Abstract
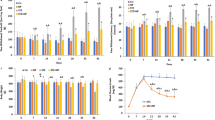
The TRPV1 channel is activated in neurons by capsaicin, oxidative stress, acidic pH and heat factors, and these factors are attenuated by the antioxidant role of calorie restriction (CR). Hence, we investigated the hypothesis that the antioxidant roles of CR and food frequency (FF) may modulate TRPV1 activity and apoptosis through inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative stress in hippocampal (HIPPON) and dorsal root ganglion neurons (DRGN). We investigated the contribution of FF and CR to neuronal injury and apoptosis through inhibition of TRPV1 in rats. We assigned rats to control, FF and FF + CR groups. A fixed amount of food ad libitum was supplemented to the control and FF groups for 20 weeks, respectively. FF + CR group were fed the same amount of food as the control group but with 20% less calories during the same period. In major results, TRPV1 currents, intracellular Ca2+ levels, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial depolarization, PARP-1 expression, caspase 3 and 9 activity and expression values were found to be increased in the HIPPON and DRGN following FF treatment, and these effects were decreased following FF + CR treatment. The FF-induced decrease in cell viability of HIPPO and DRGN, and vitamin E concentration of brain, glutathione peroxidase, vitamin A, and β-carotene values of the HIPPO, DRGN, plasma, liver and kidney were increased by FF + DR treatment, although lipid peroxidation levels in the same samples were decreased. In conclusion, CR reduces FF-induced increase of oxidative stress, apoptosis and Ca2+ entry through TRPV1 in the HIPPON and DRGN. Our findings may be relevant to the etiology and treatment of obesity following CR treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- [Ca2+]i :
-
intracellular free calcium ion
- CapN:
-
capsaicin
- CapZ:
-
capsazepine
- CR:
-
calorie restriction
- DHR:
-
dihydrorhodamine
- DRGN:
-
dorsal root ganglion neuron
- FF:
-
food frequency
- GPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
reduced glutathione
- HIPPON:
-
hippocampal neuron
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- PARP-1:
-
Poly-ADPR polymerase 1
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- TRP:
-
transient receptor potential
- TRPV1:
-
transient receptor potential vanilloid 1
- W.C.:
-
whole cell
References
Akpınar H, Nazıroğlu M, Övey İS, Çiğ B, Akpınar O (2016) The neuroprotective action of dexmedetomidine on apoptosis, calcium entry and oxidative stress in cerebral ischemia-induced rats: contribution of TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels. Sci Rep 6:37196
Babenko NA, Shakhova EG (2014) Long-term food restriction prevents aging-associated sphingolipid turnover dysregulation in the brain. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 58:420–426
Bak DH, Kang SH, Choi DR, Gil MN, Yu KS, Jeong JH, Lee NS, Lee JH, Jeong YG, Kim DK, Kim DK, Kim JJ, Han SY (2016) Intermittent fasting is neuroprotective in focal cerebral ischemia by minimizing autophagic flux disturbance and inhibiting apoptosis. Exp Ther Med 12:3021–3028
Bankoglu EE, Seyfried F, Rotzinger L, Nordbeck A, Corteville C, Jurowich C, Germer CT, Otto C, Stopper H (2016) Impact of weight loss induced by gastric bypass or caloric restriction on oxidative stress and genomic damage in obese Zucker rats. Free Radic Biol Med 94:208–217
Benemei S, Fusi C, Trevisan G, Geppetti P (2014) The TRPA1 channel in migraine mechanism and treatment. Br J Pharmacol 171:2552–2567
Carrasco C, Rodríguez BA, Pariente JA (2015) Melatonin as a stabilizer of mitochondrial function: role in diseases and aging. Turk J Biol 39:822–831
Carrasco C, Naziroglu M, Rodriguez AB, Pariente JA (2018) Neuropathic pain: delving into the oxidative origin and the possible implication of transient receptor potential channels. Front Physiol 9:95
Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M, Rosen TA, Levine JD, Julius D (1997) The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature 389(6653):816–824
Cossarizza A, Baccarani-Contri M, Kalashnikova G, Franceschi C (1993) A new method for the cytofluorimetric analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential using the J-aggregate forming lipophilic cation 5,5′,6,6′-tetrachloro-1,1′,3,3′-tetraethylbenzimidazolcarbocyanine iodide (JC-1). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 197:40–45
Cristino L, de Petrocellis L, Pryce G, Baker D, Guglielmotti V, Di Marzo V (2006) Immunohistochemical localization of cannabinoid type 1 and vanilloid transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 receptors in the mouse brain. Neuroscience 139:1405–1415
Damms-Machado A, Weser G, Bischoff SC (2012) Micronutrient deficiency in obese subjects undergoing low calorie diet. Nutr J 11:34
de Oliveira SL, Diniz DB, Amaya-Farfan J (2003) Carbohydrate-energy restriction may protect the rat brain against oxidative damage and improve physical performance. Br J Nutr 89:89–96
Desai ID (1984) Vitamin E analysis methods for animal tissues. Methods Enzymol 105:138–147
Espino J, Bejarano I, Redondo PC, Rosado JA, Barriga C, Reiter RJ, Pariente JA, Rodríguez AB (2010) Melatonin reduces apoptosis induced by calcium signaling in human leukocytes: evidence for the involvement of mitochondria and Bax activation. J Membr Biol 233:105–118
Fann DY, Santro T, Manzanero S, Widiapradja A, Cheng YL, Lee SY, Chunduri P, Jo DG, Stranahan AM, Mattson MP, Arumugam TV (2014) Intermittent fasting attenuates inflammasome activity in ischemic stroke. Exp Neurol 257:114–119
Gan SK, Watts GF (2008) Is adipose tissue lipolysis always an adaptive response to starvation?: implications for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 114(8):543–545
Godoy JA, Zolezzi JM, Braidy N, Inestrosa NC (2014) Role of Sirt1 during the ageing process: relevance to protection of synapses in the brain. Mol Neurobiol 50:744–756
Gotthardt JD, Bello NT (2017) Meal pattern alterations associated with intermittent fasting for weight loss are normalized after high-fat diet re-feeding. Physiol Behav 174:49–56
Grynkiewicz C, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3440–3450
Harder-Lauridsen NM, Rosenberg A, Benatti FB, Damm JA, Thomsen C, Mortensen EL, Pedersen BK, Krogh-Madsen R (2017) Ramadan model of intermittent fasting for 28 d had no major effect on body composition, glucose metabolism, or cognitive functions in healthy lean men. Nutrition 37:92–103
Harvie M, Howell A (2017) Potential benefits and marms of intermittent energy restriction and intermittent fasting amongst obese, overweight and normal weight subjects-A narrative review of human and animal Evidence. Behav Sci (Basel) 7(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/bs7010004
Ito H, Kamei J, Aizawa N, Fujita Y, Suzuki M, Fukuhara H, Fujimura T, Kojima T, Homma Y, Kubota Y, Ito M, Andersson KE, Igawa Y (2016) Preventive effects of long-term caloric restriction on aging related in vivo bladder dysfunction and molecular biological changes in the bladder and dorsal root ganglia in rats. J Urol 196:1575–1583
Kahya MC, Nazıroğlu M, Övey İS (2017) Modulation of diabetes-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis, and ca(2+) entry through TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels in dorsal root ganglion and hippocampus of diabetic rats by melatonin and selenium. Mol Neurobiol 54:2345–2360
Kaptan Z, Akgün-Dar K, Kapucu A, Dedeakayoğulları H, Batu Ş, Üzüm G (2015) Long term consequences on spatial learning-memory of low-calorie diet during adolescence in female rats; hippocampal and prefrontal cortex BDNF level, expression of NeuN and cell proliferation in dentate gyrus. Brain Res 1618:194–204
Kim JY, Ko AR, Kim JE (2015) P2X7 receptor-mediated PARP1 activity regulates astroglial death in the rat hippocampus following status epilepticus. Front Cell Neurosci 9:352
Lawrence RA, Burk RF (1976) Glutathione peroxidase activity in selenium-deficient rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 71:952–958
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG, Earnshaw WC (1994) Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 371:346–347
Lee E, Jung DY, Kim JH, Patel PR, Hu X, Lee Y, Azuma Y, Wang HF, Tsitsilianos N, Shafiq U, Kwon JY, Lee HJ, Lee KW, Kim JK (2015) Transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 channel regulates diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance, and leptin resistance. FASEB J 29:3182–3192
Nakato J, Ho YY, Omae R, Mizushige T, Uchida K, Tominaga M, Kim M, Goto T, Takahashi N, Kawada T, Akiduki S, Kanamoto R, Ohinata K (2017) L-ornithine and L-lysine stimulate gastrointestinal motility via transient receptor potential vanilloid 1. Mol Nutr Food Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201700230
Nazıroğlu M (2011) TRPM2 cation channels, oxidative stress and neurological diseases: where are we now? Neurochem Res 36:355–366
Nazıroğlu M (2012) Molecular role of catalase on oxidative stress-induced ca(2+) signaling and TRP cation channel activation in nervous system. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 32:134–141
Nazıroğlu M (2015) TRPV1 channel: a potential drug target for treating epilepsy. Curr Neuropharmacol 13:239–247
Nazıroğlu M (2017) Activation of TRPM2 and TRPV1 channels in dorsal root ganglion by NADPH oxidase and protein kinase C molecular pathways: a patch clamp study. J Mol Neurosci 61:425–435
Nazıroğlu M, Braidy N (2017) Thermo-sensitive TRP channels: novel targets for treating chemotherapy-induced peripheral pain. Front Physiol 8:1040
Nazıroğlu M, Brandsch C (2006) Dietary hydrogenated soybean oil affects lipid and vitamin E metabolism in rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 52:83–88
Nazıroğlu M, Güler M, Özgül C, Saydam G, Küçükayaz M, Sözbir E (2014) Apple cider vinegar modulates serum lipid profile, erythrocyte, kidney, and liver membrane oxidative stress in ovariectomized mice fed high cholesterol. J Membr Biol 247:667–673
Okumi H, Tashima K, Matsumoto K, Namiki T, Terasawa K, Horie S (2012) Dietary agonists of TRPV1 inhibit gastric acid secretion in mice. Planta Med 78:1801–1806
Opalach K, Rangaraju S, Madorsky I, Leeuwenburgh C, Notterpek L (2010) Lifelong calorie restriction alleviates age-related oxidative damage in peripheral nerves. Rejuvenation Res 13:65–74
Placer ZA, Cushman L, Johnson BC (1966) Estimation of products of lipid peroxidation (malonyl dialdehyde) in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 16:359–364
Ristoiu V, Shibasaki K, Uchida K, Zhou Y, Ton BH, Flonta ML, Tominaga M (2011) Hypoxia-induced sensitization of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 involves activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and PKC. Pain 152:936–945
Rohm B, Riedel A, Ley JP, Widder S, Krammer GE, Somoza V (2015) Capsaicin, nonivamide and trans-pellitorine decrease free fatty acid uptake without TRPV1 activation and increase acetyl-coenzyme a synthetase activity in Caco-2 cells. Food Funct 6:173–185
Sedlak J, Lindsay RHC (1968) Estimation of total, protein bound and non-protein sulfhydryl groups in tissue with Ellmann' s reagent. Anal Biochem 25:192–205
Shimazu T, Hirschey MD, Newman J, He W, Shirakawa K, Le Moan N, Grueter CA, Lim H, Saunders LR, Stevens RD, Newgard CB, Farese RV Jr, de Cabo R, Ulrich S, Akassoglou K, Verdin E (2013) Suppression of oxidative stress by β-hydroxybutyrate, an endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitor. Science 339:211–214
Singh H, Kaur T, Manchanda S, Kaur G (2017) Intermittent fasting combined with supplementation with Ayurvedic herbs reduces anxiety in middle aged female rats by anti-inflammatory pathways. Biogerontology 18:601–614
Sohal RS, Forster MJ (2014) Caloric restriction and the aging process: a critique. Free Radic Biol Med 73:366–382
Suzuki J, Katoh N (1990) A simple and cheap method for measuring vitamin a in cattle using only a spectrophotometer. Jpn J Vet Sci 52:1282–1284
Uchida K, Dezaki K, Yoneshiro T, Watanabe T, Yamazaki J, Saito M, Yada T, Tominaga M, Iwasaki Y (2017) Involvement of thermosensitive TRP channels in energy metabolism. J Physiol Sci 67:549–560
Uguz AC, Cig B, Espino J, Bejarano I, Naziroglu M, Rodríguez AB, Pariente JA (2012) Melatonin potentiates chemotherapy-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in rat pancreatic tumor cells. J Pineal Res 53:91–98
Uslusoy F, Nazıroğlu M, Övey İS, Sönmez TT (2017) Hypericum perforatum L. supplementation protects sciatic nerve injury-induced apoptotic, inflammatory and oxidative damage to muscle, blood and brain in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12741
Vasconcelos LH, Souza IL, Pinheiro LS, Silva BA (2016) Ion channels in obesity: pathophysiology and potential therapeutic targets. Front Pharmacol 7:58
Ward MW, Rego AC, Frenguelli BG, Nicholls DG (2000) Mitochondrial membrane potential and glutamate excitotoxicity in cultured cerebellar granule cells. J Neurosci 20:7208–7219
Yoshimura M, Mikami T, Kuroda K, Nishida M, Ito K, Mondal A, Koyama K, Jogahara T, Sakata I, Sakai T (2016) Involvement of transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor 1, (TRPV1)-expressing vagal nerve in the inhibitory effect of gastric acidification on exogenous motilin induced gastric phase III contractions in Suncus murinus. Dig Dis Sci 16:1501–1511
Acknowledgements
The abstract of the study will be published in the 2nd International Brain Research School, 6-12 November 2017, Isparta, Turkey (http://www.cmos.org.tr/brs2017/en/). The study was supported by the Scientific Project Unit of Alanya Alaaddin Keykubat University (Protocol No: 2017-04-01-MAP01). All authors approved the final manuscript. There is no disclosure for the current study. MN and FG formulated the present hypothesis and were responsible for writing the report. HBŞ was responsible for animal experiments. BÇ was responsible for isolation of HIPPO and DRGN and analyses of intracellular Ca2+ concentration. The authors wish to thank Dr. Nady Braidy (School of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine, University of New South Wales, Randwick, Australia) and technician Fatih Şahin (Neuroscience Research Center, SDU, Isparta, Turkey) for helping with patch-clamp and polishing English, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None of the authors have any to disclose. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gültekin, F., Nazıroğlu, M., Savaş, H.B. et al. Calorie restriction protects against apoptosis, mitochondrial oxidative stress and increased calcium signaling through inhibition of TRPV1 channel in the hippocampus and dorsal root ganglion of rats. Metab Brain Dis 33, 1761–1774 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0289-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0289-0