Abstract
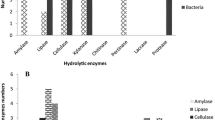
This report describes cultivation-dependent diversity, phylogeny and enzymatic potential of the haloalkaliphilic bacteria isolated from the unvegetated desert soil of yet unexplored, saline desert of Little Rann of Kutch (LRK), India. The LRK is a unique ecosystem displaying a combination of Dry Rann and Wet Rann. A total of 25 bacteria were isolated and characterized on the basis of colony morphology, biochemical profile, sugar utilization, secretion of the extracellular enzymes and antibiotic sensitivity. Further, the identification and phylogenetic relatedness of 23 bacteria were established by the analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequences. The phylogenetic analysis indicated that the isolates belong to the phylum Firmicutes, comprising low G + C, Gram-positive bacteria, with different genera: Bacillus (~ 39%), Staphylococcus (~ 30%), Halobacillus (~ 13%), Virgibacillus (~ 13%), Oceanobacillus (~ 4%). Majority of the bacterial isolates produced proteases (30% isolates) followed by cellulases (24% isolates), CMCases (24% isolates) and amylases (20% isolates). Halobacillus, Virgibacillus and Bacillus predominantly produced hydrolases, while many produced multiple enzymes at high salinity and alkaline pH. Highest antibiotic resistance was observed against Ampicillin and Penicillin (32%) followed by Cefaclor (20%); Colistin, Cefoperazone and Cefotaxime (16%); Cefuroxime (12%); Gentamycin and Cefixime (8%); Erythromycin, Cefadroxil, Azithromycin, Co-trimoxazole, Amoxycillin, Norfloxacin, Cefpodoxime, Amikacin and Augmentin (4%). KJ1-10-99 and KJ1-10-93 representing < 97% of 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity belong to a novel lineage within the family Bacillaceae. Comparison of the phenogram and phylogram revealed the contradiction of the phenogram pattern and the phylogenetic placement of the isolates. The isolates belonging to same species have shown considerable phenotypic variation. The study on the cultivable haloalkaliphilic bacteria of an unexplored enigmatic niche reflects ecological and biotechnological significance.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoozegar MA, Malekzadeh F, Malik KA (2003) Production of amylase by newly isolated moderate halophile, Halobacillus sp. strain MA-2. J Microbiol Methods 52:353–359
An S, Couteau C, Luo F, Neveu J, DuBow MS (2013) Bacterial diversity of surface sand samples from the Gobi and Taklamaken deserts. Microb Ecol 66:850–860
Andrew DR, Fitak RR, Munguia-Vega A, Racolta A, Martinson VG, Dontsova K (2012) Abiotic factors shape microbial diversity in Sonoran desert soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:7527
Arahal DR, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ, Volcani BE, Ventosa A (1996) Phylogenetic analyses of some extremely halophilic archaea isolated from Dead Sea water, determined on the basis of their 16S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3779–3786
Baati H, Amdouni R, Gharsallah N, Sghir A, Ammar E (2010) Isolation and characterisation of moderately halophilic bacteria from Tunisia solar saltern. Curr Microbiol 60:157–161
Bhatt HB, Singh SP (2016) Phylogenetic and phenogram based diversity of haloalkaliphilic bacteria from the saline desert. In: Bhukya B, Tangutur AD (eds) Microbial biotechnology-technological challenges and developmental trends. Apple Academic Press, Oakville, pp 373–386. https://doi.org/10.1201/b19978-24
Bhatt HB, Begum AM, Chintalapati S, Chintalapati VR, Singh SP (2017) Desertibacillus haloalkaliphilus gen. nov. sp. nov., isolated from a saline desert. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67(11):4435–4442
Cappuccino JG, Sherman N (2004) Microbiology, a laboratory manual, 6th edn. Pearson education, Singapore
Casamayor EO, Triadó-Margarit X, Castañeda C (2013) Microbial biodiversity in saline shallow lakes of the Monegros Desert, Spain. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 85:503–518
Caton TM, Witte LR, Ngyuen HD, Buchheim JA, Buchheim MA, Schneegurt MA (2004) Halotolerant aerobic heterotrophic bacteria from the Great Salt Plains of Oklahoma. Microb Ecol 48:449–462
Demergasso C, Casamayor EO, Chong G, Galleguillos P, Escudero L, Pedrós-Alió C (2004) Distribution of prokaryotic genetic diversity in athalassohaline lakes of the Atacama Desert, Northern Chile. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:57–69
Dong HL, Rech JA, Jiang HC, Sun H, Buck BJ (2007) Endolithic cyanobacteria in soil gypsum: occurrences in Atacama (Chile), Mojave (United States), and Al-Jafr Basin (Jordan) deserts. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 112:2005–2012
Duckworth AW, Grant WD, Jones BE, Steenbergen RV (1996) Phylogenetic diversity of Soda lake alkaliphiles. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 19:181–191
Essoussi I, Boujmil R, Nouioui I, Abbassi-Ghozzi I, Hamza A, Boudabous A, Gtari M (2012) Genetic diversity and esterase-profiling of actinobacteria isolated from Sahara desert stones and monuments. Geomicrobiol J 29:23–28
Falkowski PG, Fenchel T, Delong EF (2008) The microbial engines that drive Earth’s biogeochemical cycles. Science 320:1034–1039
Foti MJ, Sorokin DY, Zacharova EE, Pimenov NV, Kuenen JG, Muyzer G (2008) Bacterial diversity and activity along a salinity gradient in soda lakes of the Kulunda steppe (Altai, Russia). Extremophiles 12:133–145
Guesmi A, Ettoumi B, Hidri DE, Essanaa J, Cherif H, Mapelli F, Marasco R, Rolli E, Boudabous A, Cherif A (2013) Uneven distribution of Halobacillus trueperi species in arid natural saline systems of Southern Tunisian Sahara. Microb Ecol 66:831–839
Gupta V, Ansari AA (2014) Geomorphic portrait of the Little Rann of Kutch. Arab J Geosci 1:527–536
Hacĕne H, Rafa F, Chebhouni N, Boutiba S, Bhatnagar T, Baratti JC, Ollivier B (2004) Biodiversity of prokaryotic microflora in El GoleaSalt, Algerian Sahara. J Arid Environ 58:273–284
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4:1–9
Hedi A, Sadfi N, Fardeau M-L, Rebib H, Cayol J-L, Ollivier B, Boudabous A (2009) Studies on the biodiversity of halophilic microorganisms isolated from El-Djerid Salt Lake (Tunisia) under aerobic conditions. Int J Microbiol 2009:1–17
Horikoshi K (1999) Alkaliphiles: some applications of their products for biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:735–750
Horner-Devine MC, Carney KM, Bohannan BJM (2003) An ecological perspective on bacterial diversity. Proc R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 271:113–122
Ishnava K, Ramarao V, Mohan JSS, Kothari IL (2011) Ecologically important and life supporting plants of little Rann of Kachchh, Gujarat. J Ecol Nat Environ 3:33–38
Joshi AA, Kanekar PP, Kelkar AS, Shouche YS, Vani AA, Borgave SB, Sarnaik SA (2008) Cultivable bacterial diversity of alkaline Lonar Lake, India. Microb Ecol 55:163–172
Joshi RH, Dodia MS, Singh SP (2009) Production and optimization of a commercially viable alkaline protease from a haloalkaliphilic bacterium. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 13:552–559
Kasana RC, Salwan R, Dhar H, Dutt S, Gulati A (2008) A rapid and easy method for the detection of microbial cellulases on agar plates using Gram’s iodine. Curr Microbiol 57:503–507
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kim TY, Kim SJ, Park SJ, Kim JG, Cha IT, Jung MY, Lee SA, Roh SW, Yim KJ, Itoh T, Rhee SK (2013) Natronomonas gomsonensis sp. nov. isolated from a solar saltern. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 104:627–635
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Langenheder S, Bulling MT, Solan M, Prosser JI (2010) Bacterial biodiversity-ecosystem functioning relations are modified by environmental complexity. PLoS One 5:e10834
Li K, Liu R, Zhang H, Yun J (2013) The diversity and abundance of bacteria and oxygenic phototrophs in saline biological desert crusts in Xinjiang, Northwest China. Microb Ecol 66:40–48
Lima-Bittencourt CI, Astolfi-Filho S, Chartone-Souza E, Santos FR, Nascimento AMA (2007) Analysis of Chromobacterium sp. natural isolates from different Brazilian ecosystems. BMC Microbiol 7:58
Litzner BR, Caton TM, Schneegurt MA (2006) Carbon substrate utilization, antibiotic sensitivity, and numerical taxonomy of bacterial isolates from the Great Salt Plains of Oklahoma. Arch Microbiol 185:286–296
Madsen EL (2005) Identifying microorganisms responsible for ecologically significant biogeochemical processes. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:439–446
Margesin R, Schinner F (2001) Potential of halotolerant and halophilic microorganisms for biotechnology. Extremophiles 5:73–83
Monier JM, Lindow SE (2003) Differential survival of solitary and aggregated bacterial cells promotes aggregate formation on leaf surfaces. PNAS 100:15977–15982
Nowlan B, Dodia MS, Singh SP, Patel BKC (2006) Bacillus okhensis sp. nov., a halotolerant and alkalitolerant bacterium from an Indian saltpan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1073–1077
Pandey S, Rakholiya K, Raval VH, Singh SP (2012) Catalysis and stability of an alkaline protease from a haloalkaliphilic bacterium under non-aqueous conditions as a function of pH, salt and temperature. J Biosci Bioeng 114:251–256
Petraitis PS, Latham RE, Niesenbaum RA (1989) The maintenance of species diversity by disturbance. Q Rev Biol 64:393–418
Phillips K, Zaidan F, Elizondo OR, Lowe KL (2012) Phenotypic characterization and 16S rDNA identification of culturable non-obligate halophilic bacterial communities from a hypersaline lake, La Sal del Rey, in extreme South Texas (USA). Aquat Biosyst 8:5
Pilania PK, Panchal NS (2016) Influence of sodium and calcium on vegetation at Saline Desert (Little Rann of Kutch) of Gujarat State in India. Ann Arid Zone 55(1&2):1
Purohit MK, Singh SP (2011) Comparative analysis of enzymatic stability and amino acids sequences of thermostable alkaline proteases from two haloalkaliphilic bacteria isolated from coastal region of Gujarat, India. Int J Biol Macromol 49:103–112
Quesada E, Bejar V, Valderrama MJ, Ventosa A, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1985) Isolation and characterization of moderately halophilic non motile rods from different saline habitats. Microbiologia 1:89–96
Raeid MM, Kharusi ASA, Schramm A, Robinson MD (2010) Bacterial diversity, pigments and nitrogen fixation of biological desert crusts from the Sultanate of Oman. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72:418–428
Rao S, Chan Y, Bugler-Lacap DC, Bhatnagar A, Bhatnagar M, Pointing SB (2016) Microbial diversity in soil, sand dune and rock substrates of the Thar Monsoon Desert, India. Indian J Microbiol 56:35–45
Rasuk MC, Fernández AB, Kurth D, Contreras M, Novoa F, Poiré D, Farías ME (2016) Bacterial diversity in microbial mats and sediments from the Atacama Desert. Microb Ecol 71:44–56
Raval VH, Pillai S, Rawal CM, Singh SP (2014) Biochemical and structural characterization of a detergent-stable serine alkaline protease from seawater haloalkaliphilic bacteria. Process Biochem 49:955–962
Rohban R, Amoozegar MA, Ventosa A (2009) Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolases from Howz Soltan Lake, Iran. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:333–340
Romano I, Giordano A, Lama L, Nicolaus B, Gambacorta A (2005) Halomonas campaniensis sp. nov. a haloalkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a mineral pool of Campania Region, Italy. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:610–618
Sahay H, Mahfooz S, Singh AK, Singh S, Kaushik R, Saxena AK, Arora DK (2012) Exploration and characterization of agriculturally and industrially important haloalkaliphilic bacteria from environmental samples of hypersaline Sambhar Lake, India. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:3207–3217
Sass AM, McKew BA, Sass H, Fichtel J, Timmis KN, McGenity TJ (2008) Diversity of Bacillus-like organisms isolated from deep-sea hypersaline anoxic sediments. Saline Syst 4:1–11
Saul-Tcherkas V, Unc A, Steinberger Y (2013) Soil microbial diversity in the vicinity of desert shrubs. Microb Ecol 65:689–699
Schlesner H, Lawson PA, Collins MD, Weiss N, Wehmeyer U, Volker H, Thomm M (2001) Filobacillus milensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new halophilic spore-forming bacterium with Orn-d-Glutypepeptidoglycan. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:425–431
Schnider-Keel U, Lejbølle KB, Baehler E, Haas D, Keel C (2001) The sigma factor AlgU (AlgT) controls exopolysaccharide production and tolerance towards desiccation and osmotic stress in the biocontrol agent pseudomonas fluorescence CHA0. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5683–5693
Scola V, Ramond JB, Frossard A, Zablocki O, Adriaenssens EM, Johnson RM, Seely M, Cowan DA (2018) Namib Desert soil microbial community diversity, assembly, and function along a natural xeric gradient. Microb Ecol 193–203
Su J, Wu Y, Ma X, Zhang G, Feng H, Zhang Y (2004) Soil microbial counts and identification of culturable bacteria in an extreme by arid zone. Folia Microbiol 49:423–429
Subrahmanyam G, Khonde N, Maurya DM, Chamyal LS, Archana G (2014) Microbial activity and culturable bacterial diversity in sediments of the Great Rann of Kachchh, Western India. Pedosphere 24(1):45–55
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Taprig T, Akaracharanya A, Sitdhipol J, Visessanguan W, Tanasupawat S (2013) Screening and characterization of protease-producing Virgibacillus, Halobacillus and Oceanobacillus strains from Thai fermented fish. J Appl Pharm Sci 3:025–030
Thomas M, Pal KK, Dey R, Saxena AK, Dave SR (2012) A novel haloarchael lineage widely distributed in the hypersaline marshy environment of Little and Great Rann of Kutch in India. Curr Sci 10:1078–1084
Torsvik V, Øvreas L (2002) Microbial diversity and function in soil: from genes to ecosystems. Curr Opin Microbiol 5:240–245
UNESCO (2006) World Heritage Centre-Nomination entry. http://whc.unesco.org/en/tentativelists/2105/. Accessed 3 June 2017
Yeon SH, Jeong WJ, Park JS (2005) The diversity of culturable organotrophic bacteria from local solar salterns. J Microbiol 43(1):1–10
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to University Grants Commission (UGC), India and Saurashtra University for the infrastructural and financial support. Support under the UGC-Centre of Advanced Study and DST-FIST programs is acknowledged. Award of Research Associateship to SDG by CSIR, New Delhi is duly acknowledged. HB is grateful to the UGC, New Delhi for Meritorious Fellowship under BSR Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhatt, H.B., Gohel, S.D. & Singh, S.P. Phylogeny, novel bacterial lineage and enzymatic potential of haloalkaliphilic bacteria from the saline coastal desert of Little Rann of Kutch, Gujarat, India. 3 Biotech 8, 53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1075-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1075-0