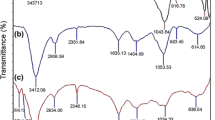
Abstract
Different carbon xerogels (CXs) were synthesized by the polymerization of resorcinol (R) and formaldehyde (F) catalyzed by cesium carbonate (Cs), and by varying the molar ratio R/Cs. The CXs were labeled as XCs-100, XCs-500, XCs-1000, and XCS-2000, corresponding to the R/Cs ratio of 100, 500, 1000, and 2000, respectively. The surface chemistry of the CXs varied very slightly with the R/Cs ratio because the point of zero charge (pHPZC) and the concentrations of basic and acid sites were almost independent on the R/Cs ratio. The surface areas of the four CXs decreased slightly by increasing the R/Cs ratio; however, XCs-500 presented the highest volume of pores and mesopores and mesopore surface area. At a concentration of diclofenac (DCF) at equilibrium of 800 mg/L, the adsorption capacities of XCs-100, XCs-500, XCs-1000, and XCs-2000 towards DCF in aqueous solution were 132.0, 184.6, 126.5, and 126.4 mg/g, respectively. Hence, the adsorption capacity of XCs-500 was about 1.4 times larger than those of the other CXs. The adsorption capacity of XCs-500 was reduced by increasing the solution pH due to electrostatic interactions, whereas the adsorption capacity was increased by raising the temperature, confirming that the adsorption was endothermic. The bacteria Escherichia coli adhered to the surface of XCs-500 forming a biofilm, and the presence of bacteria enhanced 1.3 times the adsorption capacity of XCs-500 towards DCF from water solutions.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Khateeb, L. A., Hakami, W., & Abdel Salam, M. (2017). Removal of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from water using high surface area nanographene: kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 241, 733–741.
Álvarez, A., Ribeiro, R. S., Gomes, H. T., Sotelo, J. L., & García, J. (2015). Synthesis of carbon xerogels and their application in adsorption studies of caffeine and diclofenac as emerging contaminants. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 95, 229–238.
Bautista-Toledo, M. I., Méndez-Díaz, J. D., Sánchez-Polo, M., Rivera-Utrilla, J., & Ferro-García, M. A. (2008). Adsorption of sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate on activated carbons: effects of solution chemistry and presence of bacteria. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 317, 11–17.
Bautista-Toledo, I., Espinosa-Iglesias, D., Carrasco-Marín, F., Pérez-Cadenas, A. F., & Maldonado-Hódar, F. J. (2015). Influence of the physicochemical properties of inorganic supports on the activity of immobilized bacteria for water denitrification. Journal of Environmental Management, 156, 81–88.
Boehm, H. P. (1966). Chemical identification of surface groups. Advances in Catalysis, 16, 179–274.
Brunauer, S., Emmett, P. H., & Teller, E. (1938). Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 60, 309–319.
Carabineiro, S. A. C., Thavorn-Amornsri, T., Pereira, M. F. R., Serp, P., & Figueiredo, J. L. (2012). Comparison between activated carbon, carbon xerogel and carbon nanotubes for the adsorption of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin. Catalysis Today, 186, 29–34.
Chapman, M., Robinson, L. S., Pinkner, J. S., Roth, R., Heuser, J., Hammar, M., et al. (2002). Role of Escherichia coli curli operons in directing amyloid fiber formation. Science, 295, 851–855.
Coughlin, R. W., & Ezra, F. S. (1968). Role of surface acidity in the adsorption of organic pollutants on the surface of carbon. Environmental Science & Technology, 2, 291–297.
Do, D. D. (1998). Adsorption analyses: equilibria and kinetics, ed. London: Imperial College Press.
Duprey, A., Chansavang, V., Frémion, F., Gonthier, C., Louis, Y., Lejeune, P., et al. (2014). “NiCo buster”: engineering E. coli for fast and efficient capture of cobalt and nickel. Journal of Biological Engineering, 8, 1–11.
El Naga, A. O. A., El Saied, M., Shaban, S. A., & El Kady, F. Y. (2019). Fast removal of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solution using sugar cane bagasse-derived activated carbon. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 285, 9–19.
Fathy, N. A., Attia, A. A., & Hegazi, B. (2016). Nanostructured activated carbon xerogels for removal of methomyl pesticide. Desalination Water Treatment, 57, 9957–9970.
Fernández, C., González-Doncel, M., Pro, J., Carbonell, G., & Tarazona, J. V. (2010). Occurrence of pharmaceutically active compounds in surface waters of the henares-jarama-tajo river system (Madrid, Spain) and a potential risk characterization. Science of the Total Environment, 408, 543–551.
Ferro-García, M. A., Rivera-Utrilla, J., Bautista-Toledo, I., & Moreno-Castilla, C. (1998). Adsorption of humic substances on activated carbon from aqueous solutions and their effect on the removal of Cr(III) ions. Langmuir, 14, 1880–1886.
Gil, A., Santamaría, L., & Korili, S. A. (2018). Removal of caffeine and diclofenac from aqueous solution by adsorption on multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 22, 25–28.
Girgis, B. S., Attia, A. A., & Fathy, N. A. (2011). Potential of nano-carbon xerogels in the remediation of dye-contaminated water discharges. Desalination, 265, 169–176.
Girgis, B. S., El-Sherif, I. Y., Attia, A. A., & Fathy, N. A. (2012). Textural and adsorption characteristics of carbon xerogel adsorbents for removal of Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 358, 741–747.
Gros, M., Petrović, M., Ginebreda, A., & Barceló, D. (2010). Removal of pharmaceuticals during wastewater treatment and environmental risk assessment using hazard indexes. Environment International, 36, 15–26.
Larsson, D. G. J. (2014). Pollution from drug manufacturing: review and perspectives. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal London Society B: Biological Science, 369, 1–7.
León y León, C. A., Solar, J. M., Calemma, V., & Radovic, L. R. (1992). Evidence of the protonation of basal plane sites on carbon. Carbon, 30(5), 797–811.
Leyva-Ramos, R. (2007). Importancia y aplicaciones de la adsorción en fase liquida. In J. Moreno Pirajan (Ed.), Sólidos Porosos. Preparación, Caracterización y Aplicaciones (pp. 164–211). Bogotá: Uniandes.
Liang, X. X., Omer, A. M., Hu, Z., Wang, Y., Yu, D., & Ouyang, X. (2019). Efficient adsorption of diclofenac sodium from aqueous solutions using magnetic amine-functionalized chitosan. Chemosphere, 217, 270–278.
Licona, K. P. M., Geaquinto, L. R., De, O., Nicolini, J. V., Figueiredo, N. G., Chiapetta, S. C., Habert, A. C., et al. (2018). Assessing potential of nanofiltration and reverse osmosis for removal of toxic pharmaceuticals from water. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 25, 195–204.
Lippens, B. C., & de Boer, J. H. (1965). Studies on pore systems in catalysts: V. The t method. Journal of Catalysis, 4(3), 319–323.
Liu, F., Liang, J., Chen, L., Tong, M., & Liu, W. (2019). Photocatalytic removal of diclofenac by Ti doped BiOI microspheres under visible light irradiation: kinetics, mechanism, and pathways. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 275, 807–814.
Long, Y., Feng, Y., Li, X., Suo, N., Chen, H., Wang, Z., et al. (2019). Removal of diclofenac by three-dimensional electro-Fenton-persulfate (3D electro-Fenton-PS). Chemosphere., 219, 1024–1031.
Loos, R., Gawlik, B. M., Locoro, G., Rimaviciute, E., Contini, S., & Bidoglio, G. (2009). EU-wide survey of polar organic persistent pollutants in European river waters. Environmental Pollution, 157, 561–568.
Maia, G. S., De Andrade, J. R., Da Silva, M. G. C., & Vieira, M. G. A. (2019). Adsorption of diclofenac sodium onto commercial organoclay: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic study. Powder Technology, 345, 140–150.
Maier, R. M., & Gentry, T. J. (2015). Microorganisms and organic pollutants. In I. L. Pepper, C. P. Gerba, & T. J. Gentry (Eds.), Environmental microbiology (pp. 377–413). San Diego: Academic Press.
Martínez-Costa, J. I., Rivera-Utrilla, J., Leyva-Ramos, R., Sánchez-Polo, M., Velo-Gala, I., & Mota, A. J. (2018a). Individual and simultaneous degradation of the antibiotics sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in aqueous solutions by Fenton, Fenton-like and photo-Fenton processes using solar and UV radiations. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 360, 95–108.
Martínez-Costa, J. I., Rivera-Utrilla, J., Leyva-Ramos, R., Sánchez-Polo, M., & Velo-Gala, I. (2018b). Individual and simultaneous degradation of the antibiotics sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim by UV and solar radiation in aqueous solution using bentonite and vermiculite as photocatalysts. Applied Clay Science, 160, 217–225.
Martínez-Costa, J. I., Maldonado Rubio, M. I., & Leyva-Ramos, R. (2018c). Degradation of emerging contaminants diclofenac, sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim and carbamazepine by bentonite and vermiculite at a pilot solar compound parabolic collector. Catalysis Today.
Morales-Torres, S., Maldonado-Hódar, F. J., Pérez-Cadenas, A. F., & Carrasco-Marín, F. (2012). Structural characterization of carbon xerogels: from film to monolith. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 153, 24–29.
Morales-Torres, S., Maldonado-Hódar, F. J., Pérez-Cadenas, A. F., & Carrasco-Marín, F. (2010). Textural and mechanical characteristics of carbon aerogels synthesized by polymerization of resorcinol and formaldehyde using alkali carbonates as basification agents. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 12, 10365–10372.
Moral-Rodríguez, A. I., Leyva-Ramos, R., Ania, C. O., Ocampo-Pérez, R., Isaacs-Páez, E. D., Carrales-Alvarado, D. H., et al. (2019). Tailoring the textural properties of an activated carbon for enhancing its adsorption capacity towards diclofenac from aqueous solution. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26, 6141–6152.
Moreno-Castilla, C., Bautista-Toledo, I., Ferro-García, M. A., & Rivera-Utrilla, J. (2003). Influence of support surface properties on activity of bacteria immobilised on activated carbons for water denitrification. Carbon, 41, 1743–1749.
Nikaido, H., & Vaara, M. (1987). Outer membrane. In F. C. Neidhardt (Ed.), Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology (pp. 3–22). Washington: ASM Press.
Pekala, R. W. (1989). Organic aerogels from the polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde. Journal of Materials Science, 24, 3221–3227.
Radjenović, J., Petrović, M., & Barceló, D. (2009). Fate and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater and sewage sludge of the conventional activated sludge (CAS) and advanced membrane bioreactor (MBR) treatment. Water Research, 43, 831–841.
Rivera-Utrilla, J., Bautista-Toledo, I., Ferro-García, M. A., & Moreno-Castilla, C. (2001). Activated carbon surface modifications by adsorption of bacteria and their effect on aqueous lead adsorption. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 76, 1209–1215.
Roane, T. M., Pepper, I. L., & Gentry, T. J. (2015). Microorganisms and metal pollutants. In I. Pepper, C. Gerba, & T. Gentry (Eds.), Environmental microbiology (pp. 415–439). San Diego: Academic Press.
Rouquerol, J., Rouquerol, F., Llewellyn, P., Maurin, G., & Sing, K. S. W. (2014). Adsorption by powders and porous solids: principles, methodology and applications. New York: Academic Press.
Sim, W. J., Lee, J. W., Lee, E. S., Shin, S. K., Hwang, S. R., & Oh, J. E. (2011). Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceuticals in wastewater from households, livestock farms, hospitals and pharmaceutical manufactures. Chemosphere, 82, 179–186.
Tambosi, J. L., Yamanaka, L. Y., José, H. J., Muñiz Moreira, R. F. P., & Schröder, H. F. (2010). Recent research data on the removal of pharmaceuticals from sewage treatment plants (STP). Química Nova, 33, 411–420.
Ternes, T. A. (1998). Occurrence of drugs in German sewage treatment plants and rivers. Water Research, 32, 3245–3260.
Thelusmond, J. R., Kawka, E., Strathmann, T. J., & Cupples, A. M. (2018). Diclofenac, carbamazepine and triclocarban biodegradation in agricultural soils and the microorganisms and metabolic pathways affected. Science of the Total Environment, 640-641, 1393–1410.
Vivo-Vilches, J. F., Pérez-Cadenas, A. F., Maldonado-Hódar, F. J., & Carrasco-Marín, F. (2018). Resorcinol–formaldehyde carbon xerogel as selective adsorbent of carbon dioxide present on biogas. Adsorption, 24, 169–177.
Yu, Y., Wu, L., & Chang, A. C. (2012). Seasonal variation of endocrine disrupting compounds, pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater treatment plants. Science of the Total Environment, 442, 310–316.
Yu, J., Guo, M., Muhammad, F., Wang, A., Yu, G., Ma, H., et al. (2014). Simple fabrication of an ordered nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon with resorcinol–melamine–formaldehyde resin. Microporous Mesoporous Materials, 190, 117–127.
Zhang, X. Q., Li, W. C., & Lu, A. H. (2015). Designed porous carbon materials for efficient CO2 adsorption and separation. New Carbon Materials, 30, 481–501.
Funding
This work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia, CONACyT, Mexico (grant number CB-2012-02-182779). This research was also financed by the Junta de Andalucía, Spain (grant number RNM-172).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moral-Rodriguez, A.I., Leyva-Ramos, R., Carrasco-Marín, F. et al. Adsorption of Diclofenac from Aqueous Solution onto Carbon Xerogels: Effect of Synthesis Conditions and Presence of Bacteria. Water Air Soil Pollut 231, 17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4385-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4385-5