Abstract
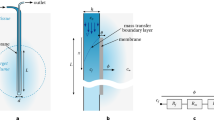
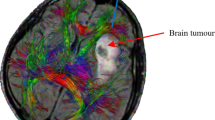
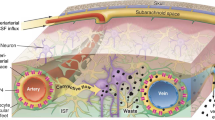
Microdialysis can be used in parallel to deep brain stimulation (DBS) to relate biochemical changes to the clinical outcome. The aim of the study was to use the finite element method to predict the tissue volume of influence (TVImax) and its cross-sectional radius (r TVImax) when using brain microdialysis, and visualize the TVImax in relation to patient anatomy. An equation based on Fick’s law was used to simulate the TVImax. Factorial design and regression analysis were used to investigate the impact of the diffusion coefficient, tortuosity and loss rate on the r TVImax. A calf brain tissue experiment was performed to further evaluate these parameters. The model was implemented with pre-(MRI) and post-(CT) operative patient images for simulation of the TVImax for four patients undergoing microdialysis in parallel to DBS. Using physiologically relevant parameter values, the r TVImax for analytes with a diffusion coefficient D = 7.5 × 10−6 cm2/s was estimated to 0.85 ± 0.25 mm. The simulations showed agreement with experimental data. Due to an implanted gold thread, the catheter positions were visible in the post-operative images. The TVImax was visualized for each catheter. The biochemical changes could thereby be related to their anatomical origin, facilitating interpretation of results.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amberg G, Lindefors N (1989) Intracerebral microdialysis: II. Mathematical studies of diffusion kinetics. J Pharmacol Methods 22(3):157–183
Astrom M, Zrinzo LU, Tisch S, Tripoliti E, Hariz MI, Wårdell K (2009) Method for patient-specific finite element modeling and simulation of deep brain stimulation. Med Biol Eng Comput 47(1):21–28
Bungay PM, Morrison PF, Dedrick RL (1990) Steady-state theory for quantitative microdialysis of solutes and water in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci 46(2):105–119
Bungay PM, Sumbria RK, Bickel U (2011) Unifying the mathematical modeling of in vivo and in vitro microdialysis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 55(1):54–63
Chefer VI, Thompson AC, Zapata A, Shippenberg TS (2009) Overview of brain microdialysis. Curr Protoc Neurosci, Chap 7:Unit 7.1
Chen KC, Hoistad M, Kehr J, Fuxe K, Nicholson C (2002) Quantitative dual-probe microdialysis: mathematical model and analysis. J Neurochem 81(1):94–107
Cragg SJ, Rice ME (2004) DAncing past the DAT at a DA synapse. Trends Neurosci 27(5):270–277
Cragg SJ, Nicholson C, Kume-Kick J, Tao L, Rice ME (2001) Dopamine-mediated volume transmission in midbrain is regulated by distinct extracellular geometry and uptake. J Neurophysiol 85(4):1761–1771
DeLong MR, Wichmann T (2007) Circuits and circuit disorders of the basal ganglia. Arch Neurol 64(1):20–24
Dykstra KH, Hsiao JK, Morrison PF, Bungay PM, Mefford IN, Scully MM, Dedrick RL (1992) Quantitative examination of tissue concentration profiles associated with microdialysis. J Neurochem 58(3):931–940
Fuxe K, Agnati L (1991) Volume transmission in the brain: novel mechanisms for neural transmission. Raven Press, New York
Galati S, Mazzone P, Fedele E, Pisani A, Peppe A, Pierantozzi M, Brusa L, Tropepi D, Moschella V, Raiteri M et al (2006) Biochemical and electrophysiological changes of substantia nigra pars reticulata driven by subthalamic stimulation in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 23(11):2923–2928
Hillman J, Aneman O, Persson M, Andersson C, Dabrosin C, Mellergard P (2007) Variations in the response of interleukins in neurosurgical intensive care patients monitored using intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurosurg 106(5):820–825
Kalyanasundaram S, Calhoun VD, Leong KW (1997) A finite element model for predicting the distribution of drugs delivered intracranially to the brain. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 273(5):R1810–R1821
Kilpatrick M, Church E, Danish S, Stiefel M, Jaggi J, Halpern C, Kerr M, Maloney E, Robinson M, Lucki I et al (2010) Intracerebral microdialysis during deep brain stimulation surgery. J Neurosci Methods 190(1):106–111
Linninger AA, Somayaji MR, Erickson T, Guo X, Penn RD (2008) Computational methods for predicting drug transport in anisotropic and heterogeneous brain tissue. J Biomech 41(10):2176–2187
Mamata H, Jolesz FA, Maier SE (2004) Characterization of central nervous system structures by magnetic resonance diffusion anisotropy. Neurochem Int 45(4):553–560
Mazel T, Simonova Z, Sykova E (1998) Diffusion heterogeneity and anisotropy in rat hippocampus. Neuroreport 9(7):1299–1304
Morel A (2007) Stereotactic atlas of the human thalamus and basal ganglia. Informa Healthcare USA Inc, New York
Nicholson C (1995) Interaction between diffusion and Michaelis–Menten uptake of dopamine after iontophoresis in striatum. Biophys J 68(5):1699–1715
Nicholson C (2001) Diffusion and related transport mechanisms in brain tissue. Rep Prog Phys 64:815–884
Nicholson C, Phillips JM (1981) Ion diffusion modified by tortuosity and volume fraction in the extracellular microenvironment of the rat cerebellum. J Physiol 321:225–257
Nicholson C, Rice ME (1986) The migration of substances in the neuronal microenvironment. Ann N Y Acad Sci 481:55–71
Nicholson C, Sykova E (1998) Extracellular space structure revealed by diffusion analysis. Trends Neurosci 21(5):207–215
Reddy KA, Doraiswamy LK (1967) Estimating liquid diffusivity. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 6(1):77–79
Rice ME, Nicholson C (1991) Diffusion characteristics and extracellular volume fraction during normoxia and hypoxia in slices of rat neostriatum. J Neurophysiol 65(2):264–272
Rice ME, Gerhardt GA, Hierl PM, Nagy G, Adams RN (1985) Diffusion coefficients of neurotransmitters and their metabolites in brain extracellular fluid space. Neuroscience 15(3):891–902
Rice ME, Okada YC, Nicholson C (1993) Anisotropic and heterogeneous diffusion in the turtle cerebellum: implications for volume transmission. J Neurophysiol 70(5):2035–2044
Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W, Hassler RG (1977) Atlas for stereotaxy of the human brain. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago
Stefani A, Fedele E, Galati S, Raiteri M, Pepicelli O, Brusa L, Pierantozzi M, Peppe A, Pisani A, Gattoni G et al (2006) Deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease patients: biochemical evidence. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:401–408
Sykova E, Nicholson C (2008) Diffusion in brain extracellular space. Physiol Rev 88(4):1277–1340
Sykova E, Vargova L (2008) Extrasynaptic transmission and the diffusion parameters of the extracellular space. Neurochem Int 52(1–2):5–13
Sykova E, Mazel T, Simonova Z (1998) Diffusion constraints and neuron–glia interaction during aging. Exp Gerontol 33(7–8):837–851
Tisdall MM, Smith M (2006) Cerebral microdialysis: research technique or clinical tool. Br J Anaesth 97(1):18–25
Westerink BH, De Vries JB (2001) A method to evaluate the diffusion rate of drugs from a microdialysis probe through brain tissue. J Neurosci Methods 109(1):53–58
Wilke CR, Chang P (1955) Correlation of diffusion coefficients in dilute solutions. AIChE J 1(2):264–270
Zsigmond P, Nezirevic D, Kullman A, Richter J, Augustinsson L-E, Dizdar N (2011) Stereotactic microdialysis of the basal ganglia in Parkinson’s disease (submitted)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Johan Richter, MD, and the staff at Neurosurgical Department of Linköping University Hospital for skillful help during the surgical procedure. The authors would also like to thank Mattias Åström, PhD and Johannes Johansson, PhD at the Department of Biomedical Engineering, for help with the simulations, Pontus Lindblom, MSc at the Department of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, for assistance with microscope software, and associate professor Eva Enqvist, Department of Mathematics, Linköping University, for valuable aid with the statistical design and analysis. The study was supported by the Swedish Governmental Agency for Innovation Systems (Vinnova), Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research (SSF), Swedish Research Council (VR) (Group grant no. 311-2006-7661), Research Foundation of the County Council of Östergötland, Medical Research Council of Southeast Sweden and Linköping University’s Foundation for Parkinson’s Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diczfalusy, E., Zsigmond, P., Dizdar, N. et al. A model for simulation and patient-specific visualization of the tissue volume of influence during brain microdialysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 49, 1459–1469 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-011-0841-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-011-0841-0