Abstract
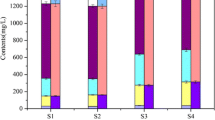
Dissolved oxygen (DO) in the overlying water is important in influencing internal phosphorus (P) release. However, the potentially associative effect of DO on the P adsorption and immobilization by La-modified bentonite (LMB) has not been quantified. This 80-day incubation experiment showed the synergistic effect of DO and LMB in the overlying water, which caused the reduction of dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) by 51% (DO = 5 mg L−1) and 77% (DO = 7 mg L−1) on average, respectively, compared with the DO of 3 mg L−1. In addition, the DIP in the pore water decreased from 1.12 mg P L−1 (control) to 0.014 mg P L−1 (5 mg L−1) and 0.004 mg P L−1 (7 mg L−1). Besides, the Fe2+ and NH4+ concentrations were also reduced significantly in the pore water, suggesting the rise in the redox potential in the sediment, which helped P immobilization. Chemical P-fractionation experiments indicate that the Fe-P reduction in sediment was the most significant, reduced by 14%, followed by NH4Cl-P (12%), causing a reduction by 13% (3 mg L−1), 23% (5 mg L−1) and 27% (7 mg L−1) of mobile P in the surface 7-cm sediment, respectively. However, the released P ions were rapidly adsorbed by the Al ions and Ca ions, as well as their compounds, thereby leading to the obvious rise in inert P in the sediment. Accordingly, it was suggested that DO and LMB had a synergistic effect on external P adsorption and immobilization.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
[APHA]. (1995). American Public Health Association, Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th ed. Water Environment Federation.
Conley, D. J., Paerl, H. W., Howarth, R. W., Boesch, D. F., Seitzinger, S. P., Havens, K. E., Lancelot, C., & Likens, G. E. (2009). Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and P. Science, 323(5917), 1014–1015.
Cooke, G. D., Welch, E. B., Martin, A. B., Fulmer, D. G., Hyde, J. B., & Schrieve, G. D. (1993). Effectiveness of Al, Ca, and Fe salts for control of internal phosphorus loading in shallow and deep lakes. Hydrobiologia, 253(1–3), 323–335.
Copetti, D., Finsterle, K., Marziali, L., Stefani, F., Tartari, G., Douglas, G., Reitzel, K., Spears, B. M., Winfield, L. J., Crosa, G., D’Haese, P., Vasseri, S., & Lürling, M. (2016). Eutrophication management in surface waters using lanthanum modified bentonite: A review. Water Research, 97, 162–174.
Ding, S. M., Sun, Q., Chen, X., Liu, Q., Wang, D., Lin, J., Zhang, C. S., & Tsang, D. C. W. (2018). Synergistic adsorption of phosphorus by iron in lanthanum modified bentonite (Phoslock®): New insight into sediment phosphorus immobilization. Water Research, 134, 32–43.
Dithmer, L., Nielsen, U. G., Lürling, M., Spears, B. M., Yasseri, S., Lundberg, D., Moore, A., Jensen, N. D., & Reitzel, K. (2016). Responses in sediment phosphorus and lanthanum concentrations and composition across 10 lakes following applications of lanthanum modified bentonite. Water Research, 97, 101–110.
Douglas, G. B. (1997) Remediation material and remediation process for sediments. Australian National phase entry PO5896.
Gibbs, M., & Özkundakci, D. (2011). Effects of a modified zeolite on P and N processes and fluxes across the lake sediment–water interface using core incubations. Hydrobiologia, 661(1), 21–35.
Gomez, E., Durillon, C., Rofes, G., & Picot, B. (1999). Phosphate adsorption and release from sediments of brackish lagoons: pH, O2 and loading influence. Water Research, 33(10), 2437–2447.
Hart, S. C., Stark, J. M., Davidson, E. A., & Firestone, M. K. (1994). Nitrogen mineralization, immobilization, and nitrification. In R. V. Weaver (Ed.), Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. SSSA Book Series 5 (pp. 985–1018). Madison: Soil Sci Soc Am Soc Agron.
Horppila, J., Holmroos, H., Niemistö, J., Massa, I., Nygrén, N., Schönach, P., Tapio, P., & Tammeorg, O. (2017). Variations of internal phosphorus loading and water quality in a hypertrophic lake during 40 years of different management efforts. Ecological Engineering, 103, 264–274.
Huang, X., Shi, W., Ni, J., & Li, Z. (2017). Evaluation of laboratory-scale in situ capping sediments with purple parent rock to control the eutrophication. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 24(8), 7114–7123.
Joy, A., Anoop, P., Rajesh, R., Mathew, J., Mathew, A., & Gopinath, A. (2019). Spatial variation of phosphorus fractionation in the coral reef sediments of Lakshadweep Archipelago, Indian Ocean. Chemistry and Ecology, 35(7), 592–612.
Katarzyna, K. M., Renata, D., Ryszard, G., Anna, K., & Beata, M. (2018). Internal phosphorus loading from the bottom sediments of a dimictic lake during its sustainable restoration. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 229(8), 280–298.
Kumar, E., Bhatnagar, A., Hogland, W., Marques, M., & Sillanpää, M. (2014). Interaction of inorganic anions with iron-mineral adsorbents in aqueous media -a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 203, 11–21.
Li, D. P., & Huang, Y. (2013). Phosphorus uptake by suspended sediments from a heavy eutrophic and standing water system in Suzhou, China. Ecological Engineering, 60, 29–36.
Li, D. P., Huang, Y., Fan, C. X., & Yan, Y. (2011). Contributions of phosphorus on sedimentary phosphorus bioavailability under sediment resuspension conditions. Chemical Engineering Journal, 168(3), 1049–1054.
Lin, J., Sun, Q., Ding, S. M., Wang, D., Wang, Y., Chen, M. S., Shi, L., Fan, X. F., & Tsang, D. C. W. (2017). Mobile phosphorus stratification in sediments by aluminum immobilization. Chemosphere, 186, 644–651.
Lin, J. W., Jiang, B. H., & Zhan, Y. H. (2018). Effect of pre-treatment of bentonite with sodium and calcium ions on phosphate adsorption onto zirconium-modified bentonite. Journal of Environmental Management, 217, 183–195.
Lürling, M., & Faassen, E. J. (2012). Controlling toxic cyanobacteria: Effects of dredging and phosphorus-binding clay on cyanobacteria and microcystins. Water Research, 46(5), 1447–1459.
Meis, S., Spears, B. M., Maberly, S. C., O’Malley, M. B., & Perkins, R. G. (2012). Sediment amendment with phoslock® in Clatto Reservoir (Dundee, UK): Investigating changes in sediment elemental composition and phosphorus fractionation. Journal of Environmental Management, 93(1), 185–193.
Meis, S., Spears, B. M., Maberly, S. C., & Perkins, R. G. (2013). Assessing the mode of action of phoslock® in the control of phosphorus release from the bed sediments in a shallow lake (Loch Flemington, UK). Water Research, 47(13), 4460–4473.
Miao, S., Delaune, R. D., & Jugsujinda, A. (2006). Influence of sediment redox conditions on release/solubility of metals and nutrients in a Louisiana Mississippi River deltaic plain freshwater lake. Science of the Total Environment, 371(1–3), 334–343.
Özkundakci, D., Hamilton, D. P., & Scholes, P. (2010). Effect of intensive catchment and in-lake restoration procedures on phosphorus concentrations in a eutrophic lake. Ecological Engineering, 36(4), 396–405.
Perkins, R. G., & Underwood, G. J. C. (2001). The potential for phosphorus release across the sediment-water interface in a eutrophic reservoir dosed with ferric sulphate. Water Research, 35(6), 1399–1406.
Rahutomo, S., Kovar, J. L., & Thompson, M. L. (2018). Inorganic and organic phosphorus in sediments in the walnut creek watershed of Central Iowa, USA. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 229(3), 72.
Ribeiro, D. C., Martins, G., Nogueira, R., Cruz, J. V., & Brito, A. G. (2008). Phosphorus fractionation in volcanic lake sediments (Azores – Portugal). Chemosphere, 70(7), 1256–1263.
Robb, M., Greenop, B., Goss, Z., Douglas, G., & Adeney, J. (2003). Application of Phoslock™, an innovative phosphorus binding clay, to two Western Australian waterways: Preliminary findings. Hydrobiologia, 494(1–3), 237–243.
Ross, G., Haghseresht, F., & Cloete, T. E. (2008). The effect of pH and anoxia on the performance of phoslock®, a phosphorus binding clay. Harmful Algae, 7(4), 545–550.
Rydin, E. (2000). Potentially mobile phosphorus in Lake Erken sediment. Water Research, 34(7), 2037–2042.
Shen, Y., Duan, Y. H., Mclaughlin, N., Huang, S. M., Guo, D. D., & Xu, M. G. (2019). Phosphorus desorption from calcareous soils with different initial Olsen-P levels and relation to phosphate fractions. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(7), 2997–3007.
Søndergaard, M., Jensen, J. P., & Jeppesen, E. (2003). Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia, 506-509(1–3), 135–145.
Stookey, L. L. (1970). Ferrozine a new spectrophoto metric reagent for iron. Analytical Chemistry, 42(7), 779–781.
Tu, L. Y., Jarosch, K. A., Schneider, T., & Grosjean, M. (2019). Phosphorus fractions in sediments and their relevance for historical lake eutrophication in the Ponte Tresa basin (Lake Lugano, Switzerland) since 1959. Science of the Total Environment, 685, 806–817.
Vopel, K., Gibbs, M., Hickey, C. W., & Quinn, J. (2008). Modification of sediment–water solute exchange by sediment-capping materials: Effects on O2 and pH. Marine and Freshwater Research, 59(12), 1101–1110.
Waajen, G., Oosterhout, F. V., Douglas, G., & Lürling, M. (2015). Management of eutrophication in Lake De Kuil (the Netherlands) using combined flocculant - lanthanum modified bentonite treatment. Water Research, 97, 83–95.
Wang, C. H., & Jiang, H. L. (2016). Chemicals used for in situ immobilization to reduce the internal phosphorus loading from lake sediments for eutrophication control. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 46(10), 947–997.
Wang, C. H., Bai, L. L., Jiang, H. L., & Xu, H. C. (2016). Algal bloom sedimentation induces variable control of lake eutrophication by phosphorus inactivating agents. Science of the Total Environment, 557, 479–488.
Wu, Y., Wang, X. X., Zhou, J., Bing, H. J., Sun, H. Y., & Wang, J. P. (2016). The fate of phosphorus in sediments after the full operation of the Three Gorges Reservoir. China Environmental Pollution, 214, 282–289.
Xu, D., Ding, S. M., Sun, Q., Zhong, J. C., Wu, W., & Jia, F. (2012). Evaluation of in situ capping with clean soils to control phosphate release from sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 438(3), 334–341.
Xu, Y., Han, F. E., Li, D. P., Zhou, J., & Huang, Y. (2018). Transformation of internal sedimentary phosphorus fractions by point injection of CaO2. Chemical Engineering Journal, 343, 408–415.
Yang, M. J., Lin, J. W., Zhan, Y. H., Zhu, Z. L., & Zhang, H. H. (2015). Immobilization of phosphorus from water and sediment using zirconium-modified zeolites. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 22(5), 3606–3619.
Yin, H. B., & Kong, M. (2015). Reduction of sediment internal P-loading from eutrophic lakes using thermally modified calcium-rich attapulgite-based thin-layer cap. Journal of Environmental Management, 151, 178–185.
Yin, H. B., Kong, M., & Fan, C. X. (2013). Batch investigations on P immobilization from wastewaters and sediment using natural calcium rich sepiolite as a reactive material. Water Research, 47(13), 4247–4258.
Yin, H. B., Kong, M., Han, M. X., & Fan, C. X. (2016). Influence of sediment resuspension on the efficacy of geoengineering materials in the control of internal phosphorous loading from shallow eutrophic lakes. Environmental Pollution, 219, 568–579.
Yin, H. B., Du, Y. X., Kong, M., & Liu, C. (2017). Interactions of riverine suspended particulate matter with phosphorus inactivation agents across sediment-water interface and the implications for eutrophic lake restoration. Chemical Engineering Journal, 327, 150–161.
Zamparas, M., & Zacharias, I. (2014). Restoration of eutrophic freshwater by managing internal nutrient loads. A review. Science of the Total Environment, 496, 551–562.
Zamparas, M., Gianni, A., Stathi, P., Deligiannakis, Y., & Zacharias, I. (2012). Removal of phosphate from natural waters using innovative modified bentonites. Applied Clay Science, 62–63, 101–106.
Zhang, H., Boegman, L., Scavia, D., & Culver, D. A. (2016a). Spatial distributions of external and internal phosphorus loads in Lake Erie and their impacts on phytoplankton and water quality. Journal of Great Lakes Research, 42(6), 1212–1227.
Zhang, Y., He, F., Liu, Z. S., Liu, B. Y., Zhou, Q. H., & Wu, Z. B. (2016b). Release characteristics of sediment phosphorus in all fractions of West Lake, Hang Zhou, China. Ecological Engineering, 95, 645–651.
Zhang, W. Q., Jin, X., Meng, X., Tang, W. Z., & Shan, B. Q. (2018). Phosphorus transformations at the sediment–water interface in shallow freshwater ecosystems caused by decomposition of plant debris. Chemosphere, 201, 328–334.
Zhou, A. M., Wang, D. S., & Tang, H. X. (2005). Phosphorus fractionation and bio-availability in Taihu Lake (China) sediments. Journal of Environmental Science, 17(3), 384–388.
Zhou, J., Li, D. P., Chen, S. T., Xu, Y., Geng, X., Guo, C. R., & Huang, Y. (2019). Sedimentary phosphorus immobilization with the addition of amended calcium peroxide material. Chemical Engineering Journal, 357, 288–297.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 51778393) and Graduate Research and Innovation Projects of Jiangsu Province (SJCX18_0870). Financial support was also provided by the Collaborative Innovation Center of Water Treatment Technology and Material of Jiangsu Province and National and Local Joint Engineering Laboratory of Municipal Sewage Resource Utilization Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Li, D., Xu, C. et al. Using Aeration to Enhance Phosphorus Adsorption and Immobilization by the Sediment and LMB. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 93 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4451-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-4451-z