Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to explore the adsorption behaviors and mechanisms of chlorobenzene compounds (CBs; monochlorobenzene (MCB); 1,2-dichlorobenzene (1,2-DCB); pentachlorobenzene (PeCB); and hexachlorobenzene (HCB)) on corn straw-based biochar.
Materials and methods
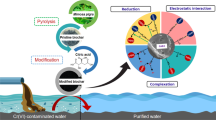
The adsorption kinetics and isotherms of the four CBs were investigated in mono- or multi-CB adsorption experiments with the corn straw–based biochar which was pyrolyzed at 500 °C and modified with 1 mol/L HCl. Moreover, the surface morphology and porosity of the biochar were characterized. The molecular orbitals, electron cloud distribution, and configuration of the CBs were calculated by the quantum chemical method. The relationships were investigated among the adsorption behaviors and quantum chemical parameters of the CBs as well as the morphology characteristics of the biochar to explore the adsorption mechanisms of the CBs on the biochar.
Results and discussion
The results showed that in both mono- and multi-adsorbate systems, the adsorption of the CBs was well fitted by the pseudo-second-order, Elovich, and the Freundlich model. The adsorption rates, affinities, and amounts indicated that the biochar preferably absorbed highly chlorinated CBs (PeCB and HCB) over low-chlorinated CBs (MCB and 1,2-DCB). The absolute electronegativity (χ), electrophilicity index (ω), polarizability (α), and molecular volume (Vm) followed the increasing order MCB < 1,2-DCB < PeCB < HCB. The values of energy gap of molecular frontier orbitals (ΔEGap) and molecular hardness (η) decreased with increasing halogen number of the CBs. The lower energy gap of molecular frontier orbitals, the less molecular stability, and higher deformability could favor the adsorption of highly chlorinated CBs (PeCB and HCB) on the biochar.
Conclusions
During the adsorption process of the CBs on the biochar, physisorption and pore filling might be the two associated mechanisms. The biochar with properties (aromatization and porosity) matchable to the CBs in energy gap of molecular frontier orbitals, electrophilicity, and polarizability is available to enhance adsorption capacity to the greatest extent. The competitive adsorption might enhance the risk of CB mobility and bioavailability by reducing the adsorption amount and delaying the equilibrium time.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batool S, Shah AA, Abu Bakar AF, Maah MJ, Abu Bakar NK (2022) Removal of organochlorine pesticides using zerovalent iron supported on biochar nanocomposite from Nephelium lappaceum (Rambutan) fruit peel waste. Chemosphere 289:133011
Boparai HK, Joseph M, O’Carroll DM (2011) Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles. J Hazard Mater 186:458–465
Braida WJ, Pignatello JJ, Lu YF, Ravikovitch PI, Neimark AV, Xing BS (2003) Sorption hysteresis of benzene in charcoal particles. Environ Sci Technol 37:409–417
Bulut E, Oezacar M, Sengil IA (2008) Adsorption of malachite green onto bentonite: equilibrium and kinetic studies and process design. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 115:234–246
Cai J, Gu C, Ti Q, Liu C, Bian Y, Sun C, Jiang X (2019) Mechanistic studies of congener-specific adsorption and bioaccumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalates in soil by novel QSARs. Environ Res 179:108838
Chang MY, Juang RS (2004) Adsorption of tannic acid, humic acid, and dyes from water using the composite of chitosan and activated clay. J Colloid Interface Sci 278:18–25
Chen L, Qian Y, Jia Q, Weng R, Zhang X, Li Y, Qiu J (2023) A national-scale distribution of organochlorine pesticides (OCPs) in cropland soils and major types of food crops in China: co-occurrence and associated risks. Sci Total Environ 861:160637–160637
Chen Q, Wang X, Yi P, Zhang P, Zhang L, Wu M, Pan B (2021) Key roles of electron cloud density and configuration in the adsorption of sulfonamide antibiotics on carbonaceous materials: molecular dynamics and quantum chemical investigations. Appl Surf Sci 536:147757
Chen Q, Zheng J, Yang Q, Dang Z, Zhang L (2019) Effect of carbon chain structure on the phthalic acid esters (PAEs) adsorption mechanism by mesoporous cellulose biochar. Chem Eng J 362:383–391
Chen W, Wei R, Ni J, Yang L, Qian W, Yang Y (2018) Sorption of chlorinated hydrocarbons to biochars in aqueous environment: effects of the amorphous carbon structure of biochars and the molecular properties of adsorbates. Chemosphere 210:753–761
Chen Z, Chen B, Zhou D (2013) Composition and sorption properties of rice-straw derived biochars. Acta Sci Circum 33:9–19
Dai Z, Tian L, Liu C, Weng H (2017) Chlorobenzene release during thermal drying of sludge: mechanism and source. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:368
Ghanty TK, Ghosh SK (1993) Correlation between hardness, polarizability, and size of atoms, molecules, and clusters. J Phys Chem 97:4951–4953
Gu CG, Jiang X, Ju XH, Yang XL, Yu GF (2007) DFT study on the structure-toxicity relationship of dioxin compounds using PLS analysis. SAR QSAR Environ Res 18:603–619
Han L, Qian L, Yan J, Chen M (2016) Contributions of different biomass components to the sorption of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene under a series of pyrolytic temperatures. Chemosphere 156:262–271
Han L, Qian L, Yan J, Chen M (2017) Effects of the biochar aromaticity and molecular structures of the chlorinated organic compounds on the adsorption characteristics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:5554–5565
Han L, Wu W, Chen X, Chen M (2022) Co-sorption/co-desorption mechanism of the mixed chlorobenzenes by fresh bulk and aged residual biochar. J Hazard Mater 429:128349
Hassan M, Du J, Liu Y, Naidu R, Zhang J, Ahsan MA, Qi F (2022) Magnetic biochar for removal of perfluorooctane sulphonate (PFOS): interfacial interaction and adsorption mechanism. Environ Technol Innov 28:102593
He M, Xiong X, Wang L, Hou D, Bolan NS, Ok YS, Rinklebe J, Tsang DCW (2021) A critical review on performance indicators for evaluating soil biota and soil health of biochar-amended soils. J Hazard Mater 414:125378
Hu B, Gao Z, Wang H, Wang J, Cheng M (2020) Computational insights into the sorption mechanism of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by carbon nanotube through density functional theory calculation and molecular dynamics simulation. Comput Mater Sci 179:109677
Hunter CA, Sanders JKM (1990) The nature of π-π interactions. J Am Chem Soc 112:5525–5534
Imai YN, Inoue Y, Nakanishi I, Kitaura K (2009) Cl-π interactions in protein-ligand complexes. QSAR Comb Sci 28:869–873
Inyang M, Dickenson E (2015) The potential role of biochar in the removal of organic and microbial contaminants from potable and reuse water: a review. Chemosphere 134:232–240
Jevrosimov I, Isakovski MK, Apostolovic T, Maletic S, Razic S, Mihajlovic M, Trickovic J (2021) Mechanisms of alachlor and pentachlorobenzene adsorption on biochar and hydrochar originating from Miscanthus giganteus and sugar beet shreds. Chem Pap 75:2105–2120
Ji R, Wu Y, Bian Y, Song Y, Sun Q, Jiang X, Zhang L, Han J, Cheng H (2021) Nitrogen-doped porous biochar derived from marine algae for efficient solid-phase microextraction of chlorobenzenes from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 407:124785
Joseph L, Sylas VP, Cyril N, Sanu KS, Jose S, Anila BN, Jose JM (2021) Removal of endrin from aqueous medium using Accacia wood biochar: kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Biomass Conv Bioref: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-021-01435-8
Ju DY, Young TM (2004) Effects of competitor and natural organic matter characteristics on the equilibrium sorption of 1,2-dichlorobenzene in soil and shale. Environ Sci Technol 38:5863–5870
Koopmans T (1934) Über die zuordnung von wellenfunktionen und eigenwerten zu den einzelnen elektronen eines atoms. Phys Chem Chem Phys 1:104–113
Li Y, Song Y, Wang F, Bian Y, Jiang X (2015) Effect of wheat straw biochar on high chlorinated benzene sorption process and mechanism. Acta Pedol Sin 52:1096–1105
Liu Z, Lu T, Chen Q (2021) Intermolecular interaction characteristics of the all-carboatomic ring, cyclo 18 carbon: focusing on molecular adsorption and stacking. Carbon 171:514–523
Luo Z, Yao B, Yang X, Wang L, Xu Z, Yan X, Tian L, Zhou H, Zhou Y (2022) Novel insights into the adsorption of organic contaminants by biochar: a review. Chemosphere 287:132113
Magid ASIA, Islam MS, Chen Y, Weng L, Sun Y, Chang X, Zhou B, Ma J, Li Y (2021) Competitive adsorption of dibutyl phthalate (DBP) and di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) onto fresh and oxidized corncob biochar. Chemosphere 280:130639
Majd MM, Kordzadeh-Kermani V, Ghalandari V, Askari A, Sillanpaa M (2022) Adsorption isotherm models: a comprehensive and systematic review (2010–2020). Sci Total Environ 812:151334
Mancini SA, Lacrampe-Couloume G, Lollar BS (2008) Source differentiation for benzene and chlorobenzene groundwater contamination: a field application of stable carbon and hydrogen isotope analyses. Environ Forensics 9:177–186
Muir DCG, Norstrom RJ, Simon M (1988) Organochlorine contaminants in arctic marine food-chains-accmulation of specific polychlorinated-biphenyls and chlordane-related compounds. Environ Sci Technol 22:1071–1079
Nguyen TH, Cho HH, Poster DL, Ball WP (2007) Evidence for a pore-filling mechanism in the adsorption of aromatic hydrocarbons to a natural wood char. Environ Sci Technol 41:1212–1217
Parr RG, Von Szentpaly L, Liu SB (1999) Electrophilicity index. J Am Chem Soc 121:1922–1924
Pitkaaho S, Ojala S, Kinnunen T, Silvonen R, Keiski RL (2011) Catalytic oxidation of dichloromethane and perchloroethylene: laboratory and industrial scale Studies. Top Catal 54:1257–1265
Potapowicz J, Lambropoulou D, Nannou C, Koziol K, Polkowska Z (2020) Occurrences, sources, and transport of organochlorine pesticides in the aquatic environment of Antarctica. Sci Total Environ 735
Rill C, Kolar ZI, Kickelbick G, Wolterbeek HT, Peters JA (2009) Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption on hydroxyapatite of the Tb-160 terbium complexes of the bone-targeting ligands DOTP and BPPED. Langmuir 25:2294–2301
Sangon S, Hunt AJ, Attard TM, Mengchang P, Ngernyen Y, Supanchaiyamat N (2018) Valorisation of waste rice straw for the production of highly effective carbon based adsorbents for dyes removal. J Clean Prod 172:1128–1139
Shang X, Yang L, Ouyang D, Zhang B, Zhang W, Gu M, Li J, Chen M, Huang L, Qian L (2020) Enhanced removal of 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene by modified biochar supported nanoscale zero-valent iron and palladium. Chemosphere 249
Shi Z, Li X, Wang J, Wang F, Sun R, Song C (2018) Thespatial distribution characteristics and utilization model of crop straw in China. China Popul Resour Environ 28:202–205
Shriver D, Weller M, Overton T, Rourke J, Armstrong F (2014) Inorganic chemistry. Oxford University Press, Great Britain
Shu Y, Liu P, Zhang Q, Wei D (2013) Competitive sorption between 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene/tetrachloroethene and 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene by soils/sediments from South China. Sci Total Environ 463:258–263
Song Y, Wang F, Bian Y, Zhang Y, Jiang X (2012) Chlorobenzenes and organochlorinated pesticides in vegetable soils from an industrial site, China. J Environ Sci 24:362–368
Tang Y, Li Y, Zhan L, Wu D, Zhang S, Pang R, Xie B (2022) Removal of emerging contaminants (bisphenol A and antibiotics) from kitchen wastewater by alkali-modified biochar. Sci Total Environ 805:150158
Tong Y, McNamara PJ, Mayer BK (2019) Adsorption of organic micropollutants onto biochar: a review of relevant kinetics, mechanisms and equilibrium. Environ Sci: Water Res Technol 5:821–838
Tournus F, Latil S, Heggie MI, Charlier JC (2005) π-stacking interaction between carbon nanotubes and organic molecules. Phys Rev B 72:075431
Wang J, Guo X (2022) Rethinking of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption kinetics model: Interpretation, solving methods and applications. Chemosphere 309:136732
Yang CH (1998) Statistical mechanical study on the Freundlich isotherm equation. J Colloid Interface Sci 208:379–387
Yang L, Chen Y, Ouyang D, Yan J, Qian L, Han L, Chen M, Li J, Gu M (2020) Mechanistic insights into adsorptive and oxidative removal of monochlorobenzene in biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron/persulfate system. Chem Eng J 400:125811
Yao S, Li X, Cheng H, Zhang C, Bian Y, Jiang X, Song Y (2019) Resource utilization of a typical vegetable waste as biochars in removing phthalate acid esters from water: a sorption case study. Bioresour Technol 293:122081
Yuan Y, Ning X-a, Zhang Y, Lai X, Li D, He Z, Chen X (2020) Chlorobenzene levels, component distribution, and ambient severity in wastewater from five textile dyeing wastewater treatment plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 193
Zhang K, Sun P, Faye MCAS, Zhang Y (2018) Characterization of biochar derived from rice husks and its potential in chlorobenzene degradation. Carbon 130:730–740
Zhao D, Qiu S, Li M, Luo Y, Zhang L, Feng M, Yuan M, Zhang K, Wang F (2022) Modified biochar improves the storage capacity and adsorption affinity of organic phosphorus in soil. Environ Res 205:112455
Zheng L, Peng D, Zhang S, Yang Y, Zhang L, Meng P (2020) Adsorption of sulfamethoxazole and sulfadiazine on phosphorus-containing stalk cellulose under different water pH studied by quantitative evaluation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:43246–43261
Funding
The project was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (2020YFC1808601); and National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 41830642); and Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX22_1355).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhaohui Wang
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Han, W., Zhao, W. et al. Mono-/multiadsorption of chlorobenzene compounds on biochar: influence of the properties of the chlorobenzene molecules and biochar. J Soils Sediments 23, 2120–2135 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03478-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-023-03478-y