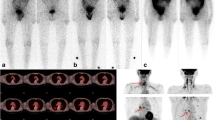
Abstract
Objective
To investigate predictors for successful ablation and disease-free status after high-dose radioiodine therapy in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer.
Methods
We enrolled 173 consecutive patients with differentiated thyroid cancer between November 2001 and December 2004 retrospectively (female 145, 46 ± 12 years). All patients underwent total thyroidectomy and I-131 ablative therapy (IAT) (3.7–5.4 GBq). The success or failure of ablation was assessed 6–9 months after the IAT with reference to undetectable thyroglobulin (Tg) and negative I-131 whole body scan (WBS). Afterward, the decision for disease-free status was evaluated using Tg and WBS (follow-up period after 1st IAT 7–81 months, median 43 months, criteria of disease-free: less than 10 ng/ml TSH-stimulated Tg or less than 2 ng/ml TSH-unstimulated Tg and/or negative WBS). Clinical and tumoral factors such as sex, age, pathologic type, the size of tumor, quantified cervical uptake in WBS1, pattern in WBS1, ablative therapy dose, AJCC stage, lymph node (LN) stage, Tg just before IAT (Tg1), and ablation status were assessed using logistic regression analyses.
Results
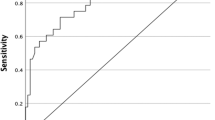
There were 93 successful ablations (54 %). Significant predictors for the ablation failure were Tg1 (OR = 8.42; 95 % CI = 2.76–25.69; p < 0.0001), LN metastasis (OR = 3.05; 95 % CI = 1.11–8.37; p = 0.031), and quantified cervical uptake in WBS1 (OR = 4.95; 95 % CI = 1.07–22.88; p = 0.041). One hundred fifty-five patients were determined as disease-free after follow-up. All the eighteen patients with persistent disease were identified as ablation failure after first IAT. Significant predictors for the disease-free status were Tg1 (OR = 0.98; 95 % CI = 0.97–0.99; p = 0.028), tumor size (OR = 0.53; 95 % CI = 0.28–0.96; p = 0.044), and quantified cervical uptake in WBS1 (OR = 0.87; 95 % CI = 0.76–0.98; p = 0.024).
Conclusions
The thyroglobulin and quantified cervical uptake in whole body scan are significant predictors for the successful ablation and disease-free status after follow-up.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mazzaferri EL, Jhiang SM. Long-term impact of initial surgical and medical therapy on papillary and follicular thyroid cancer. Am J Med. 1994;97:418–28.
Maxon HR 3rd, Smith HS. Radioiodine-131 in the diagnosis and treatment of metastatic well differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocrinol Metab Clin N Am. 1990;19:685–718.
Samaan NA, Schultz PN, Hickey RC, Goepfert H, Haynie TP, Johnston DA, et al. The results of various modalities of treatment of well differentiated thyroid carcinomas: a retrospective review of 1599 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992;75:714–20.
Schlumberger MJ. Papillary and follicular thyroid carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:297–306.
Sherman SI, Tielens ET, Sostre S, Wharam MD Jr, Ladenson PW. Clinical utility of posttreatment radioiodine scans in the management of patients with thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994;78:629–34.
Toubeau M, Touzery C, Arveux P, Chaplain G, Vaillant G, Berriolo A, et al. Predictive value for disease progression of serum thyroglobulin levels measured in the postoperative period and after I-131 ablation therapy in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:988–94.
Pacini F, Schlumberger M, Harmer C, Berg GG, Cohen O, Duntas L, et al. Post-surgical use of radioiodine (I-131) in patients with papillary and follicular thyroid cancer and the issue of remnant ablation: a consensus report. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005;153:651–9.
Verburg FA, de Keizer B, Lips CJ, Zelissen PM, de Klerk JM. Prognostic significance of successful ablation with radioiodine of differentiated thyroid cancer patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2005;152:33–7.
Cailleux AF, Baudin E, Travagli JP, Ricard M, Schlumberger M. Is diagnostic iodine-131 scanning useful after total thyroid ablation for differentiated thyroid cancer? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:175–8.
Menendez Torre E, Lopez Carballo MT, Rodriguez Erdozain RM, Forga Llenas L, Goni Iriarte MJ, Barberia Layana JJ. Prognostic value of thyroglobulin serum levels and I-131 whole-body scan after initial treatment of low-risk differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2004;14:301–6.
Baudin E, Do Cao C, Cailleux AF, Leboulleux S, Travagli JP, Schlumberger M. Positive predictive value of serum thyroglobulin levels, measured during the first year of follow-up after thyroid hormone withdrawal, in thyroid cancer patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:1107–11.
Kim TY, Kim WB, Kim ES, Ryu JS, Yeo JS, Kim SC, et al. Serum thyroglobulin levels at the time of I-131 remnant ablation just after thyroidectomy are useful for early prediction of clinical recurrence in low-risk patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:1440–5.
Cooper DS, Doherty GM, Haugen BR, Kloos RT, Lee SL, Mandel SJ, et al. Management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2006;16:109–42.
Robbins RJ, Chon JT, Fleisher M, Larson SM, Tuttle RM. Is the serum thyroglobulin response to recombinant human thyrotropin sufficient, by itself, to monitor for residual thyroid carcinoma? J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:3242–7.
Lind P, Kohlfurst S. Respective roles of thyroglobulin, radioiodine imaging, and positron emission tomography in the assessment of thyroid cancer. Semin Nucl Med. 2006;36:194–205.
Lee HJ, Rha SY, Jo YS, Kim SM, Ku BJ, Shong M, et al. Predictive value of the preablation serum thyroglobulin level after thyroidectomy is combined with postablation I-131 whole body scintigraphy for successful ablation in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2007;30:63–8.
Pacini F, Capezzone M, Elisei R, Ceccarelli C, Taddei D, Pinchera A. Diagnostic 131-iodine whole-body scan may be avoided in thyroid cancer patients who have undetectable stimulated serum Tg levels after initial treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:1499–501.
Bernier MO, Morel O, Rodien P, Muratet JP, Giraud P, Rohmer V, et al. Prognostic value of an increase in the serum thyroglobulin level at the time of the first ablative radioiodine treatment in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:1418–21.
Muratet JP, Giraud P, Daver A, Minier JF, Gamelin E, Larra F. Predicting the efficacy of first iodine-131 treatment in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 1997;38:1362–8.
Rosario PW, Maia FF, Cardoso LD, Barroso A, Rezende L, Padrao EL, et al. Correlation between cervical uptake and results of postsurgical radioiodine ablation in patients with thyroid carcinoma. Clin Nucl Med. 2004;29:358–61.
Rosario PW, Reis JS, Barroso AL, Rezende LL, Padrao EL, Fagundes TA. Efficacy of low and high I-131 doses for thyroid remnant ablation in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma based on post-operative cervical uptake. Nucl Med Commun. 2004;25:1077–81.
Beierwaltes WH, Rabbani R, Dmuchowski C, Lloyd RV, Eyre P, Mallette S. An analysis of “ablation of thyroid remnants” with I-131 in 511 patients from 1947–1984: experience at University of Michigan. J Nucl Med. 1984;25:1287–93.
Sisson JC. Applying the radioactive eraser: I-131 to ablate normal thyroid tissue in patients from whom thyroid cancer has been resected. J Nucl Med. 1983;24:743–5.
Logue JP, Tsang RW, Brierley JD, Simpson WJ. Radioiodine ablation of residual tissue in thyroid cancer: relationship between administered activity, neck uptake and outcome. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:1127–31.
Samuel AM, Rajashekharrao B. Radioiodine therapy for well-differentiated thyroid cancer: a quantitative dosimetric evaluation for remnant thyroid ablation after surgery. J Nucl Med. 1994;35:1944–50.
Snyder J, Gorman C, Scanlon P. Thyroid remnant ablation: questionable pursuit of an ill-defined goal. J Nucl Med. 1983;24:659–65.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported partly by a grant from the National Cancer Center (0910030) and by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MEST) (2011-0019794). The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors thank Mr. Woo Jae Won, and Mr. Young Seok Kim for their excellent technical and generous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, I., Kim, Sk., Hwang, Ss. et al. Prognostic implication of thyroglobulin and quantified whole body scan after initial radioiodine therapy on early prediction of ablation and clinical response for the patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Ann Nucl Med 26, 777–786 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-012-0640-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-012-0640-1