Abstract
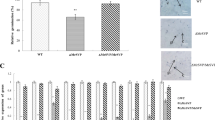
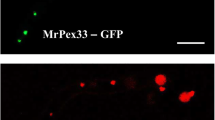
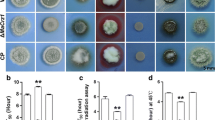
Metarhizium robertsii, a vital entomopathogenic fungus for pest management, relies on various virulence-related proteins for infection. Identifying these proteins, especially those with unknown functions, can illuminate the fungus’s virulence mechanisms. Through RNA-seq, we discovered that the hypothetical protein MAA_07646 was significantly upregulated during appressorium formation in M. robertsii. In this study, we characterized MAA_07646, finding its presence in both the nucleus and cytoplasm. Surprisingly, it did not affect vegetative growth, conidiation, or chemical tolerance. However, it played a role in heat and UV radiation sensitivity. Notably, ΔMAA_07646 exhibited reduced virulence in Galleria mellonella larvae due to impaired appressorium formation and decreased expression of virulence-related genes. In conclusion, MAA_07646 contributes to thermotolerance, UV resistance, and virulence in M. robertsii. Understanding its function sheds light on the insecticidal potential of M. robertsii’s hypothetical proteins.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All datasets generated for this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material.
References
Chen X, Xu C, Qian Y, Liu R, Zhang Q, Zeng G, Zhang X, Zhao H, Fang W (2016) MAPK cascade-mediated regulation of pathogenicity, conidiation and tolerance to abiotic stresses in the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii. Environ Microbiol 18:1048–1062
Fang W, Bidochka MJ (2006) Expression of genes involved in germination, conidiogenesis and pathogenesis in Metarhizium anisopliae using quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Mycol Res 110:1165–1171
Fang W, Pei Y, Bidochka MJ (2006) Transformation of Metarhizium anisopliae mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Can J Microbiol 52:623–626
Fang W, Azimzadeh P, St Leger RJ (2012) Strain improvement of fungal insecticides for controlling insect pests and vector-borne diseases. Curr Opin Microbiol 15:232–238
Gao Q, Shang Y, Huang W, Wang C (2013) Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase contributes to triacylglycerol biosynthesis, lipid droplet formation, and host invasion in Metarhizium robertsii. Appl Environ Microb 79:7646–7653
Guo L, Wang J, Liang C, Yang L, Zhou Y, Liu L, Huang J (2022) Fosp9, a novel secreted protein, is essential for the full virulence of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense on banana (Musa spp.). Appl Environ Microb 88:e0060421
Huang W, Shang Y, Chen P, Cen K, Wang C (2015a) Basic leucine zipper (bZIP) domain transcription factor MBZ1 regulates cell wall integrity, spore adherence, and virulence in Metarhizium robertsii. J Biol Chem 290:8218–8231
Huang W, Shang Y, Chen P, Gao Q, Wang C (2015b) MrpacC regulates sporulation, insect cuticle penetration and immune evasion in Metarhizium robertsii. Environ Microbiol 17:994–1008
Lin L, Cao J, Du A, An Q, Chen X, Yuan S, Batool W, Shabbir A, Zhang D, Wang Z et al (2021) eIF3k domain-containing protein regulates conidiogenesis, appressorium turgor, virulence, stress tolerance, and physiological and pathogenic development of Magnaporthe oryzae. Front Plant Sci 12:748120
Meng Y, Zhang X, Guo N, Fang W (2019) MrSt12 implicated in the regulation of transcription factor AFTF1 by Fus3-MAPK during cuticle penetration by the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii. Fungal Genet Biol 131:103244
Muniz-Paredes F, Miranda-Hernandez F, Loera O (2017) Production of conidia by entomopathogenic fungi: from inoculants to final quality tests. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:57
Ortiz-Urquiza A, Keyhani NO (2016) Molecular genetics of Beauveria bassiana infection of insects. Adv Genet 94:165–249
Peng H, Zhang YL, Ying SH, Feng MG (2024) Rad2, Rad14 and Rad26 recover Metarhizium robertsii from solar UV damage through photoreactivation in vivo. Microbiol Res 280:127589
Qu S, Wang S (2018) Interaction of entomopathogenic fungi with the host immune system. Dev Comp Immunol 83:96–103
Tong SM, Feng MG (2019) Insights into regulatory roles of MAPK-cascaded pathways in multiple stress responses and life cycles of insect and nematode mycopathogens. Appl Microbiol Biot 103:577–587
Tong Y, Wu H, Liu Z, Wang Z, Huang B (2020) G-protein subunit Gα(i) in mitochondria, MrGPA1, affects conidiation, stress resistance, and virulence of entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii. Front Microbiol 11:1251
Wang D, Wen S, Zhao Z, Long Y, Fan R (2023a) Hypothetical protein VDAG_07742 is required for Verticillium dahliae pathogenicity in potato. Int J Mol Sci 24:3630
Wang P, Yang G, Shi N, Zhao C, Hu F, Coutts RHA, Kotta-Loizou I, Huang B (2023b) A novel partitivirus orchestrates conidiation, stress response, pathogenicity, and secondary metabolism of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium majus. PLoS Pathog 19:e1011397
Yu L, Xu SY, Luo XC, Ying SH, Feng MG (2023) Comparative roles of Rad4A and Rad4B in photoprotection of Beauveria bassiana from solar ultraviolet damage. J Fungi (Basel, Switzerland) 9:154
Zhang LB, Feng MG (2018) Antioxidant enzymes and their contributions to biological control potential of fungal insect pathogens. Appl Microbiol Biot 102:4995–5004
Zhao X, Luo T, Huang S, Peng N, Yin Y, Luo Z, Zhang Y (2021) A novel transcription factor negatively regulates antioxidant response, cell wall integrity and virulence in the fungal insect pathogen, Beauveria bassiana. Environ Microbiol 23:4908–4924
Zhou R, Zhou X, Fan A, Wang Z, Huang B (2018) Differential functions of two metalloproteases, Mrmep1 and Mrmep2, in growth, sporulation, cell wall integrity, and virulence in the filamentous fungus Metarhizium robertsii. Front Microbiol 9:1528
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31972332).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, B.H.; methodology, M.C. and Y.Y.; validation, Y.T., H.W., J.Q., and Y.Y.; formal analysis, B.H.; data curation, B.H.; writing—review and editing, B.H.; supervision, B.H.; funding acquisition, B.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Yu, Y., Tong, Y. et al. Hypothetical protein MAA_07646 is required for stress resistance and pathogenicity in Metarhizium robertsii. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 40, 141 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03934-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-024-03934-y