Abstract
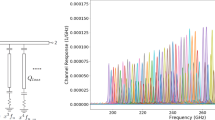
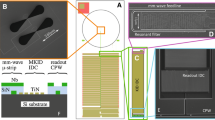
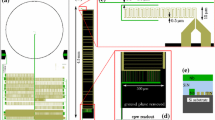
SuperSpec is a new technology for mm and sub-mm spectroscopy. It is an on-chip spectrometer being developed for multi-object, moderate-resolution (\(R\sim 300\)), large bandwidth survey spectroscopy of high-redshift galaxies for the 1 mm atmospheric window. This band accesses the CO ladder in the redshift range of \(z =\) 0–4 and the [CII] 158 \(\upmu \)m line from redshift \(z =\) 5–9. SuperSpec employs a novel architecture in which detectors are coupled to a series of resonant filters along a single microwave feedline instead of using dispersive optics. This construction allows for the creation of a full spectrometer occupying only \(\sim 10\,\hbox {cm}^2\) of silicon, a reduction in size of several orders of magnitude when compared to standard grating spectrometers. This small profile enables the production of future multi-beam spectroscopic instruments envisioned for the millimeter band to measure the redshifts of dusty galaxies efficiently. The SuperSpec collaboration is currently pushing toward the deployment of a SuperSpec demonstration instrument in fall of 2018. The progress with the latest SuperSpec prototype devices is presented; reporting increased responsivity via a reduced inductor volume (2.6 \(\upmu \hbox {m}^3\)) and the incorporation of a new broadband antenna. A detector NEP of 3–4 \(\times 10^{-18}\) W/Hz\(^{0.5}\) is obtained, sufficient for background-limited observation on mountaintop sites. In addition, beam maps and efficiency measurements of a new wide-band dual bow-tie slot antenna are shown.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Wheeler, S. Hailey-Dunsheath, E. Shirokoff, P.S. Barry, C.M. Bradford, S. Chapman, G. Che, J. Glenn, M. Hollister, A. Kovács, H.G. LeDuc, P. Mauskopf, R. McGeehan, C.M. McKenney, R. OBrient, S. Padin, T. Reck, C. Rosset, C. Shiu, C.E. Tucker, R. Williamson, J. Zmuidzinas, Proc. SPIE (2016). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2233798
S. Hailey-Dunsheath, E. Shirokoff, P.S. Barry, C.M. Bradford, S. Chapman, G. Che, J. Glenn, M. Hollister, A. Kovács, H.G. LeDuc, P. Mauskopf, C. McKenney, R. OBrient, S. Padin, T. Reck, C. Shiu, C.E. Tucker, J. Wheeler, R. Williamson, J. Zmuidzinas, J. Low Temp. Phys. 84, 180 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-015-1375-x
S. Hailey-Dunsheath, E. Shirokoff, P.S. Barry, C.M. Bradford, G. Chattopadhyay, P. Day, S. Doyle, M. Hollister, A. Kovács, H.G. LeDuc, P. Mauskopf, C.M. McKenney, R. Monroe, R. O’Brient, S. Padin, T. Reck, L. Swenson, C.E. Tucker, J. Zmuidzinas, Proc. SPIE (2014). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2057229
A. Kovács, P.S. Barry, C.M. Bradford, G. Chattopadhyay, P. Day, S. Doyle, S. Hailey-Dunsheath, M. Hollister, C. McKenney, H.G. LeDuc, N. Llombart, D.P. Marrone, P. Mauskopf, R.C. OBrient, S. Padin, L.J. Swenson, J. Zmuidzinas, Proc. SPIE 8452, 84522G84522G10 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.927160
E. Shirokoff, P.S. Barry, C.M. Bradford, G. Chattopadhyay, P. Day, S. Doyle, S. Hailey-Dunsheath, M.I. Hollister, A. Kovács, C. McKenney, H.G. Leduc, N. Llombart, D.P. Marrone, P. Mauskopf, R. O’Brient, S. Padin, T. Reck, L.J. Swenson, J. Zmuidzinas, Proc. SPIE (2012). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.927070
P.S. Barry, E. Shirokoff, A. Kovács, T.J. Reck, S. Hailey-Dunsheath, C.M. McKenney, L.J. Swenson, M.I. Hollister, H.G. Leduc, S. Doyle, R. O’Brient, N. Llombart, D. Marrone, G. Chattopadhyay, P.K. Day, S. Padin, C.M. Bradford, P.D. Mauskopf, J. Zmuidzinas, Proc. SPIE (2012). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.927089
A.T. Crites, J.J. Bock, C.M. Bradford, T.C. Chang, A.R. Cooray, L. Duband, Y. Gong, S. Hailey-Dunsheath, J. Hunacek, P.M. Koch, C.T. Li, R.C. O’Brient, T. Prouve, E. Shirokoff, M.B. Silva, Z. Staniszewski, B. Uzgil, M. Zemcov, Proc. SPIE (2014). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2057207
R. McGeehan, Noise performance of SuperSpec: an on-chip, TiN KID based mm-wave spectrometer. J. Low Temp. Phys. This Special Issue LTD17 (2018) (under review)
J. Zmuidzinas, Annu. Rev. Condens. Matter Phys. 3(1), 169–214 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-conmatphys-020911-125022
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by NASA Space Technology Research Fellowship NSTRF NNX15AQ09H and NSF AST ATI Grant 1407457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wheeler, J., Hailey-Dunsheath, S., Shirokoff, E. et al. SuperSpec, The On-Chip Spectrometer: Improved NEP and Antenna Performance. J Low Temp Phys 193, 408–414 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-018-1926-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10909-018-1926-z