Abstract
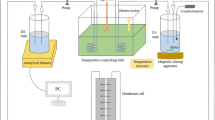
Forward osmosis (FO) has emerged as a viable technology to alleviate the global water crisis. The greatest challenge facing the application of FO technology is the lack of an ideal draw solution with high water flux and low reverse salt flux. Hence, the objective of this study was to enhance FO by lowering reverse salt flux and maintaining high water flux; the method involved adding small concentrations of Al2(SO4)3 to a MgCl2 draw solution. Results showed that 0.5 M MgCl2 mixed with 0.05 M of Al2(SO4)3 at pH 6.5 achieved a lower reverse salt flux (0.53 gMH) than that of pure MgCl2 (1.55 gMH) using an FO cellulose triacetate nonwoven (CTA-NW) membrane. This was due possibly to the flocculation of aluminum hydroxide in the mixed draw solution that constricted membrane pores, resulting in reduced salt diffusion. Moreover, average water fluxes of 4.09 and 1.74 L/m2-h (LMH) were achieved over 180 min, respectively, when brackish water (5 g/L) and sea water (35 g/L) were used as feed solutions. Furthermore, three types of membrane distillation (MD) membranes were selected for draw solution recovery; of these, a polytetrafluoroethylene membrane with a pore size of 0.45 μm proved to be the most effective in achieving a high salt rejection (99.90%) and high water flux (5.41 LMH) in a diluted draw solution.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achilli A, Cath TY, Childress AE (2010) Selection of inorganic-based draw solutions for forward osmosis applications. J Membr Sci 364:233–241
Adnan S, Hoang M, Wang H, Xie Z (2012) Commercial PTFE membranes for membrane distillation application: effect of microstructure and support material. Desalination 284:297–308
Bai H, Liu Z, Sun DD (2011) Highly water soluble and recovered dextran coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for brackish water desalination. Sep Purif Technol 81:392–399
Duong HC, Cooper P, Nelemans B, Cath TY, Nghiem LD (2015) Optimising thermal efficiency of direct contact membrane distillation by brine recycling for small-scale seawater desalination. Desalination 374:1–9
Elimelech M, Phillip WA (2011) The future of seawater desalination: energy, technology, and the environment. Science 333:712–717
Gadelha G, Nawaz MS, Hankins NP, Khan SJ, Wang R, Tang CY (2014) Assessment of micellar solutions as draw solutions for forward osmosis. Desalination 354:97–106
Ge Q, Su J, Amy GL, Chung T-S (2012) Exploration of polyelectrolytes as draw solutes in forward osmosis processes. Water Res 46:1318–1326
Ge Q, Fu F, Chung T-S (2014) Ferric and cobaltous hydroacid complexes for forward osmosis (FO) processes. Water Res 58:230–238
Hau NT, Chen S-S, Nguyen NC, Huang KZ, Ngo HH, Guo W (2014) Exploration of EDTA sodium salt as novel draw solution in forward osmosis process for dewatering of high nutrient sludge. J Membr Sci 455:305–311
Jin X, Shan J, Wang C, Wei J, Tang CY (2012) Rejection of pharmaceuticals by forward osmosis membranes. J Hazard Mater 227(28):55–61
Khawaji AD, Kutubkhanah IK, Wie J-M (2008) Advances in seawater desalination technologies. Desalination 221:47–69
Kumar R, Al-Haddad S, Al-Rughaib M, Salman M (2016) Evaluation of hydrolyzed poly(isobutylene-alt-maleic anhydride) as a polyelectrolyte draw solution for forward osmosis desalination. Desalination 394:148–154
Ling MM, Wang KY, Chung TS (2010) Highly water-soluble magnetic nanoparticles as novel draw solutes in forward osmosis for water reuse. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:5869–5876
Lutchmiah K, Lauber L, Roest K, Harmsen DJH, Post JW, Rietveld LC, van Lier JB, Cornelissen ER (2014) Zwitterions as alternative draw solutions in forward osmosis for application in wastewater reclamation. J Membr Sci 460:82–90
McCutcheon JR, McGinnis RL, Elimelech M (2006) Desalination by ammonia-carbon dioxide forward osmosis: influence of draw and feed solution concentrations on process performance. J Membr Sci 278:114–123
Nguyen NC, Chen SS, Yang HY, Hau NT (2013) Application of forward osmosis on dewatering of high nutrient sludge. Bioresour Technol 132:224–229
Nguyen NC, Chen S-S, Nguyen HT, Ray SS, Ngo HH, Guo W, Lin P-H (2016) Innovative sponge-based moving bed-osmotic membrane bioreactor hybrid system using a new class of draw solution for municipal wastewater treatment. Water Res 91:305–313
Schiermeier Q (2008) Water: purification with a pinch of salt. Nature 452:260–261
Semiat R (2008) Energy issues in desalination processes. Environmental Science & Technology 42:8193–8201
Stone ML, Rae C, Stewart FF, Wilson AD (2013b) Switchable polarity solvents as draw solutes for forward osmosis. Desalination 312:124–129
Stone ML, Wilson AD, Harrup MK, Stewart FF (2013a) An initial study of hexavalent phosphazene salts as draw solutes in forward osmosis. Desalination 312:130–136
Tan CH, Ng HY (2010) A novel hybrid forward osmosis-nanofiltration (FO-NF) process for seawater desalination: draw solution selection and system configuration. Desalin Water Treat 13:356–361
Xie M, Nghiem LD, Price WE, Elimelech M (2012a) Comparison of the removal of hydrophobic trace organic contaminants by forward osmosis and reverse osmosis. Water Res 46:2683–2692
Xie M, Price WE, Nghiem LD (2012b) Rejection of pharmaceutically active compounds by forward osmosis: role of solution pH and membrane orientation. Sep Purif Technol 93:107–114
Yen SK, Mehnas Haja NF, Su M, Wang KY, Chung T-S (2010) Study of draw solutes using 2-methylimidazole-based compounds in forward osmosis. J Membr Sci 364:242–252
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Southern Taiwan Science Park and the Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of China under the grant number of 104-2221-E-027-004-MY3. The authors are also grateful for the support of the Institute of Environmental Engineering and Management, National Taipei University of Technology, Taiwan and Centre for Technology in Water and Wastewater, University of Technology, Sydney, Australia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible editor: Bingcai Pan
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 457 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, N.C., Chen, SS., Jain, S. et al. Exploration of an innovative draw solution for a forward osmosis-membrane distillation desalination process. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25, 5203–5211 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9192-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9192-1