Abstract
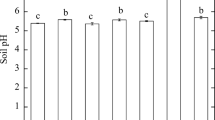
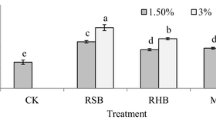
The paper aims to evaluate the effectiveness of biochar prepared from the co-pyrolysis of rice husk and cow bone (RHCBC) for in situ remediation and amelioration of Cd-contaminated soil. Effects of RHCBC on Cd bioavailability in soil and Cd uptake in corn growth were investigated through cultivation experiments and pot experiments. The results showed that the addition of RHCBC in the Cd-contaminated soil achieved the increase of soil pH, CEC, and SOM, whereas the soil available Cd content was reduced by 29.08–51.06%, which was proved by the transformation of Cd from acid soluble and exchangeable state to residual state. Furthermore, the nutrient contents of soil were also increased by 82.41–230.09% for alkali-hydrolyzable N, 66.81–144.03% for available P, and 16.20–77.70% for available K, respectively, which promoted the growth of corn. Overall, it is a promising strategy to employ RHCBC for in situ remediation of Cd-contaminated soil and promotion of plant growth as efficient soil amendment.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Ahmad, Z., Gao, B., Mosa, A., Yu, H. W., Yin, X. Q., Bashir, A., Ghoveisi, H., & Wang, S. S. (2018). Removal of Cu (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions by biochars derived from potassium-rich biomass. Journal of Cleaner Production, 180, 437–449.
Ahmed, M. J., & Hameed, B. H. (2020). Insight into the co-pyrolysis of different blended feedstocks to biochar for the adsorption of organic and inorganic pollutants: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 265, 121762.
Ajmal, Z., Muhmood, A., Dong, R. J., & Wu, S. B. (2020). Probing the efficiency of magnetically modified biomass-derived biochar for effective phosphate removal. Journal of Environmental Management, 253, 109730.
Ali, J., Kazi, T. G., Afridi, H. I., Baig, J. A., Shah, F., & Arain, M. S. (2017). Evaluates the chemical fractions of arsenic bounded to solid matrixes of thar coalfield of Pakistan by sequential extraction method. Environmental Progress and Sustainable Energy, 36(6), 1667–1675.
Altintig, E., Altundag, H., Tuzen, M., & Sari, A. (2017). Effective removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions using magnetic loaded activated carbon as novel adsorbent. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 122, 151–163.
Arain, M. B., Kazi, T. G., Jamali, M. K., Afridi, H. I., Jalbani, N., Sarfraz, R. A., Baig, J. A., Kandhro, G. A., & Memon, M. A. (2008a). Time saving modified BCR sequential extraction procedure for the fraction of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in sediment samples of polluted lake. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 160, 235–239.
Arain, M. B., Kazi, T. G., Jamali, M. K., Jalbani, N., Afridi, H. I., & Baig, J. A. (2008b). Speciation of heavy metals in sediment by conventional, ultrasound and microwave assisted single extraction methods: A comparison with modified sequential extraction procedure. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 154, 998–1006.
Awual, M. R., Khraisheh, M., Alharthi, N. H., Luqman, M., Islam, A., Karim, M. R., Rahman, M. M., & Khaleque, M. A. (2018). Efficient detection and adsorption of cadmium (II) ions using innovative nano-composite materials. Chemical Engineering Journal, 343, 118–127.
Beesley, L., & Marmiroli, M. (2011). The immobilisation and retention of soluble arsenic, cadmium and zinc by biochar. Environmental Pollution, 159(2), 474–480.
Cui, X. Q., Fang, S. Y., Yao, Y. Q., Li, T. Q., Ni, Q. J., Yang, X. E., & He, Z. L. (2016). Potential mechanisms of cadmium removal from aqueous solution by Canna indica derived biochar. Science of the Total Environment, 562, 517–525.
Fan, S. S., Tang, J., Wang, Y., Li, H., Zhang, H., Tang, J., Wang, Z., & Li, X. D. (2016). Biochar prepared from co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 220, 432–441.
Fan, J. J., Cai, C., Chia, H. F., Reid, B. J., Coulon, F., Zhang, Y. C., & Hou, Y. W. (2020). Remediation of cadmium and lead polluted soil using thiol-modified biochar. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 388, 122037.
Feng, Y. A., Gong, J. L., Zeng, G. M., Niu, Q. Y., Zhang, H. Y., Niu, C. G., Deng, J. H., & Yan, M. (2010). Adsorption of Cd (II) and Zn (II) from aqueous solutions using magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as adsorbents. Chemical Engineering Journal, 162(2), 487–494.
Ge, J., Zhang, C., Sun, Y. C., Zhang, Q., Lv, M. W., Guo, K., & Li, J. L. (2019). Cadmium exposure triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in chicken (Gallus gallus) kidney via mitochondrial UPR inhibition and Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defense activation. Science of the Total Environment, 689, 1160–1171.
Guo, X. Z., Zhang, L. J., Yan, L. Q., Yang, H., & Zhu, L. (2010). Preparation of silicon carbide using bamboo charcoal as carbon source. Materials Letters, 64(3), 331–333.
Guo, F. Y., Ding, C. F., Zhou, Z. G., Huang, G. X., & Wang, X. X. (2018). Effects of combined amendments on crop yield and cadmium uptake in two cadmium contaminated soils under rice-wheat rotation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 148, 303–310.
He, H. D., Tam, N. F. Y., Yao, A. J., Qiu, R. L., Li, W. C., & Ye, Z. H. (2017). Growth and Cd uptake by rice (Oryza sativa) in acidic and Cd-contaminated paddy soils amended with steel slag. Chemosphere, 189, 247–254.
Jamali, M. K., Kazi, T. G., Arain, M. B., Afridi, H. I., Jalbani, N., Sarfraz, R. A., & Baig, J. A. (2008). A multivariate study: Variation in uptake of trace and toxic elements by various varieties of Sorghum bicolor L. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 158(2–3), 644–651.
Jamali, M. K., Kazi, T. G., Arain, M. B., Afridi, H. I., Jalbani, N., Kandhro, G. A., Shah, A. Q., & Baig, J. A. (2009). Heavy metal accumulation in different varieties of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grown in soil amended with domestic sewage sludge. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 164(2–3), 1386–1391.
Jiang, L., Yi, X., Xu, B., & Lai, K. R. (2020). Effect of wheat straw derived biochar on immobilization of Cd and Pb in single-and binary-metal contaminated soil. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 26(9), 2420–2433.
Kazi, T. G., Brahman, K. D., Baig, J. A., & Afridi, H. I. (2019). Bioaccumulation of arsenic and fluoride in vegetables from growing media: Health risk assessment among different age groups. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 41(3), 1223–1234.
Lashari, A. A., Kazi, T. G., Baig, J. A., & Afridi, H. I. (2020). Fractionation of lead in lignite coal samples of thar coalfield, Pakistan by time-saving single-step based on BCR sequential extraction scheme. Environmental Progress and Sustainable Energy, 39(6), 13439.
Lehmann, J., Rilling, M. C., Thies, J., Masiello, C. A., Hockaday, W. C., & Crowley, D. (2011). Biochar effects on soil biota - A review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43(9), 1812–1836.
Liang, B. Q., Lehmann, J., Sohi, S. P., Thies, J. E., O’Neill, B., Trujillo, L., Gaunt, J., Solomon, D., Grossman, J., Neves, E. G., & Luizao, F. J. (2010). Black carbon affects the cycling of non-black carbon in soil. Organic Geochemistry, 41(2), 206–213.
Liu, L., & Fan, S. S. (2018). Removal of cadmium in aqueous solution using wheat straw biochar: Effect of minerals and mechanism. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 25(9), 8688–8700.
Liu, J., Yang, X. Y., Liu, H. H., Jia, X. P., & Bao, Y. C. (2021a). Mixed biochar obtained by the co-pyrolysis of shrimp shell with corn straw: Co-pyrolysis characteristics and its adsorption capability. Chemosphere, 282, 131116.
Liu, P. Y., Rao, D. A., Zou, L. Y., Teng, Y., & Yu, H. Y. (2021b). Capacity and potential mechanisms of Cd (II) adsorption from aqueous solution by blue algae-derived biochars. Science of the Total Environment, 767, 145447.
Long, Y. C., Jiang, J., Hu, J., Hu, X. J., Yang, Q., & Zhou, S. Q. (2019). Removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution by hydroxyapatite/carbon composite: Preparation and adsorption behavior. Colloids and Surfaces A, 577, 471–479.
Ma, Y. R., Yang, X. H., Ge, C. H., & Sun, J. S. (2014). Study on activating effect available P and K through application of cotton stalk biochar. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences (China), 51(4), 660–666.
Mehmood, K., Abdulaha-Al Baquy, M., & Xu, R. K. (2018). Influence of nitrogen fertilizer forms and crop straw biochars on soil exchange properties and maize growth on an acidic Ultisol. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 64(6), 834–849.
MLR (Ministry of Land and Resources), MEP (Ministry of Environmental Protection) in China. (2014). The results of a national soil survey. http://www.gov.cn/foot/site1/20140417/782bcb88840814ba158d01.pdf. Accessed 20 Dec 2022
Nowinska, K., & Adamczyk, Z. (2021). Effect of galena contained in dust from Zn-Pb metallurgical processes on environment. Environmental Earth Sciences., 80(8), 294.
Qiu, B. B., Tao, X. D., Wang, H., Li, W. K., Ding, X., & Chu, H. Q. (2021). Biochar as a low-cost adsorbent for aqueous heavy metal removal: a review. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 155, 105081.
Qureshi, A. A., Kazi, T. G., Baig, J. A., Arain, M. B., & Afridi, H. I. (2020). Exposure of heavy metals in coal gangue soil, in and outside the mining area using BCR conventional and vortex assisted and single step extraction methods. Impact on orchard grass. Chemosphere, 255, 126960.
Sahito, O. M., Afridi, H. I., Kazi, T. G., & Baig, J. A. (2015). Evaluation of heavy metal bioavailability in soil amended with poultry manure using single and BCR sequential extractions. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 95(11), 1066–1079.
Sahito, O. M., Kazi, T. G., Afridi, H. I., Baig, J. A., Talpur, F. N., Baloch, S., Memon, N. S., & Kori, N. G. (2016). Assessment of toxic metal uptake by different vegetables grown on soils amended with poultry waste: Risk Assessment. Water Air and Soil Pollution., 227(11), 423.
Saifullah, Dahlawi, S., Naeem, A., Rengel, Z., & Naidu, R. (2018). Biochar application for the remediation of salt-affected soils: Challenges and opportunities. Science of the Total Environment, 625(320), 335.
Saleh, T. A., Sari, A., & Tuzen, M. (2017a). Effective adsorption of antimony (III) from aqueous solutions by polyamide-graphene composite as a novel adsorbent. Chemical Engineering Journal, 307, 230–238.
Saleh, T. A., Tuzen, M., & Sari, A. (2017b). Magnetic activated carbon loaded with tungsten oxide nanoparticles for aluminum removal from waters. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 5(3), 2853–2860.
Shaheen, S. M., & Rinklebe, J. (2015). Impact of emerging and low cost alternative amendments on the (im)mobilization and phytoavailability of Cd and Pb in a contaminated floodplain soil. Ecological Engineering, 74, 319–326.
Tu, Z. N., Ren, X. N., Zhao, J. C., Awasthi, S. K., Wang, Q., Awasthi, M. K., Zhang, Z. Q., & Li, R. H. (2019). Synergistic effects of biochar/microbial inoculation on the enhancement of pig manure composting. Biochar, 1, 127–137.
Van Zwieten, L., Kimber, S., Morris, S., Chan, K. Y., Downie, A., Rust, J., Joseph, S., & Cowie, A. (2010). Effects of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility. Plant and Soil, 327(1–2), 235–246.
Wang, Y. Y., Liu, Y. X., Lu, H. H., Yang, R. Q., & Yang, S. M. (2018). Competitive adsorption of Pb (II), Cu (II), and Zn (II) ions onto hydroxyapatite-biochar nanocomposite in aqueous solutions. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 261, 53–61.
Waris, M., Baig, J. A., Talpur, F. N., Afridi, H. I., Kazi, T. G., & Yousa, H. (2022). Evaluation of selected halophytes for phytoextraction of Co, Cu, Zn and capability of desalination of saline soil. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology., 19(4), 2737–2746.
Xu, Y. Z., Fang, Z. Q., & Tsang, E. P. (2016). In situ immobilization of cadmium in soil by stabilized biochar-supported iron phosphate nanoparticles. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 23(19), 19164–19172.
Xu, C. B., Zhao, J. W., Yang, W. J., He, L., Wei, W. X., Tan, X., Wang, J., & Lin, A. J. (2020). Evaluation of biochar pyrolyzed from kitchen waste, corn straw, and peanut hulls on immobilization of Pb and Cd in contaminated soil. Environmental Pollution, 261, 114133.
Yuan, J. H., & Xu, R. K. (2011). The amelioration effects of low temperature biochar generated from nine crop residues on an acidic Ultisol. Soil Use and Management, 27(1), 110–115.
Zhang, X., Wang, D., Jiang, C., & Peng, S. (2013). Biochar and research advances of biochar in acidic soil improvement. Hubei Agricultural Sciences (China), 5, 997–1000.
Zhang, H., Shao, J. G., Zhang, S. H., Zhang, X., & Chen, H. P. (2020). Effect of phosphorus-modified biochars on immobilization of Cu (II), Cd (II), and As (V) in paddy soil. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 390, 121349.
Zhang, P., Xue, B., Jiao, L., Meng, X. Y., Zhang, L. Y., Li, B. X., & Sun, H. W. (2022). Preparation of ball-milled phosphorus-loaded biochar and its highly effective remediation for Cd-and Pb-contaminated alkaline soil. Science of the Total Environment, 813, 152648.
Zhou, Y. F., Xu, M. M., Huang, D. H., Xu, L., Yu, M. C., Zhu, Y. Q., & Niu, J. F. (2021). Modulating hierarchically microporous biochar via molten alkali treatment for efficient adsorption removal of perfluorinated carboxylic acids from wastewater. Science of the Total Environment, 757, 143719.
Zwetsloot, M. J., Lehmann, J., Bauerle, T., Vanek, S., Hestrin, R., & Nigussie, A. (2016). Phosphorus availability from bone char in a P-fixing soil influenced by root-mycorrhizae-biochar interactions. Plant and Soil, 408(1–2), 95–105.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51504174 and 51876148).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Liu, Y., Feng, J. et al. Co-Pyrolyzed Rice Husk and Cow Bone In Situ Cd-Remediation for Corn Plant Growth. A Comprehensive Case Study. Water Air Soil Pollut 234, 151 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06156-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06156-4