Abstract
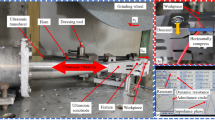
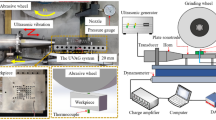
This paper describes experimental studies that were carried out to assess the enhancement in grinding productivity of AISI D2 tool steel by adopting the ultrasonic vibration-assisted dry grinding (UVADG) mode. Experimental works were conducted on a UVADG setup that was indigenously developed and manufactured. The grinding productivity in the UVADG mode was assessed by comparing the grinding forces, force ratio, surface roughness, bearing area curve (BAC), BAC ratio, ground surface morphology, and topography achieved in conventional dry grinding (CDG) and conventional wet grinding (CWG) modes. The UVADG mode at optimized amplitude and frequency results in lesser grinding forces and better surface integrity than CDG and CWG modes. With UVADG mode, the impact of overlapping induced by ultrasonic vibration resulted in a higher BAC ratio (88.71%) and a steeper BAC. This BAC ratio reflects the ground surface in UVADG mode, which is less susceptible to antifriction and antiwear characteristics than CDG and CWG modes. The experimental outcomes revealed that the UVADG mode has a greater potential for improving the grindability of AISI D2 tool steel. The current study also promotes the need for a sustainable grinding method for “difficult-to-machine” materials adopting UVADG mode.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Choudhary, H. Kumar, and S. Singh, Machining Performance and Surface Integrity of AISI D2 Die Steel Machined Using Electrical Discharge Surface Grinding Process, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2013, 22(12), p 3665–3673. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11665-013-0679-8/FIGURES/9
M.A.S. Bin Abdul Rahim, M. Bin Minhat, N.I.S.B. Hussein, and M.S. Bin Salleh, A Comprehensive Review on Cold Work of AISI D2 Tool Steel, Metall. Res. Technol., 2018, 115(1), p 104. https://doi.org/10.1051/METAL/2017048
A. Sharma, M.Z.K. Yusufzai, and M. Vashista, A Comparative Analysis of Grinding of AISI D2 Tool Steel under Different Environments, Mach. Sci. Technol., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1080/10910344.2022.2044853
T. Tawakoli, and B. Azarhoushang, Influence of Ultrasonic Vibrations on Dry Grinding of Soft Steel, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 2008, 48(14), p 1585–1591.
M.K. Sinha, D. Setti, S. Ghosh, and P. Venkateswara Rao, An Investigation on Surface Burn during Grinding of Inconel 718, J. Manuf. Process., 2016, 21, p 124–133.
H. Mao, Y. Liu, H. Mao, J. Fu, Y. Tang, and X. Li, Study for Characterizing Grinding Burn of 1045 Steel Based on Nonlinear Ultrasonic Coefficients, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2022 https://doi.org/10.1007/S11665-022-06915-0/FIGURES/19
M.K. Sinha, R. Madarkar, S. Ghosh, and P.V. Rao, Application of Eco-Friendly Nanofluids during Grinding of Inconel 718 through Small Quantity Lubrication, J. Clean. Prod., 2017, 141, p 1359–1375.
A. Chaudhari, A.S. Awale, and A.K. Chakrabarti, Surface Integrity Characterization of Austenitic, Martensitic and Ferritic Stainless Steel under Different Grinding Process, Mater Res Expres., 2019, 6(11), p 1165c9.
K. Kishore, M.K. Sinha, A. Singh, Archana, M.K. Gupta, and M.E. Korkmaz, A Comprehensive Review on the Grinding Process: Advancements, Applications and Challenges, Proc. Inst. Mech.. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci., 2022, 2022, p 095440622211107. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544062221110782
T. Yu, X. Guo, Z. Wang, P. Xu, and J. Zhao, Effects of the Ultrasonic Vibration Field on Polishing Process of Nickel-Based Alloy Inconel718, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2019, 273, p 116228.
D. Bhaduri, S.L. Soo, D.K. Aspinwall, D. Novovic, S. Bohr, P. Harden, and J.A. Webster, Ultrasonic Assisted Creep Feed Grinding of Gamma Titanium Aluminide Using Conventional and Superabrasive Wheels, CIRP Ann., 2017, 66(1), p 341–344.
A. Chaudhari, A. Sharma, A.S. Awale, M.Z.K. Yusufzai, and M. Vashista, Effect of Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Dry Grinding on Hysteresis Loop Characteristics of AISI D2 Tool Steel, Sadhana Acad. Proc. Eng. Sci., 2021, 46(4), p 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12046-021-01771-5/FIGURES/12
H. Wang, Y. Hu, W. Cong, Z. Hu, and Y. Wang, A Novel Investigation on Horizontal and 3D Elliptical Ultrasonic Vibrations in Rotary Ultrasonic Surface Machining of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic Composites, J. Manuf. Process., 2020, 52, p 12–25.
Z. Yang, L. Zhu, B. Lin, G. Zhang, C. Ni, and T. Sui, The Grinding Force Modeling and Experimental Study of ZrO2 Ceramic Materials in Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Grinding, Ceram. Int., 2019, 45(7), p 8873–8889.
P.V. Badiger, V. Desai, M.R. Ramesh, B.K. Prajwala, and K. Raveendra, Effect of Cutting Parameters on Tool Wear, Cutting Force and Surface Roughness in Machining of MDN431 Alloy Using Al and Fe Coated Tools, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6(1), p 016401.
P.V. Badiger, V. Desai, M.R. Ramesh, B.K. Prajwala, and K. Raveendra, Cutting Forces, Surface Roughness and Tool Wear Quality Assessment Using ANN and PSO Approach During Machining of MDN431 with TiN/AlN-Coated Cutting Tool, Arab. J. Sci. Eng., 2019, 44(9), p 7465.
P.V. Badiger, V. Desai, M.R. Ramesh, S. Joladarashi, and H. Gourkar, Tribological Behaviour of Monolayer and Multilayer Ti-Based Thin Solid Films Deposited on Alloy Steel, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6(2), p 026419.
P.V. Badiger, V. Desai, and M.R. Ramesh, Development and Characterization of Ti/TiC/TiN Coatings by Cathodic Arc Evaporation Technique, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2017, 70(9), p 2459.
L. Zheng, W. Chen, and D. Huo, Review of Vibration Devices for Vibration-Assisted Machining, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2020, 108(5–6), p 1631–1651. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00170-020-05483-8/FIGURES/12
M. Dogra, V.S. Sharma, J.S. Dureja, and S.S. Gill, Environment-Friendly Technological Advancements to Enhance the Sustainability in Surface Grinding- A Review, J. Clean. Prod., 2018, 197, p 218–231.
B. Azarhoushang, and T. Tawakoli, Development of a Novel Ultrasonic Unit for Grinding of Ceramic Matrix Composites, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2011, 57(9–12), p 945–955.
H. Chen, and J. Tang, Influence of Ultrasonic Assisted Grinding on Abbott-Firestone Curve, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2016, 86(9–12), p 2753–2757.
H. Chen, J. Tang, W. Shao, and B. Zhao, An Investigation on Surface Functional Parameters in Ultrasonic-Assisted Grinding of Soft Steel, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018, 97(5–8), p 2697–2702.
A. Abdullah, M. Sotoodezadeh, R. Abedini, and V. Fartashvand, Experimental Study on Ultrasonic Use in Dry Creep-Feed up-Grinding of Aluminum 7075 and Steel X210Cr12, Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf., 2013, 14(2), p 191–198.
H. Chen, J. Tang, W. Shao, and B. Zhao, An Investigation on Surface Functional Parameters in Ultrasonic-Assisted Grinding of Soft Steel, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018, 97(5), p 2697–2702. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00170-018-2164-X
H.C. Mult, G. Spur, and S.E. Holl, Ultrasonic Assisted Grinding of Ceramics, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1996, 62(4), p 287–293.
D. Li, J. Tang, H. Chen, and W. Shao, Study on Grinding Force Model in Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Grinding of Alloy Structural Steel, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2019, 101(5–8), p 1467–1479.
X. Zhang, R. Huang, K. Liu, A.S. Kumar, and H. Deng, Suppression of Diamond Tool Wear in Machining of Tungsten Carbide by Combining Ultrasonic Vibration and Electrochemical Processing, Ceram. Int., 2018, 44(4), p 4142–4153.
W.X. Xu, and L.C. Zhang, Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Machining: Principle, Design and Application, Adv. Manuf., 2015, 3(3), p 173–192.
K. Ding, Y. Fu, H. Su, H. Xu, F. Cui, and Q. Li, Experimental Studies on Matching Performance of Grinding and Vibration Parameters in Ultrasonic Assisted Grinding of SiC Ceramics, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2017, 88(9–12), p 2527–2535.
A. Awale, A.K. Shrivastava, A. Chaudhari, M. Vashista, and M.Z.K. Yusufzai, Micro-Magnetic Characterisation of Ground AISI D2 Tool Steel Using Hysteresis Loop Technique, Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol., 2021, 62(1–3), p 180–198.
K. Ding, Y. Fu, H. Su, X. Gong, and K. Wu, Wear of Diamond Grinding Wheel in Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Grinding of Silicon Carbide, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2014, 71(9), p 1929–1938. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00170-014-5625-X
A.S. Awale, A. Srivastava, M. Vashista, and M.Z. Khan Yusufzai, Influence of Minimum Quantity Lubrication on Surface Integrity of Ground Hardened H13 Hot Die Steel, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2018, 100(1), p 983–997. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00170-018-2777-0
M.K. Sinha, “Experimental Investigations in Grinding of Inconel 718 Using Different Environments and Modelling of Specific Grinding Energy. Doctoral Dissertation IIT Delhi, 2018. ,” (New Delhi), Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, 2018, http://www.eprint.iitd.ac.in/handle/2074/7536. Accessed 8 August 2022.
I.D. Marinescu, W. Brian Rowe, B. Dimitrov, and H. Ohmori, Tribosystems of Abrasive Machining Processes, Tribology of Abrasive Machining Processes. Elsevier, 2013
S. Das, and C. Pandivelan, Grinding Characteristics during Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Grinding of Alumina Ceramic in Selected Dry and MQL Conditions, Mater. Res. Express, 2020, 7, p 85404. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/abad14
A. Sharma, A. Chaudhari, A.S. Awale, M.Z.K. Yusufzai, and M. Vashista, Effect of Grinding Environments on Magnetic Response of AISI D2 Tool Steel, Russ. J. Nondestruct. Test., 2021, 57(3), p 212–221.
A.S. Awale, A. Chaudhari, A. Kumar, M.Z. Khan Yusufzai, and M. Vashista, Synergistic Impact of Eco-Friendly Nano-Lubricants on the Grindability of AISI H13 Tool Steel: A Study towards Clean Manufacturing, J. Clean. Prod., 2022, 364, p 132686.
S. Lou, Z. Zhu, W. Zeng, C. Majewski, P.J. Scott, and X. Jiang, Material Ratio Curve of 3D Surface Topography of Additively Manufactured Parts: An Attempt to Characterise Open Surface Pores, Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop., 2021, 9(1), p 015029. https://doi.org/10.1088/2051-672X/ABEDF9
P. He, S. Lu, Y. Wang, R. Li, and F. Li, Analysis of the Best Roughness Surface Based on the Bearing Area Curve Theory, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol., 2021, 236(3), p 527–540. https://doi.org/10.1177/13506501211018937
M. Jamshidinia, and R. Kovacevic, The Influence of Heat Accumulation on the Surface Roughness in Powder-Bed Additive Manufacturing, Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop., 2015, 3(1), p 014003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2051-672X/3/1/014003
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful for the funding support received from IIT (BHU) under sprouting Grant (Letter No. IIT (BHU)/Dec/2013-14/5110/L) and Institute Research Project (IIT(BHU)/R & D)/IRP/2015-16/2832).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaudhari, A., Sharma, A., Yusufzai, M.Z.K. et al. Experimental Analyses into Dry Ultrasonic Vibration-Assisted Grinding of Difficult-to-Machine Tool Steel with Alumina Wheel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 32, 4860–4870 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07444-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07444-6