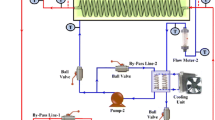
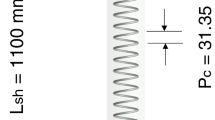
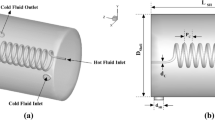
Abstract
Hydrodynamic and heat transfer characteristics of long-term stable nanofluids are very crucial for their industrial applications. Also utilization of coils is beneficial for industries as it provides a high rate of heat transfer and is compact in size too. So, the main focus of this study is to investigate the hydrodynamic and heat transfer characteristics of long-term stable f-CNT nanofluids when flowing inside a coil-based heat exchanger. f-CNT nanofluids were prepared by utilizing modified two-step method. To analyze the effect of different parameters on hydrodynamic and convective heat transfer characteristics, f-CNT concentration, \( {\varvec{D}}_{{\mathbf{c}}}\), and Re were varied from 0 to 0.048 vol%, 95 to 175 mm, and 2300 to 9500, respectively. According to results, f-CNT concentration, \( {\varvec{D}}_{{\mathbf{c}}}\), and Re substantially influenced the hydrodynamic and heat transfer characteristics of f-CNT nanofluids. It was found that improvement in h (152%) was much higher than the enhancement in friction factor (49%) when f-CNT nanofluid at 0.048 vol% was flowing through the coil of 95 mm diameter. Based on the heat transfer and hydrodynamic data, performance index was evaluated. The maximum performance index was calculated ⁓ 2.5, suggesting that the utilization of helical coils and f-CNT nanofluids is an excellent choice in industrial applications. Based on the experimental data, empirical correlations have been proposed to calculate the friction factor and Nusselt number for f-CNT nanofluids when flowing inside coils of different diameters and at different f-CNT concentrations. The proposed correlations explain the present experimental data within ± 15% and ± 20%, for friction factor and Nu, respectively.





















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A, A i :
-
Inside heat transfer area, m2
- A o :
-
Outside heat transfer area, m2
- CNT:
-
Carbon nanotubes
- \(C_{{p,\;{\text{f - CNT}}\;{\text{nanofluid}}}}\) :
-
Specific heat of f-CNT nanofluid, J/g.°C
- \(C_{{p,\;{\text{Water}}}}\) :
-
Specific heat of water, J/g.°C
- \(C_{{p,\;{\text{f - CNT}}}}\) :
-
Specific heat of f-CNT, J/g.°C
- C :
-
Constant
- \(D_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Diameter of helical coil, mm
- \(d_{{\text{t}}}\) :
-
Inside diameter of the tube, mm
- \(d_{{\text{t}}} /D_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Curvature ratio, dimensionless
- \(d_{{\text{o}}}\) :
-
Outside diameter of the tube, mm
- f-CNT:
-
–COOH functionalized carbon nanotubes
- \(f_{{\text{s}}}\), \(f_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Friction factor of straight tube and helical coil, dimensionless
- \(f_{{{\text{c }}\left( {{\text{cal}}} \right)}}\) :
-
Calculated friction factor of helical coil, dimensionless
- \(f_{{{\text{c}} \left( {{\text{exp}}} \right)}}\) :
-
Experimental friction factor of helical coil, dimensionless
- h :
-
Convective heat transfer coefficient of water or CNT nanofluids, W/m2.K
- \(h_{{\text{i}}}\) :
-
Tube side convective heat transfer coefficient, W/m2.K
- \(h_{{\text{o}}}\) :
-
Bath or shell side convective heat transfer coefficient, W/m2.K
- hr:
-
Hour
- ID:
-
Inside diameter of CNT, nm
- k w :
-
Thermal conductivity of copper tube, W/mK
- K :
-
Thermal conductivity of water or CNT nanofluids, W/mK
- \(k_{{{\text{CNT}}\;{\text{nanofluid}}}}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity, W/m.K
- \(k_{{\text{f}}}\) :
-
Thermal conductivity of fluid (water), W/m.K
- \(L_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Length of the helical coil, m
- L :
-
Length of CNT, µm
- \(\dot{m}_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Mass flow rate of coolant, kg/s
- n :
-
Exponent
- N :
-
Number of turns in helical coil
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- P :
-
Helical coil pitch, m
- ΔP :
-
Pressure drop, N/m2 or Pa
- \({\text{d}}P/L_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Pressure drop per unit length, Pa/m
- \(\dot{Q}_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Heat flow of coolant, W
- Re :
-
Reynolds number
- \( {Re}_{{\text{c}}}\) :
-
Critical Reynolds number, dimensionless
- \(\Delta T_{{{\text{lmtd}}}}\) :
-
Logarithmic mean temperature difference, °C
- \(T_{{{\text{bath}}}}\) :
-
Hot water bath temperature, °C
- \(T_{{{\text{out}}}}\) :
-
Outlet temperature, °C
- \(T_{{{\text{in}}}}\) :
-
Inlet temperature, °C
- \(T_{{\text{b, in}}}\) :
-
Bulk fluid temperature at inlet, °C
- \(T_{{\text{b, in}}}\) :
-
Bulk fluid temperature at outlet, °C
- \(U_{i}\) :
-
Overall heat transfer coefficient, W/m2.K
- \(\dot{V}\) :
-
Volumetric flow rate, m3/sec
- \(v,v_{i}\) :
-
Velocity of water or CNT nanofluids, m/s
- \(\rho_{{{\text{water}}}}\) :
-
Density of water
- \(\rho_{{\text{f - CNT}}}\) :
-
Density of f-CNT
- \(\rho_{{{\text{f - CNT}}\;{\text{nanofluid}}}}\) :
-
Density of f-CNT nanofluid
- \(\varphi\) :
-
Volumetric fraction, vol%
- µ :
-
Viscosity of water or CNT nanofluids, kg/m.s
- \(\mu_{{\text{f}}}\) :
-
Viscosity of base fluid (water), kg/m.s
- \(\mu_{{{\text{nf}}}}\) :
-
Viscosity of nanofluid, kg/m.s
Reference
Yang, L.; Ji, W.; Mao, M.; Huang, J.: Dynamic stability, sedimentation, and time-dependent heat transfer characteristics of TiO2 and CNT nanofluids. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 141, 1183–1195 (2019)
Singh, K.; Sharma, S.K.; Gupta S.M.: An experimental investigation of hydrodynamic and heat transfer characteristics of surfactant-water solution and CNT nanofluid in a helical coil-based heat exchanger. Mater. Today: Proc. (2020)
Behabadi, M.A.A.; Pakdaman, M.K.; Ghazvini, M.: Experimental investigation on the convective heat transfer of nanofluid flow insidevertical helically coiled tubes under uniform wall temperature condition. Int. Commun. Heat Mass 39, 556–564 (2012)
Sahin, B.; Manay, E.; Akyurek, E.F.: An experimental study on heat transfer and pressure drop of CuO-water nanofluid. J. Nanomater. 2015, 1–10 (2015)
Babita, S.K.; Sharma, S.M.; Shipra, J.: Preparation and evaluation of stable nanofluids for heat transfer application: a review. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 79, 202–212 (2016)
Sharma, B.; Sharma, S.K.; Gupta, S.M.; Kumar, A.: Modified two-step method to prepare long-term stable CNT nanofluids for heat transfer applications. AJSE 43, 6155–6163 (2018)
Hosseinalipour, S.M.; Mashaei, P.R.; Esmailpour, K.: Heat transfer enhancement using nanofluids in laminar impinging jet flows. In: 13th Annual & 2nd International Fluid Dynamics Conference, Shiraz Iran (2010)
Gupta, R.; Wanchoo, R.K.; Ali, T.R.M.J.: Laminar flow in helical coils: a parametric study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 50, 1150–1157 (2011)
Akbaridoust, F.; Rakhsha, M.; Abbassi, A.; Saffar-Avval, M.: Experimental and numerical investigation of nanofluid heat transfer in helically coiled tubes at constant wall temperature using dispersion model. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 58, 480–491 (2013)
Seyyedvalilu, M.H.; Ranjbar, S.F.: The effect of geometrical parameters on heat transfer and hydro dynamical characteristics of helical exchanger. Int. J. Recent Adv. Mech. Eng. 4(1), 35–46 (2015)
Ding, Y.; Alias, H.; Wen, D.; Williams, R.A.: Heat transfer of aqueous suspensions of carbon nanotubes (CNT nanofluids). Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 49, 240–250 (2006)
Rea, U.; McKrell, T.; Hu, L.; Buongiorno, J.: Laminar convective heat transfer and viscous pressure loss of alumina–water and zirconia–water nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 52, 2042–2048 (2009)
Albadr, J.; Tayal, S.; Alasadi, M.: Heat transfer through heat exchanger using Al2O3 nanofluid at different concentrations. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 1, 38–44 (2013)
Esfe, M.Z.H.; Saedodin, S.; Mahian, O.; Wongwises, S.: Thermo-physical properties, heat transfer and pressure drop of COOH-functionalized multi walled carbon nanotubes/water nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Trans. 58, 176–183 (2014)
Halelfadl, S.; Mare, T.; Estelle, P.: Efficiency of carbon nanotubes water based nanofluids as coolants. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 53, 104–110 (2014)
Walvekar, R.; Siddiqui, M.K.; Ong, S.S.; Ismail, A.F.: Application of CNT nanofluids in a turbulent flow heat exchanger. J. Exp. Nanosci. 10(1), 1–17 (2015)
Singh, R.N.; Rajat, P.; Lav, I.; Pandey, P.K.: Experimental studies of nanofluid TiO2/CuO in a heat exchanger (double pipe). Ind. J. Sci. Technol. 9(31), 1–6 (2016)
Ahammed, N.; Asivatham, L.G.; Wongwises, S.: Thermoelectronic cooling of electronic devices with nanofluid in a multiport minichannel heat exchanger. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 74, 81–90 (2016)
Akbaridoust, F.; Rakhsha, M.; Avval, A.A.M.S.: Experimental and numerical investigation of nanofluid heat transfer in helically coiled tubes at constant wall temperature using dispersion model. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 58, 480–491 (2013)
Kahani, M.; Heris, S.Z.; Mousavi, S.M.: Effects of curvature ratio and coil pitch spacing on heat transfer performance of Al2O3/Water nanofluid laminar flow through helical coils. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 34, 1703–1712 (2013)
Pakdaman, M.F.; Behabadi, M.A.A.; Razi, P.: An empirical study on the pressure drop characteristics of nanofluid flow inside helically coiled tubes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 65, 206–213 (2013)
Sharma, P.; Gupta, R.; Wanchoo, R.K.: Hydrodynamics studies on glycol based Al2O3 nanofluid flowing through straight tubes and coils. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 82, 19–31 (2017)
Sharma, B.; Sharma, S.K.; Gupta, S.M.: Hydrodynamic studies of CNT nanofluids in helical coil heat exchanger. Mat. Res. Exp. 4(1), 124002 (2017)
Seyyedvalilu, M.H.; Ranjbar, S.F.: The effect of geometrical parameters on heat transfer and hydro dynamical characteristics of helical exchanger. IJMECH 4(1), 35–46 (2015)
Khairul, M.A.; Saidur, R.; Hossain, A.; Alim, M.A.; Mahbubul, I.M.: Heat transfer performance of different nanofluids flows in a helically coiled heat exchanger. Adv. Mat. Res. 832, 160–165 (2014)
Lamas, B.; Abreu, B.; Fonseca, A.; Martins, N.; Oliveira, M.: Assessing colloidal stability of long term MWCNT based nanofluids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 381, 17–23 (2012)
Kun, Y.; Li, Y.Z.; Feng, J.Q.; Liang, Y.R.; Wei, J.; Hui, L.D.: Sonication-assisted dispersion of carbon nanotubes in aqueous solutions of the anionic surfactant SDBS: the role of sonication energy. Chin. Sci. Bull. 58(17), 2082–2090 (2013)
Babita; Sharma, S.K.; Gupta, S.M.: Experimental studies on pressure drop/friction factor of CNT nanofluids flowing through helical coils and development of a new empirical correlation. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 41, 607–617 (2019)
Salimpour, M.R.: Heat transfer coefficients of shell and coiled tube heat exchangers. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 33, 203–207 (2009)
Srinivasan, P.S.; Nandapurkar, S.S.; Holland, F.A.: Pressure drop and heat transfer in coils. Chem. Eng. 218, 113–119 (1968)
Ito, H.: Friction factors for turbulent flow in curved pipes. J. Basic Eng. Trans. ASME 81, 123–134 (1959)
Kubair, V.; Varrier, C.B.S.: Pressure drop for liquid flow in helical coils. Trans. Indian Inst. Chem. Eng. 14 (1961, 1962)
Merkel, F.; Die, W.: Grundlagen der. Springer Publishing Company, Berlin (1927)
Rogers, G.F.C.; Mayhew, Y.: Heat transfer and pressure loss in helically coiled tubes with turbulent flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 7, 1207–1216 (1964)
Mori, Y.; Nakayama, W.: Study on forced convective heat transfer in curved tubes. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 10, 37–59 (1967)
Xin, R.C.; Ebadian, M.A.: The effects of Prandtl numbers on local and average convective heat transfer characteristics in helical pipes. J. Heat Trans. 119, 467 (1997)
Seban, R.A.; McLaughlin, E.F.: Heat transfer in tube coils with laminar and turbulent flow. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 6, 387–395 (1963)
Dravid, A.N.; Smith, K.A.; Merrill, E.W.; Blian, P.L.T.: Effect of secondary fluid motion on laminar flow heat transfer in helically coiled tubes. AIChEJ 17(4), 1114–1122 (1971)
Kalb, C.E.; Seader, J.D.: Fully developed viscous flow heat transfer in curved circular tubes with uniform wall temperature. AIChE J. 20, 340–346 (1974)
Prasher, R.; Song, D.; Wang, J.: Measurements of nanofluid viscosity and its implications for thermal applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89(133108), 1–3 (2006)
Timofeeva, E.V.; Gavrilov, A.N.; McCloskey, J.M.; Tolmachev, Y.V.: Thermal conductivity and particle agglomeration in alumina nanofluids: experiment and theory. Phy. Rev. 76(6), 1–16 (2007)
Ravikanth, S.V.; Das, D.K.; Kulkarni, D.P.: Development of new correlations for convective heat transfer and friction factor in turbulent regime for nano-fluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Trans. 53, 4607–4618 (2010)
Guangbin, Y.; Dejun, G.; Juhui, C.; Bing, D.; Di, L.; Ye, S.; Xi, C.: Experimental research on heat transfer characteristics of CuO nanofluid in adiabatic condition. J. Nanomater. 2016, 3693249 (2016)
Ahammed, N.; Asirvatham, L.G.; Wongwises, S.: Thermoelectric cooling of electronic devices with nanofluid in a multiport minichannel heat exchanger. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 74, 81–90 (2016)
Prabhanjan, D.G.; Ragbavan, G.S.V.; Kennic, T.J.: Comparison of heat transfer rates between a straight tube heat exchanger and a helically coiled heat exchanger. Int. Comm. Heat Mass Trans. 29(2), 185–191 (2002)
Jong, Y.G.; Hoon-Ki, C.; Wa-Ryong, D.: Fluid flow and heat transfer characteristics of spiral coiled tube: effects of Reynolds number and curvature ratio. J. Cent. South Univ. 19, 471–476 (2012)
Srinivas, V.; Moorthy, V.K.N.S.N.; Dedeepya, V.; Manikanta, P.V.; Satish, V.: Nanofluids with CNTs for automotive applications. Heat Mass Trans. 52, 701–712 (2016)
Gajendiran, M.; Saravanakumar, E.; Raj, N.M.; Nallusamy, N.: Heat transfer enhancement of thermic fluid by using nanofluids in radiator. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 8(3), 686–692 (2016)
Sahin, B.; Manay, F.; Akyurek, E.F.: An experimental study on heat transfer and pressure drop of CuO-water nanofluid. J. Nanomater. (2015)
Xuan, Y.; Li, Q.: Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 21, 58–64 (2000)
Singh, R.N.; Rajat, P.; Lav, I.; Pandey, P.K.: Experimental studies of nanofluid TiO2/CuO in a heat exchanger (double pipe). Indian J. Sci. Technol. 9(31) (2016)
Ghahdarijani, A.M.; Hormozi, F.; Asl, A.H.: Application of nano-fluids to heat transfer enhancement in double-walled reactor. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 7(3), 1–8 (2016)
Pakdaman, M.F.; Akhavan-Behabadi, M.A.; Razi, P.: An experimental investigation on thermo-physical properties and overall performance of MWCNT/heat transfer oil nanofluid flow inside vertical helically coiled tubes. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 40, 103–111 (2012)
Acknowledgements
This study is financially supported by GGSIP University, New Delhi, India, under FRGS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, B., Sharma, S.K. & Gupta, S.M. Experimental Studies of f-CNT Nanofluids in a Helical Coil Heat Exchanger. Arab J Sci Eng 47, 5821–5840 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05573-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05573-z