Abstract
Introduction
Although improved during the past few years, high blood pressure control still remains an unmet goal of antihypertensive drug treatment. Among different antihypertensive agents, calcium channel blockers (CCBs), either as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs are recommended by several guidelines for initiation and maintenance of antihypertensive treatment.
Aim
The HYT-HYperTension survey, carried out in Turkey was aimed to assess (a) blood pressure control in hypertensive patients under treatment with dihydropyridine CCBs, either as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs and (b) the prevalence of blood pressure control in subgroups of patients with cardiovascular risk factors (previous cardiovascular disease, diabetes, renal disease, isolated systolic hypertension, visceral obesity, overweight, current smoking habit).
Methods
More than 7000 hypertensive patients (60.0 % men, mean age 61.2 ± 11.5 years), routinely visited by either a specialist or a non-specialist physician in the Primary Care Units of 26 cities across Turkey, were enrolled in the survey. Only patients treated with dihydropyridine-type CCBs, as mono- or combination therapy were included in the study, whereas individuals treated with non-dihydropyridine-type CCBs or with other drug classes (as monotherapy or combination therapy), were excluded. Demographic data (age, gender, height, weight, waist circumference, current smoker habit), clinical data and drug treatments were collected at each visit. Blood pressure was measured with a semiautomatic device (Omron-M6) with the patient in sitting position and after at least 5 min of rest. Measurements were repeated three times, at intervals of 5 min each other.
Results
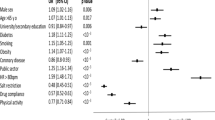
In the overall survey population blood pressure control (blood pressure <140/90 mmHg) was achieved in 31.7 % of patients and the average systolic and diastolic blood pressure was 145.3/88.2 mmHg. Prevalence of patients treated with dihydropyridine-type CCBs, either as monotherapy or combined with other drugs, was superimposable (51.6 vs 48.4 %, P = NS). Dihydropyridine-type CCBs were more frequently combined with drugs acting on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (86.4 %), particularly with ACE-inhibitors (34.1 %) and angiotensin II receptor antagonists (52.3 %), while in 13.6 % of patients CCBs were combined with diuretics and/or beta-blockers. Diabetes mellitus was detected in 22.7 % of patients, obesity in 41.5 % and history of cardiovascular disease in 23.0 % (coronary artery disease in 19.2 % and stroke in 3.8 %). Blood pressure control was more difficult to be achieved in complicated hypertension, particularly when cigarette smoking, obesity, overweight, visceral obesity and renal disease were associated with hypertension.
Conclusions
Taken together these findings provide evidence that dihydropyridine-type CCBs, particularly when combined with ACE-inhibitors or angiotensin II receptors blockers, allow to achieve a blood pressure control better than the one reported in the same geographic area by other treatment strategies based on different combinations of diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE-inhibitors, angiotensin II receptors blockers and calcium channel blockers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration. Effects of ACE inhibitors, calcium antagonists, and other blood pressure-lowering drugs: results of prospectively designed overviews of randomised trials. Lancet. 2000;355:1955–64.
Law MR, Morris JK, Wald NJ. Use of blood pressure lowering drugs in the prevention of cardiovascular disease: meta-analysis of 147 randomised trials in the context of expectations from prospective epidemiological studies. BMJ. 2009;338:b1665.
Mancia G, Laurent S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Burnier M, Caulfield MJ, Cifkova R, Clément D, Coca A, Dominiczak A, Erdine S, Fagard R, Farsang C, Grassi G, Haller H, Heagerty A, Kjeldsen SE, Kiowski W, Mallion JM, Manolis A, Narkiewicz K, Nilsson P, Olsen MH, Rahn KH, Redon J, Rodicio J, Ruilope L, Schmieder RE, Struijker-Boudier HA, Van Zwieten PA, Viigimaa M, Zanchetti A. Reappraisal of European guidelines on hypertension management: a European Society of Hypertension Task Force document. Blood Press. 2009;18(6):308–47.
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Hypertension. Clinical management of primary hypertension in adults. National Clinical Guideline Centre. London: Royal College of Physicians (UK). www.guidance.nice.org.uk/CG127 (2011).
Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration, Ninomiya T, Perkovic V, Turnbull F, Neal B, Barzi F, Cass A, Baigent C, Chalmers J, Li N, Woodward M, MacMahon S. Blood pressure lowering and major cardiovascular events in people with and without chronic kidney disease: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2013;347:1–15.
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Zanchetti A, Böhm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Galderisi M, Grobbee DE, Jaarsma T, Kirchhof P, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, Ruilope LM, Schmieder RE, Sirnes PA, Sleight P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Zannad F. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension. Blood Press. 2013;22(4):193–278.
James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, Lackland DT, LeFevre ML, MacKenzie TD, Ogedegbe O, Smith SC Jr, Svetkey LP, Taler SJ, Townsend RR, Wright JT Jr, Narva AS, Ortiz E. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA. 2014;311(5):507–20.
Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’ Collaboration, Sundström J, Arima H, Woodward M, Jackson R, Karmali K, Lloyd-Jones D, Baigent C, Emberson J, Rahimi K, MacMahon S, Patel A, Perkovic V, Turnbull F, Neal B. Blood pressure lowering treatment based on cardiovascular risk. A meta-analysis of individual patient data. Lancet. 2014;384:591–8.
Thomopoulos C, Parati G, Zanchetti A. Effects of blood pressure lowering on outcome incidence in hypertension. 1. Overview, meta-analyses and meta-regression analyses of randomized trials. J Hypertens. 2014;32:2285–95.
Volpe M, Tocci G, Trimarco B, Rosei EA, Borghi C, Ambrosioni E, Menotti A, Zanchetti A, Mancia G. Blood pressure control in Italy: results of recent surveys on hypertension J Hypertens. 2007;25:1491–8.
Grassi G, Cifkowa R, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K, Redon J, Farsang C, Viigimaa M, Erdine S, Brambilla G, Bombelli M, Dell’Oro R, Notari M, Mancia G. Blood pressure control and cardiovascular risk profile in hypertensive patients from central and eastern European countries: results of BP-Care study. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:218–35.
Banegas JR, Lopez-Garcıa E, Dallongeville J, Guallar E, Halcox JP, Borghi C, Massó-González EL, Jiménez FJ, Perk J, Steg PG, De Backer G, Rodríguez-Artalejo F. Achievement of treatment goals for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease in clinical practice across Europe: the EURIKA study. Eur Heart J. 2011;32:2143–52.
Giannattasio C, Cairo M, Cesana F, Alloni M, Sormani P, Colombo G, Grassi G, Mancia G. Blood pressure control in Italian essential hypertensives treated by general practitioners. Am J Hypertens. 2012;25:1182–7.
Bakris G, Sarafidis P, Agarwal R, Ruilope L. Review of blood pressure control rates and outcomes. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2014;8:127–41.
Tocci G, Ferrucci A, Pontremoli R, Ferri C, Rosei EA, Morganti A, Trimarco B, Mancia G, Borghi C, Volpe M. Blood pressure levels and control in Italy: comprehensive analysis of clinical data from 2000–2005 and 2005–2011 hypertension surveys. J Hum Hypertens. 2015. doi:10.1038/jhh.2015.4,10-14.
Abaci A, Kozan O, Oguz A, Sahin M, Deger N, Senocak H, Toprak N, Sur H, Erol C. Prescribing pattern of antihypertensive drugs in primary care units in Turkey: results from the TURKSAHA study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2007;63:397–402.
Sariisik A, Uzunlulu M. Control of hypertension in Turkey-is it improving? The Kocaeli-2 study. Arch Turk Soc Cardiol. 2009;37:13–6.
Altun B, Arici M, Nergizoğlu G, Derici U, Karatan O, Turgan C, Sindel S, Erbay B, Hasanoğlu E, Cağlar S, Turkish Society of Hypertension and Renal Diseases. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Turkey (the PatenT study) in 2003. J Hypertens. 2005;23:1817–23.
Sengul S, Erdem Y, Akpolat T, Derici U, Sindel S, Karatan O, Turgan C, Hasanoglu E, Caglar S, Erturk S. Controlling hypertension in Turkey: not a hopeless dream. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013;3:326–31.
Topouchian J, Agnoletti S, Blacher J, Youssef A, Chahine MN, Ibanez I, Assemani N, Asmar R. Validation of four devices: Omron M6Comfort, Omron HEM-7420, Withings BP-800, amd Polygreen KP-7670 for home blood pressure measurement according to European Society of Hypertension international protocol. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2014;10:33–44.
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, Grassi G, Heagerty AM, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope L, Rynkiewicz A, Schmieder RE, Struijker Boudier HA, Zanchetti A, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Kjeldsen SE, Erdine S, Narkiewicz K, Kiowski W, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Cifkova R, Dominiczak A, Fagard R, Heagerty AM, Laurent S, Lindholm LH, Mancia G, Manolis A, Nilsson PM, Redon J, Schmieder RE, Struijker-Boudier HA, Viigimaa M, Filippatos G, Adamopoulos S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Bertomeu V, Clement D, Erdine S, Farsang C, Gaita D, Kiowski W, Lip G, Mallion JM, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, O'Brien E, Ponikowski P, Redon J, Ruschitzka F, Tamargo J, van Zwieten P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Williams B, Zamorano JL. 2007 Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J. 2007;28(12):1462–536.
Altun B, Suleymanlar G, Utas C, Arınsoy T, Ateş K, Ecder T, Camsarı T, Serdengeçti K. Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in adults with chronic kidney disease in Turkey: results from the CREDIT study. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012;36:36–46.
Kotseva K, Wood D, De Backer G, De Bacquer D, Pyörälä K, Reiner Z, Keil U, EUROASPIRE Study Group. EUROASPIRE III. Management of cardiovascular risk factors in asymptomatic high-risk patients in general practice: cross-sectional survey in 12 European countries. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2010;17:530–40.
Satman I, Yilmaz T, Sengul A, Salman S, Salman F, Uygur S, Bastar I, Tütüncü Y, Sargin M, Dinççag N, Karsidag K, Kalaça S, Ozcan C, King H. Population-based study of diabetes and risk characteristics in Turkey. Results of the turkish diabetes epidemiology study (TURDEP). Diabetes Care. 2002;25:1551–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seravalle, G., Koylan, N., Nalbantgil, I. et al. HYT-Hypertension in Turkey: A Cross-Sectional Survey on Blood Pressure Control with Calcium Channel Blockers Alone or Combined with Other Antihypertensive Drugs. High Blood Press Cardiovasc Prev 22, 165–172 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-015-0091-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40292-015-0091-6