Abstract
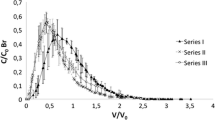
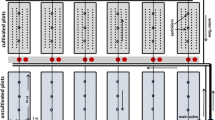
In the present study, the field dissipation and transport of quizalofop-p-ethyl by water and sediment runoff were investigated in sunflower experimental cultivation under Mediterranean conditions. The cultivation was carried out in silty clay soil plots with two different slopes of 1 and 5 %. The soil dissipation rate of quizalofop-p-ethyl was fast and can be described by both single first-order (SFO) and Gustafson and Holden (first-order multi compartment (FOMC)) kinetics. The half-life of quizalofop-p-ethyl ranged from 0.55 to 0.68 days and from 0.45 to 0.71 days when SFO and FOMC kinetics were applied, respectively. No herbicide residues were detected below the 10-cm soil layer. A single detection of quizalofop-p-ethyl was observed in runoff water (3 days after application (DAA)) at relatively low concentrations (from 1.70 to 2.04 μg L−1). In sediment, it was detected in the samplings of 3 and 25 DAA at concentrations that never exceeded 0.126 μg g−1. The estimated total losses of quizalofop-p-ethyl as percentage of the initial applied active ingredient were low both in water and sediment (less than of 0.021 and 0.005 %, respectively). Quizalofop-p-ethyl residues were detectable for 18 DAA in the stems and leaves of the plants and 6 DAA in the root system. No herbicide residues were detected in inflorescences and seeds of sunflower plants. Experimental data showed minimal risk for the contamination of soil and adjacent water bodies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Díez C, Barrado E (2010) Soil-dissipation kinetics of twelve herbicides used on a rain-fed barley crop in Spain. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:1617–1626. doi:10.1007/s00216-010-3671-2
European Commission (EC) (2009) Directive 2009/28/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 April on the promotion of the use of energy from renewable sources and amending and subsequently repealing Directives 2001/77/EC and 2003/30/EC, Off J Europ Union L140/16, Brussels
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) (2008) Conclusion regarding the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance quizalofop-p. EFSA Sci Rep 205:1–216
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAOSTAT) (2015) http://faostat.fao.org/site/567/DesktopDefault.aspx?PageID=567#ancor. Accessed 5 June 2015
Forum for the Co-ordination of Pesticide Fate Models and Their Use (FOCUS) (2006) Guidance document on estimating persistence and degradation kinetics from environmental fate studies on pesticides in EU registration. Report of the FOCUS Work Group on Degradation Kinetics, EC Document Reference Sanco/10058/2005 version, 2.0, 434 pp
Fontaras G, Skoulou V, Zanakis G, Zabaniotou A, Samaras Z (2012) Integrated environmental assessment of energy crops for biofuel and energy production in Greece. Renew Energy 43:201–209. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2011.12.010
Greek Minister of Rural Development and Food (GMRDF) (2015). www.minagric.gr/syspest/SYSPEST_CROPS_skeyasma.aspx. Accessed 5 June 2015
Guan W, Zhang H (2013) Determination and study on residue and dissipation of benazolin-ethyl and quizalofop-p-ethyl in rape and soil. Intern J Environ Anal Chem 93:679–691. doi:10.1080/03067319.2012.684047
Hu J, Deng Z, Liu C, Zheng Z (2010) Simultaneous analysis of herbicide metribuzin and quizalofop-p-ethyl residues in potato and soil by GC-ECD. Chromatographia 72:701–706. doi:10.1365/s10337-010-1717-40009-5893/10/10
Koeppe MK, Anderson JJ, Shalaby LM (1990) Metabolism of [14C] quizalofop-ethyl in soybean and cotton plants. J Agric Food Chem 38:1085–1091
Li Z, Li Q, Cheng F, Zhang W, Wang W, Li J (2012) Enantioselectivity in degradation and transformation of quizalofop-ethyl in soils. Chirality 24:552–557. doi:10.1002/chir
Mantzos N, Karakitsou A, Zioris I, Leneti E, Konstantinou I (2013) QuEChERS and solid phase extraction methods for the determination of energy crop pesticides in soil, plant and runoff water matrices. Intern J Environ Anal Chem 93:1566–1584. doi:10.1080/03067319.2013.803282
Mantzos N, Karakitsou A, Hela D, Patakioutas G, Leneti E, Konstantinou I (2014) Persistence of oxyfluorfen in soil, runoff water, sediment and plants of a sunflower cultivation. Sci Total Environ 472:767–777. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.11.016
Nie ZJ, Hang BJ, Cai S, Xie XT, He J, Li SP (2011) Degradation of cyhalofop-butyl (CyB) by pseudomonas azotoformans strain QDZ-1 and cloning of a novel gene encoding CyB-hydrolyzing esterase. J Agric Food Chem 59:6040–6046. doi:10.1021/jf200397t
Papa E, Castiglioni S, Gramatica P, Nikolayenko V, Kayumov O, Calamari D (2004) Screening the leaching tendency of pesticides applied in the AmuDarya Basin (Uzbekistan). Water Res 38:3485–3494. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2004.04.053
Roberts T (1998) Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals, part one, herbicides and plant growth regulators. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge
Sarmah AK, Close ME (2009) Modeling the dissipation kinetics of six commonly used pesticides in two contrasting soils of New Zealand. J Environ Sci Health B 44:507–517. doi:10.1080/03601230902997477
Schulz R (2001) Rainfall-induced sediment and pesticide input from orchards into the Lourens River, Western Cape, South Africa: importance of a single event. Water Res 35:1869–1876
Tang W, Zhou F, Chen J, Zhou X (2014) Resistance to ACCase-inhibiting herbicides in an Asia minor bluegrass (Polypogon fugax) population in China. Pest Biochem Physiol 108:16–20. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2013.11.001
Zeng D, Shi H, Li B, Wang M, Song B (2006) Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitative determination of quizalofop-p-ethyl. J Agric Food Chem 54:8682–8687. doi:10.1021/jf061492n
Acknowledgments
This research has been co-financed by the European Union (European Social Fund (ESF)) and Greek national funds through the Operational Program “Education and Lifelong Learning” of the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF)-Research Funding Program: ARCHIMEDES III. Investing in knowledge society through the European Social Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 228 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mantzos, N., Karakitsou, A., Nikolaki, S. et al. Dissipation and transport of quizalofop-p-ethyl herbicide in sunflower cultivation under field conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 3481–3490 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5572-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5572-6