Abstract
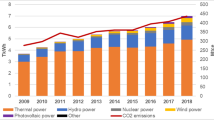
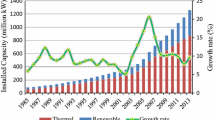
Under the policy background of “joint prevention and control” of global greenhouse gas emission reduction and regional air pollutants, the power industry, as an important target industry of energy conservation and emission reduction policies, has become an effective choice to release dual pressures. In this paper, the “bottom-up” emission factor method was used to measure the emission of CO2 and NOX from 2011 to 2019. Then, the contributions of six factors to NOX emission reduction in China’s power industry were identified using the Kaya identity and logarithmic mean divisia index (LMDI) decomposition methods. The research results show that (1) there is a significant synergistic emission reduction effect between CO2 emission reduction and NOX emission reduction; (2) the factor that inhibits the growth of NOX emissions reduction in the power industry is economic development factor; and (3) the main factors that promote the reduction of NOX emission from the power industry are synergy effect, energy intensity, power generation intensity, and power production structure factors. Several suggestions are proposed, which are the power industry should adjust its structure, improve energy intensity, focus on applying low-nitrogen combustion technology, and improve the air pollutant emission information disclosure system to reduce NOX emissions.













Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are included in Supplementary Materials. For more details, please consult the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alajmi RG (2021). Factors that impact greenhouse gas emissions in Saudi Arabia: Decomposition analysis using LMDI. Energy Policy 156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2021.112454
Ang BW (2004) Decomposition analysis for policymaking in energy: which is the preferred method? Energy Policy 32(9):1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-4215(03)00076-4
Ang BW (2005) The LMDI approach to decomposition analysis: a practical guide. Energy Policy 33(7):867–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2003.10.010
Ang BW (2015) LMDI decomposition approach: a guide for implementation. Energy Policy 86:233–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2015.07.007
Ang BW, Liu N (2007) Handling zero values in the logarithmic mean Divisia index decomposition approach. Energy Policy 35(1):238–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2005.11.001
Ang BW, Zhang FQ, Choi K-H (1998) Factorizing changes in energy and environmental indicators through decomposition. Energy 23(6):489–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(98)00016-4
Bai Y, Zhao T, Zhou Y, Kong S, Hu W, Xiong J, Liu L, Zheng H & Meng K (2021). Aggravation effect of regional transport on wintertime PM2.5 over the middle reaches of the Yangtze River under China’s air pollutant emission reduction process. Atmos Pollut Res 12(7). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2021.101111
Chen X, Li J, Liu Q, Luo H, Li B, Cheng J & Huang Y (2022). Emission characteristics and impact factors of air pollutants from municipal solid waste incineration in Shanghai, China. J Environ Manag 310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114732
China Electricity Council (CEC) (2019) Analysis and Forecast of China Power Demand-Supply Situation 2018–2019 (in Chinese). https://cec.org.cn/detail/index.html?3-6973
China Electricity Council (2020) Research on the "Fourteenth Five-Year Plan" of the power industry. https://www.cec.org.cn/detail/index.html?3-297199
de Oliveira-De Jesus PM (2019) Effect of generation capacity factors on carbon emission intensity of electricity of Latin America & the Caribbean, a temporal IDA-LMDI analysis. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 101:516–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.11.030
Ding L, Liu C, Chen K, Huang Y, Diao B (2017) Atmospheric pollution reduction effect and regional predicament: an empirical analysis based on the Chinese provincial NOx emissions. J Environ Manage 196:178–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2017.03.016
Du W, Wang J, Chen Y, Zhuo S, Wu S, Liu W, Lin N, Shen G & Tao S (2021). Field-based measurements of major air pollutant emissions from typical porcelain kiln in China. Environ Pollut 288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117810
Fang D, Hao P, Hao J (2019) Study of the influence mechanism of China’s electricity consumption based on multi-period ST-LMDI model. Energy 170:730–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.12.212
Feng Y, Chen H, Chen Z, Wang Y, Wei W (2021) Has environmental information disclosure eased the economic inhibition of air pollution? J Clean Prod 284:125412. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2020.125412
Fu J & Yuan Z (2017). Evaluation of Effect and Analysis of Expansion Mechanism of Synergic Emission Abatement in China’s Power Industry. China Ind Econ. https://doi.org/10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2017.02.004.html
Gao C, You H, Gao C, Na H, Xu Q, Li X, Liu H (2022) Analysis of passenger vehicle pollutant emission factor based on on-board measurement. Atmos Pollut Res 13(6):101421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2022.101421
Hasan MM & Liu K (2022). Decomposition analysis of natural gas consumption in Bangladesh using an LMDI approach. Energy Strateg Rev 40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2021.100724
He Y, Xing Y, Zeng X, Ji Y, Hou H, Zhang Y & Zhu Z (2022). Factors influencing carbon emissions from China’s electricity industry: analysis using the combination of LMDI and K-means clustering. Environ Impact Assess Rev 93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2021.106724
Jeong K, Kim S (2013) LMDI decomposition analysis of greenhouse gas emissions in the Korean manufacturing sector. Energy Policy 62:1245–1253. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2013.06.077
Jiang X (2022) Drivers of air pollution reduction paradox: Empirical evidence from directly measured unit-level data of Chinese power plants. Energy 254:124389. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2022.124389
Jiang J, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Zhang C, Tian G (2016) Estimating nitrogen oxides emissions at city scale in China with a nightlight remote sensing model. Sci Total Environ 544:1119–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.11.113
Jiang L, Chen Y, Zhou H, He S (2020b) NOx emissions in China: Temporal variations, spatial patterns and reduction potentials. Atmos Pollut Res 11(9):1473–1480. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APR.2020.06.003
Jiang S, Zhu Y, He G, Wang Q & Lu Y (2020a). Factors influencing China’s non-residential power consumption: Estimation using the Kaya–LMDI methods. Energy 201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.117719
Li M, Patiño-Echeverri D, Zhang J, (Jim). (2019) Policies to promote energy efficiency and air emissions reductions in China’s electric power generation sector during the 11th and 12th five-year plan periods: achievements, remaining challenges, and opportunities. Energy Policy 125:429–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2018.10.008
Li L, Mi Y, Lei Y, Wu S, Li L, Hua E, Yang J (2022) The spatial differences of the synergy between CO2 and air pollutant emissions in China’s 296 cities. Science of The Total Environment 846:157323. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2022.157323
Liao C, Wang S, Fang J, Zheng H, Liu J, Zhang Y (2019) Driving forces of provincial-level CO2 emissions in China’s power sector based on LMDI method. Energy Procedia 158:3859–3864. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EGYPRO.2019.01.860
Liu J, Yang Q, Ou S & Liu J (2022a). Factor decomposition and the decoupling effect of carbon emissions in China’s manufacturing high-emission subsectors. Energy 248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2022.123568
Liu S, Lin Z, Jiang Y, Zhang T, Yang L, Tan W, Lu F (2022) Modelling and discussion on emission reduction transformation path of China’s electric power industry under “double carbon” goal. Heliyon 8(9):e10497. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.HELIYON.2022.E10497
Liu M, Zhang X, Zhang M, Feng Y, Liu Y, Wen J & Liu L (2021). Influencing factors of carbon emissions in transportation industry based on C–D function and LMDI decomposition model: China as an example. Environ Impact Assess Rev 90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eiar.2021.106623
Lu Z, Huang L, Liu J, Zhou Y, Chen M, Hu J (2019) Carbon dioxide mitigation co-benefit analysis of energy-related measures in the Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan in the Jing-Jin-Ji region of China. Resources Conserv Recycl X 1:100006. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RCRX.2019.100006
Lyu W, Li Y, Guan D, Zhao H, Zhang Q, Liu Z (2016) Driving forces of Chinese primary air pollution emissions: an index decomposition analysis. J Clean Prod 133:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2016.04.093
Ma T, Takeuchi K (2017) Technology choice for reducing NOx emissions: an empirical study of Chinese power plants. Energy Policy 102:362–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2016.12.043
Mousavi B, Lopez NSA, Biona JBM, Chiu ASF, Blesl M (2017) Driving forces of Iran’s CO2 emissions from energy consumption: an LMDI decomposition approach. Appl Energy 206:804–814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.08.199
National Development and Reform Commission (2014) Announcement of the National Development and Reform Commission of the People's Republic of China. https://www.ndrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zcfb/gg/201409/t20140905_961102.html
Pan J, Ding N, Lu B, Ma S, Yang J (2020) Patterns change and determinants of urban nitrogen metabolism in Chinese megacities. J Clean Prod 264:121597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121597
Pardo Martínez CI, Silveira S (2012) Analysis of energy use and CO2 emission in service industries: Evidence from Sweden. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(7):5285–5294. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2012.04.051
Quan C, Cheng X, Yu S & Ye X (2020). Analysis on the influencing factors of carbon emission in China’s logistics industry based on LMDI method. Sci Total Environ 734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138473
Saidi K & Omri A (2020). Reducing CO2 emissions in OECD countries: do renewable and nuclear energy matter? Progress Nucl Energy 126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnucene.2020.103425
She Q, Cao S, Zhang S, Zhang J, Zhu H, Bao J, Meng X, Liu M, Liu Y (2021) The impacts of comprehensive urbanization on PM2.5 concentrations in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Ecol Indic 132:108337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108337
Shi D, Bu C, Xue H (2021) Deterrence effects of disclosure: The impact of environmental information disclosure on emission reduction of firms. Energy Econ 104:105680. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENECO.2021.105680
State Council of China (2012) Notice of the State Council on Printing and Distributing the 12th Five-Year Plan for Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction. http://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2012/content_2217291.htm
Sui Z, Zhang Y, Peng Y, Norris P, Cao Y, Pan WP (2016) Fine particulate matter emission and size distribution characteristics in an ultra-low emission power plant. Fuel 185:863–871. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FUEL.2016.08.051
Sun W & Huang C (2022) Predictions of carbon emission intensity based on factor analysis and an improved extreme learning machine from the perspective of carbon emission efficiency. J Clean Prod 338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130414
Tang C, Zhong L, Ng P (2017) Factors that influence the tourism industry’s carbon emissions: a tourism area life cycle model perspective. Energy Policy 109:704–718. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2017.07.050
Tang L, Qu J, Mi Z, Bo X, Chang X, Anadon LD, Wang S, Xue X, Li S, Wang X, Zhao X (2019) Substantial emission reductions from Chinese power plants after the introduction of ultra-low emissions standards. Nat Energy 4(11):929–938. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41560-019-0468-1
The International Energy Agency (2020) https://www.iea.org/reports/sdg7-data-and-projections
The State Council Information Office of the People's Republic of China (2020) Energy in China's New Era. http://www.scio.gov.cn/ss/
Tian Y, Wang Y, Hang Y, Wang Q (2022) The two-stage factors driving changes in China’s industrial SO2 emission intensity: a production-theoretical decomposition analysis. Sci Total Environ 814:152426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152426
Tong L, Zhang H, Yu J, He M, Xu N, Zhang J, Qian F, Feng J, Xiao H (2017) Characteristics of surface ozone and nitrogen oxides at urban, suburban and rural sites in Ningbo, China. Atmos Res 187:57–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.12.006
Wang J, Zhao B, Wang S, Yang F, Xing J, Morawska L, Ding A, Kulmala M, Kerminen VM, Kujansuu J, Wang Z, Ding D, Zhang X, Wang H, Tian M, Petäjä T, Jiang J, Hao J (2017a) Particulate matter pollution over China and the effects of control policies. Sci Total Environ 584–585:426–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2017.01.027
Wang Y, Lai N, Mao G, Zuo J, Crittenden J, Jin Y, Moreno-Cruz J (2017b) Air pollutant emissions from economic sectors in China: A linkage analysis. Ecol Ind 77:250–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOLIND.2017.02.016
Wang J, Qiu Y, He S, Liu N, Xiao C, Liu L (2018) Investigating the driving forces of NOx generation from energy consumption in China. J Clean Prod 184:836–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2018.02.305
Wang S, Zhu X, Song D, Wen Z, Chen B, Feng K (2019a) Drivers of CO2 emissions from power generation in China based on modified structural decomposition analysis. J Clean Prod 220:1143–1155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.199
Wang J, Qiu Y, Ma Y, He S, Liu N, Feng Y, Dong Z, Liu L (2019b) Quantifying the geographical distribution effect on decreasing aggregated nitrogen oxides intensity in the Chinese electrical generation system. J Clean Prod 222:856–864. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2019.03.101
Wang Y, Song J, Yang W, Dong L, Duan H (2019) Unveiling the driving mechanism of air pollutant emissions from thermal power generation in China: A provincial-level spatiotemporal analysis. Resources Conserv Recycl 151:104447. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RESCONREC.2019.104447
Wang L, Wang Y, He H, Lu Y, Zhou Z (2020) Driving force analysis of the nitrogen oxides intensity related to electricity sector in China based on the LMDI method. J Clean Prod 242:118364. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2019.118364
Wang F, Shan J, Liu J, Fan W, Yan B, Zhao H, Luo S (2022) How does high-speed rail construction affect air pollutant emissions? Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration in China. J Clean Prod 350:131471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131471
Wang J, Dong K, Hochman G, Timilsina GR (2023) Factors driving aggregate service sector energy intensities in Asia and Eastern Europe: A LMDI analysis. Energy Policy 172:113315. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2022.113315
Wei Y, Gu J, Wang H, Yao T, Wu Z (2018) Uncovering the culprits of air pollution: Evidence from China’s economic sectors and regional heterogeneities. J Clean Prod 171:1481–1493. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2017.09.246
Wu T, Cui Y, Lian A, Tian Y, Li R, Liu X, Yan J, Xue Y, Liu H, Wu B (2023) Vehicle emissions of primary air pollutants from 2009 to 2019 and projection for the 14th Five-Year Plan period in Beijing, China. J Environ Sci (china) 124:513–521. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2021.11.038
Xu S-C, He Z-X, Long R-Y (2014) Factors that influence carbon emissions due to energy consumption in China: decomposition analysis using LMDI. Appl Energy 127:182–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.03.093
Xu SC, Miao YM, Gao C, Long RY, Chen H, Zhao B, Wang SX (2019) Regional differences in impacts of economic growth and urbanization on air pollutants in China based on provincial panel estimation. J Clean Prod 208:340–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2018.10.114
Xu M & Tan R (2022) How to reduce CO2 emissions in pharmaceutical industry of China: evidence from total-factor carbon emissions performance. J Clean Prod 337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130505
Yang W, Song J (2021) Simulating optimal development of clean coal-fired power generation for collaborative reduction of air pollutant and CO2 emissions. Sustain Prod Consump 28:811–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2021.07.010
Yang S, Chen B, Ulgiati S (2016a) Co-benefits of CO2 and PM2.5 emission reduction. Energy Procedia 104:92–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2016.12.017
Yang X, Wang S, Zhang W, Li J, Zou Y (2016b) Impacts of energy consumption, energy structure, and treatment technology on SO2 emissions: a multi-scale LMDI decomposition analysis in China. Appl Energy 184:714–726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.11.013
Yang JC, Lin X, Dong Z, Wang J (2023) Research on characteristics and division analysis of provincial NOx emissions in electricity lndustry China. J Ecol Environ https://kns-cnki-net-443.webvpn.ncepu.edu.cn/KXReader/Detail?invoice=tu9UdDi438uEmzkfR1X5uS9tac5pJywJIUALUH9iZjNyYEHcPR4zIAUq57Zi1Apj74h%2Bh56HCGsLdxbQYDWDxpv%2F3aTHAII76HtQFkJfIsLKqQ2hBhjlbaTKciBbi6PW33foXC83gOIgg1fglxYj727WoUBKXVB6Hp6tJheQ8uQ%3D&DBCODE=
Yao C, Feng K, Hubacek K (2015) Driving forces of CO2 emissions in the G20 countries: An index decomposition analysis from 1971 to 2010. Eco Inform 26(P1):93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOINF.2014.02.003
Yi H, Zhong T, Liu J, Yu Q, Zhao S, Gao F, Zhou Y, Wang S & Tang X (2021) Emissions of air pollutants from sintering flue gas in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area and proposed reduction measures. J Clean Prod 304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126958
Yirong Q (2022) Does environmental policy stringency reduce CO2 emissions? Evidence from high-polluted economies. J Clean Prod 341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130648
Yu Y, Liu H (2020) Economic growth, industrial structure and nitrogen oxide emissions reduction and prediction in China. Atmos Pollut Res 11(7):1042–1050. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.03.011
Zeng QH, He LY (2023) Study on the synergistic effect of air pollution prevention and carbon emission reduction in the context of “dual carbon”: Evidence from China’s transport sector. Energy Policy 173:113370. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2022.113370
Zhang Y, Shuai C, Bian J, Chen X, Wu Y, Shen L (2019) Socioeconomic factors of PM2.5 concentrations in 152 Chinese cities: decomposition analysis using LMDI. J Clean Prod 218:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.01.322
Zhang H, Chen B, Deng H, Du H, Yang R, Ju L, Liu S (2022a) Analysis on the evolution law and influencing factors of Beijing’s power generation carbon emissions. Energy Rep 8:1689–1697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.02.297
Zhang QY, Cai BF, Wang MD, Wang JX, Xing YK, Dong GX, Zhang Z, Mao XQ (2022b) City level CO2 and local air pollutants co-control performance evaluation: a case study of 113 key environmental protection cities in China. Adv Clim Chang Res 13(1):118–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACCRE.2021.10.002
Zhang G, Han J, Su B (2023) Contributions of cleaner production and end-of-pipe treatment to NOx emissions and intensity reductions in China, 1997–2018. J Environ Manag 326:116822. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JENVMAN.2022.116822
Zhang C, Zhao Y, Shi C & Chiu YH (2021). Can China achieve its water use peaking in 2030? A scenario analysis based on LMDI and Monte Carlo method. J Clean Prod 278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123214
Zhao Y, Wang S, Duan L, Lei Y, Cao P, Hao J (2008) Primary air pollutant emissions of coal-fired power plants in China: current status and future prediction. Atmos Environ 42(36):8442–8452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.08.021
Zhao Y, Wang C, Sun Y, Liu X (2018) Factors influencing companies’ willingness to pay for carbon emissions: Emission trading schemes in China. Energy Econ 75:357–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eneco.2018.09.001
Zhou X, Zhang M, Zhou M, Zhou M (2017) A comparative study on decoupling relationship and influence factors between China’s regional economic development and industrial energy–related carbon emissions. J Clean Prod 142:783–800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.115
Zhu C, Chang Y, Li X & Shan M (2022). Factors influencing embodied carbon emissions of China’s building sector: an analysis based on extended STIRPAT modeling. Energy Build 255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2021.111607
Zhu X, Zhang C (2012) Reducing information asymmetry in the power industry: mandatory and voluntary information disclosure regulations of sulfur dioxide emission. Energy Policy 45:704–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENPOL.2012.03.024
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the editor and anonymous reviewers for their work.
Funding
This study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 71801092.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sen Guo: methodology, conceptualization. Guolei Liu: conceptualization, writing—original draft preparation. ShiXuan Liu: data curation, reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ilhan Ozturk
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, S., Liu, G. & Liu, S. Driving factors of NOX emission reduction in China’s power industry: based on LMDI decomposition model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 51042–51060 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25873-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-25873-1