physa.2020.124203
Khan A, Tyagi A (2018) Fractional order disturbance observer based adaptive sliding mode hybrid projective synchronization of fractional order Newton-Leipnik chaotic system. Int J Dyn Control 6(3):1136–1149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-017-0370-2
Modiri A, Mobayen S (2020) Adaptive terminal sliding mode control scheme for synchronization of fractional-order uncertain chaotic systems. ISA Trans 105:33–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2020.05.039
Deepika D, Kaur S, Narayan S (2018) Uncertainty and disturbance estimator based robust synchronization for a class of uncertain fractional chaotic system via fractional order sliding mode control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 115:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2018.07.028
Song C, Fei S, Cao J, Huang C (2019) Robust synchronization of fractional-order uncertain chaotic systems based on output feedback sliding mode control. Mathematics 7(7):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7070599
Xu Y, Wang H, Liu D, Huang H (2015) Sliding mode control of a class of fractional chaotic systems in the presence of parameter perturbations. J Vib Control 21(3):435–448. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546313486283
Wang YL, Jahanshahi H, Bekiros S, Bezzina F, Chu YM, Aly AA (2021) Deep recurrent neural networks with finite-time terminal sliding mode control for a chaotic fractional-order financial system with market confidence. Chaos Solitons Fractals 146(146):110881. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2021.110881
Faieghi MR, Delavari H, Baleanu D (2012) Control of an uncertain fractional-order Liu system via fuzzy fractional-order sliding mode control. J Vib Control 18(9):1366–1374. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546311422243
Mirrezapour SZ, Zare A, Hallaji M (2021) A new fractional sliding mode controller based on nonlinear fractional-order proportional integral derivative controller structure to synchronize fractional-order chaotic systems with uncertainty and disturbances. J Vib Control. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546320982453
Shahri ESA, Alfi A, Tenreiro Machado JA (2017) Stabilization of fractional-order systems subject to saturation element using fractional dynamic output feedback sliding mode control. J Comput Nonlinear Dyn 12(3):031014. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4035196
David SA, de Sousa RV, Valentim CA Jr, Tabile RA, Machado JAT (2016) Fractional PID controller in an active image stabilization system for mitigating vibration effects in agricultural tractors. Comput Electron Agric 131:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2016.11.001
Wang R, YunNing Z, Chen Y, Chen X, Lei X (2020) Fuzzy neural network-based chaos synchronization for a class of fractional-order chaotic systems: an adaptive sliding mode control approach. Nonlinear Dyn 100(2):1275–1287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05574-x
Chen T, Yang H, Yuan J (2021) Event-triggered adaptive neural network backstepping sliding mode control for fractional order chaotic systems synchronization with input delay. IEEE Access 9:100868–100881. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3097159
Khan A, Jahanzaib LS (2019) Synchronization on the adaptive sliding mode controller for fractional order complex chaotic systems with uncertainty and disturbances. Int J Dyn Control 7(4):1419–1433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-019-00585-y
Mofid O, Mobayen S (2018) Adaptive synchronization of fractional-order quadratic chaotic flows with nonhyperbolic equilibrium. J Vib Control 24(21):4971–4987. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546317740021
Sun Z (2018) Synchronization of fractional-order chaotic systems with non-identical orders, unknown parameters and disturbances via sliding mode control. Chin J Phys 56(5):2553–2559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjph.2018.08.007
Shao K, Xu Z, Wang T (2021) Robust finite-time sliding mode synchronization of fractional-order hyper-chaotic systems based on adaptive neural network and disturbances observer. Int J Dyn Control 9(2):541–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-020-00657-4
Deepika D (2022) Hyperbolic uncertainty estimator based fractional order sliding mode control framework for uncertain fractional order chaos stabilization and synchronization. ISA Trans 123:76–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2021.05.036
Dalir M, Bigdeli N (2020) The design of a new hybrid controller for fractional-order uncertain chaotic systems with unknown time-varying delays. Appl Soft Comput 87:106000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.106000
Lopes AM, Machado JT (2021) Multidimensional scaling analysis of generalized mean discrete-time fractional order controllers. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 95:105657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cnsns.2020.105657
Vafaei V, Kheiri H, Akbarfam AJ (2019) Synchronization of fractional-order chaotic systems with disturbances via novel fractional-integer integral sliding mode control and application to neuron models. Math Methods Appl Sci 42(8):2761–2773. https://doi.org/10.1002/mma.5548
Jiang J, Cao D, Chen H (2020) Sliding mode control for a class of variable-order fractional chaotic systems. J Franklin Inst 357(15):10127–10158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2019.11.036
Li RG, Wu HN (2019) Secure communication on fractional-order chaotic systems via adaptive sliding mode control with teaching–learning–feedback-based optimization. Nonlinear Dyn 95(2):1221–1243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4625-z
Moghaddam TV, Yadavar Nikravesh SK, Khosravi MA (2020) Adaptive constrained sliding mode control of uncertain nonlinear fractional-order input affine systems. J Vib Control 26(5–6):318–330. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077546319879484
Rabah K, Ladaci S, Lashab M (2017) A novel fractional sliding mode control configuration for synchronizing disturbed fractional-order chaotic systems. Pramana 89(3):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12043-017-1443-7
Al-sawalha MM (2020) Synchronization of different order fractional-order chaotic systems using modify adaptive sliding mode control. Adv Diff Equ 2020(1):1–17
Zhu D, Zhang W, Liu C, Duan J (2021) Fractional-order hyperbolic tangent sliding mode control for chaotic oscillation in power system. Math Probl Eng 2021:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6691941
Tong Y, Cao Z, Yang H, Li C, Yu W (2022) Design of a five-dimensional fractional-order chaotic system and its sliding mode control. Indian J Phys 96(3):855–867. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12648-021-02181-3
Chen Y, Tang C, Roohi M (2021) Design of a model-free adaptive sliding mode control to synchronize chaotic fractional-order systems with input saturation: an application in secure communications. J Franklin Inst 358(16):8109–8137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.08.007
Gu W, Yu Y, Hu W (2017) Artificial bee colony algorithmbased parameter estimation of fractional-order chaotic system with time delay. IEEE/CAA J Automatica Sinica 4(1):107–113. https://doi.org/10.1109/JAS.2017.7510340
Gu W, Yu Y, Hu W (2016) Parameter estimation of unknown fractional-order memristor-based chaotic systems by a hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm combined with differential evolution. Nonlinear Dyn 84(2):779–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2527-x
Mohammadzadeh A, Ghaemi S (2017) Optimal synchronization of fractional-order chaotic systems subject to unknown fractional order, input nonlinearities and uncertain dynamic using type-2 fuzzy CMAC. Nonlinear Dyn 88(4):2993–3002
Sabzalian MH, Mohammadzadeh A, Lin S, Zhang W (2019) Robust fuzzy control for fractional-order systems with estimated fraction-order. Nonlinear Dyn 98(3):2375–2385
Joya G, Atencia MA, Sandoval F (2002) Hopfield neural networks for optimization: study of the different dynamics. Neurocomputing 43(1–4):219–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-2312(01)00337-X
Kinderlehrer D, Stampacchia G (2000) An introduction to variational inequalities and their applications. Soc Ind Appl Math. https://doi.org/10.1137/1023111
Liu Q, Wang J (2008) A one-layer recurrent neural network with a discontinuous activation function for linear programming. Neural Comput 20(5):1366–1383. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.2007.03-07-488
Xia Y, Wang J (2015) A bi-projection neural network for solving constrained quadratic optimization problems. IEEE Transactions Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(2):214–224. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2500618
Xia Y, Wang J, Guo W (2019) Two projection neural networks with reduced model complexity for nonlinear programming. IEEE Transactions Neural Netw Learn Syst 31(6):2020–2029. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2927639
Liu Q, Wang J (2015) A projection neural network for constrained quadratic minimax optimization. IEEE Transactions Neural Netw Learn Syst 26(11):2891–2900. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2425301
Liu C, Li C, Li W (2020) Computationally efficient MPC for path following of underactuated marine vessels using projection neural network. Neural Comput Appl 32(11):7455–7464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04273-y
Hassan AA, El-Habrouk M, Deghedie S (2020) Inverse kinematics of redundant manipulators formulated as quadratic programming optimization problem solved using recurrent neural networks: a review. Robotica 38(8):1495–1512. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0263574719001590
Monje CA, Chen YQ, Vinagre BM, Xue D, and Feliu-Batlle V (2010) Fractional-order systems and controls: fundamentals and applications. Springer https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-84996-335-0
Yu Y, Li HX, Wang S, Yu J (2009) Dynamic analysis of a fractional-order Lorenz chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fractals 42(2):1181–1189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2009.03.016
Diethelm K, Ford NJ, Freed AD (2002) A predictor-corrector approach for the numerical solution of fractional differential equations. Nonlinear Dyn 29(1):3–22. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016592219341
Xia Y, Wang J (1998) A general methodology for designing globally convergent optimization neural networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 9(6):1331–1343. https://doi.org/10.1109/72.728383
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kariminia, A., Zarabadipour, H. A projection recurrent neural network based sliding mode control to stabilize unknown fractional-order chaotic systems. Int. J. Dynam. Control 11, 1736–1750 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-022-01072-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-022-01072-7