Abstract
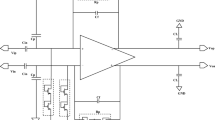
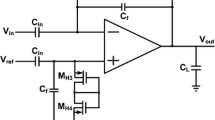
This paper deals with the noise optimization of a low-power front-end amplifier (FEA) integrating a band-pass filter for EEG signal recording. The AC-coupled and capacitive feedback structures have been adopted in order to reject the large DC offset generated at the electrode–skin interface. A high open-loop gain with acceptable phase margin was obtained with the proposed operational transconductance amplifier architecture. The methodology to reach a low noise-to-power trade-off is based on selecting the suitable operation region of each transistor, especially the input differential pair by considering the gm/ID parameter. The proposed amplifier was implemented in both 0.13 μm and 0.18 μm CMOS processes with a supply voltage set to ± 1 V. For both technologies, the obtained gain and bandwidth are practically similar, while the phase margin obtained in the first process (0.13 μm) is higher than the one obtained in the second process (0.18 μm); however, both values insure system stability. A lower total input-referred noise of 1.7 µVrms with a noise efficiency factor of 3.4 was obtained in 0.18 µm CMOS process. The designed FEA has been found suitable for ECG biopotential recording.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morikawa, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Patki, S.; Grundlehner, B.; Verwegen, A.; Xu, J.; Mitra, S.; Penders, J.: Compact wireless EEG system with active electrodes for daily life healthcare monitoring. In: IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics, pp. 204–205, Las Vegas, USA (2013)
Sawan, M.; Salam, M.T.; Lan, J.L.; Kassab, A.; Élinas, S.; Vannasing, P.; Lesage, F.; Lassonde, M.; Nguyen, D.K.: Wireless recording systems: from noninvasive EEG-NIRS to invasive EEG devices. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 7(2), 186–195 (2013)
Lin, C.T.; Chuang, C.H.; Huang, C.S.; Tsai, S.F.; Lu, S.W.; Che, Y.H.; Ko, L.W.: Wireless and wearable EEG system for evaluating driver vigilance. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 8(2), 165–176 (2014)
Hasan, Md.K.; Rusho, R.Z.; Hossain, T.Md.; Ghosh, T.K.; Ahmad, M.: Design and simulation of cost effective wireless EEG acquisition system for patient monitoring. In: International Conference on Informatics, Electronics and Vision, pp. 1–5, Dhaka, Bangladesh (2014)
Brown, L.; Molengraft, J.V.; Yazicioglu, R.F.; Torfs, T.; Penders, J.; Van Hoof, C.: A low power wireless 8 channel EEG monitoring headset. In: IEEE EMBS Annual International Conference, pp. 4197–4200, Buenos Aires, Argentina (2010)
Alchalcabi, A.E.; Nour Eddin, A.; Shirmohammadi, S.: More attention, less deficit: Wearable EEG-based serious game for focus improvement. In: IEEE International Conference on Serious Games and Applications for Health, pp. 1–8, Perth, WA, Australia (2017)
Xu, J.; Mitra, S.; Matsumoto, A.; Patki, S.; Hoof, C.V.; Makinawa, K.A.A.; Yazicioglu, R.F.: A wearable 8 channel active-electrode EEG/ETI acquisition system for body area networks. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 9(9), 2005–2016 (2014)
Abdallah, A.; Mahmoud, S.: Electroencephalogram system based on CMOS analog front-end interleaved chain architecture. In: International Conference on Microelectronics, pp. 5–8, Giza, Egypt (2016)
Feng, J.; Yan, N.; Min, H.: A low power low noise amplifier for EEG/ECG signal recording applications. In: IEEE International Conference on ASIC, pp. 145–148, Xiamen, China (2011)
Liu, H.; Tang, K.T.; Wu, J.Y.; Wang, G.: A digitally trimmable low noise low power analog front end for EEG signal acquisition. In: IEEE-EMBS International Conference Biomedical and Health Infomatics, pp. 208–210. Hong Kong, China (2012)
Casson, A.J.; Abdullal, M.; Dulabh, M.; Kohli, S.; Krachunov, S.; Trimble, E.: Electroencephalogram. In: Tamura, T., Chen, W. (eds.) Seamless Healthcare Monitoring, Chap. 2, pp. 45–81. Springer, Berlin (2018)
Bronzino, J.D. (ed.): Principles of electroencephalography. In: The Biomedical Engineering Handbook, Chap. 3, vol. 1, 2nd edn. CRC and IEEE Press, USA (2000)
Yin, M.; Ghovanloo, M.: A low noise preamplifier with adjustable gain and bandwidth for biopotential recording applications. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 321–324, New Orleans, LA (2007)
Harrison, R.R.; Watkins, P.T.; Kier, R.J.; Lovejoy, R.O.; Black, D.J.; Greger, B.; Solzbacher, F.: A low power integrated circuit for a wireless 100 electrode neural recording system. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 42(1), 125–130 (2007)
Chandran, A.P.; Nadjafi, K.; Wise, K.D.: A new DC baseline stabilization scheme for neural recording microprobes. In: Proceedings of the First Joint BMES/EMBS Conference Serving Humanity, vol. 1, Atlanta, GA (1999)
Olsson, R.H.; Buhl, D.L.; Sirota, A.M.; Buzsaki, G.; Wise, K.D.: Band-tunable and multiplexed integrated circuits for simultaneous recording and stimulation with microelectrode arrays. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 52(7), 1303–1311 (2005)
Yazicioglu, R.F.; Merken, P.; Puers, R.; Van Hoof, C.: A 60 μW 60 nV/√Hz readout front-end for portable biopotential acquisition systems. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 42(5), 1100–1110 (2007)
Dagtekin, M.; Liu, W.; Bashirullah, R.: A multi-channel chopper modulated neural recording system. In: EMBS International Conference, Istanbul, Turkey (2001)
Denison, T.; Consoer, K.; Santa, W.; Avestruz, A.; Cooley, J.; Kelly, A.: A 2 µW 100 nV/√Hz chopper stabilized instrumentation amplifier for chronic measurement of neural field potentials. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 42(12), 2934–2945 (2007)
Harrison, R.R.; Charles, C.: A low-power low-noise CMOS amplifier for neural recording applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 38(6), 958–965 (2003)
Moreno, R.; Pimenta, T.; Crepaldi, P.; Dutra, O.; Colletta, G.D.; Zoccal, L.: A low noise low power OTA with adjustable gain PID feedback network for EEG Soc arrays. In: Hudak, R., Penhaker, M., Majernik, J. (eds.) Biomedical Engineering Technical Applications in Medicine, Chap. 18. IntechOpen (2012)
El Guindy, M.; Madian, A.H.: Low voltage digitally programmable gain and bandwidth fully differential CMOS neural amplifier. In: IEEE RAS -EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, pp. 477–481, Roma, Italy (2012)
Xiaofei, P.; Lei, W.; Hui, Z.; Yajie, Q.; Zhiliang, H.: A low power portable ECG sensor interface with dry electrodes. J. Semiconduc. 34(5), 055002-1–055002-6 (2013)
Xu, Z.; Weihua, P.; Beiju, H.; Hongda, C.: Low power CMOS preamplifier for neural recording applications. J. Semiconduc. 31(4), 045002-1–045002-6 (2000)
Seo, I.; Fox, R.: Comparison of quasi-pseudo-floating gate techniques and low voltage applications. Anal. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 47, 183–192 (2006)
Mohseni, P.; Najafi, K.: A fully integrated neural recording amplifier with DC input stabilization. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51(5), 832–837 (2004)
Aghtar, S.; Haslett, J.W.; Trofimenkoff, F.N.: Subthreshold analysis of an MOS analog switch. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 44(1), 89–96 (1997)
Razavi, B.: Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits. McGraw Hill, New York (2001)
Enz, C.C.; Krummenacher, F.; Vittoz, E.A.: An analytical MOS transistor model valid in all region of operation and dedicated to low voltage and low current applications. Anal. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 8, 83–114 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saadi, H., Attari, M. & Escid, H. Noise Optimization of CMOS Front-End Amplifier for Embedded Biomedical Recording. Arab J Sci Eng 45, 1961–1968 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04347-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-04347-3