Abstract
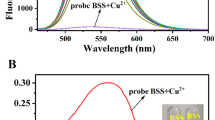
A novel D-π-A type fluorescent probe L(NO3) for Cu (II) sensing was designed and fully characterized. The probe consists of a styryl-pyridine cation fluorescent group and a di-(2-picolyl)amine (DPA) receptor unit, which are linked by a phenyl group to form an electron donor-π-acceptor (D-π-A) conjugate system, especially the introduction of a nitrate counter anion for significantly enhanced water solubility of the probe. Fluorescence titration studies of the probe L(NO3) showed a higher selectivity for Cu2+ than other metal ions, and the emission spectrum was strongly quenched upon binding. The competitive binding assay and the low detection limit (0.932 µM) showed that the probe L(NO3) had strong anti-interference ability and excellent Cu2+ detection performance. The binding ratio of probe L(NO3) and Cu2+ was determined from Job’s plot to be 1:1, which is consistent with the results obtained from X-ray crystal structures. Meanwhile, the probe showed instantaneous chemical reversibility when titrated with EDTA solution, indicating potential recycling properties of the probe. In addition, the design of inexpensive fluorescent test strips can perform the on-site and real-time detection Cu2+ with a color recognition application.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Chen J, Chen H, Wang T, Li J, Wang J, Lu X (2019) Copper ion fluorescent probe based on Zr-MOFs composite material. Anal Chem 91(7):4331–4336. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b03924
Wang Y, Chen T, Zhang Z, Ni Y (2018) Cytidine-stabilized copper nanoclusters as a fluorescent probe for sensing of copper ions and hemin. RSC Adv 8(17):9057–9062. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra11383h
Chen J, Jiang Y, Shi H, Peng Y, Fan X, Li C (2020) The molecular mechanisms of copper metabolism and its roles in human diseases. Pflugers Arch 472(10):1415–1429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02412-2
Crisponi G, Nurchi VM, Fanni D, Gerosa C, Nemolato S, Faa G (2010) Copper-related diseases: from chemistry to molecular pathology. Coord Chem Rev 254(7–8):876–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.018
Gauthier L, Charbonnier P, Chevallet M, Delangle P, Texier I, Gateau C, Deniaud A (2021) Development, formulation, and cellular mechanism of a lipophilic copper chelator for the treatment of Wilson’s disease. Int J Pharm 609:121193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121193
Zhou Z, Chen S, Huang Y, Gu B, Li J, Wu C, Yin P, Zhang Y, Li H (2022) Simultaneous visualization and quantification of copper (II) ions in Alzheimer’s disease by a near-infrared fluorescence probe. Biosens Bioelectron 198:113858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113858
Bisaglia M, Bubacco L (2020) Copper ions and Parkinson’s Disease. Why is homeostasis so relevant? Biomolecules 10(2):195–207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020195
Horn N, Wittung Stafshede P (2021) ATP7A-Regulated enzyme metalation and trafficking in the Menkes Disease Puzzle. Biomedicines 9(4):391–428. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9040391
Sanchez Lopez C, Rossetti G, Quintanar L, Carloni P (2018) Structural determinants of the prion protein N-Terminus and its adducts with copper ions. Int J Mol Sci 20(1):18–32. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010018
Jung HS, Kwon PS, Lee JW, Kim JI, Hong CS, Kim JW, Yan S, Lee JY, Lee JH, Joo T, Kim JS (2009) Coumarin-derived Cu2+-selective fluorescence sensor: synthesis, mechanisms, and applications in living cells. J Am Chem Soc 131(5):2008–2012. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja808611d
Jin X, Ma X, Zhong W, Cao Y, Zhao H, Leng X, Yang J, Zhou H, She M (2021) Fluorescent sensing film decorated with ratiometric probe for visual and recyclable monitoring of Cu2+. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 249:119217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.119217
Gerdan Z, Saylan Y, Ugur M, Denizli A (2022) Ion-imprinted polymer-on-a-Sensor for copper detection. Biosens (Basel) 12(2):91–102. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020091
Xu Z, Meng Q, Cao Q, Xiao Y, Liu H, Han G, Wei S, Yan J, Wu L (2020) Selective sensing of copper ions by mesoporous porphyrinic metal-organic framework nanoovals. Anal Chem 92(2):2201–2206. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04900
Liu Y, Liang P, Guo L (2005) Nanometer titanium dioxide immobilized on silica gel as sorbent for preconcentration of metal ions prior to their determination by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Talanta 68(1):25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.04.035
Soylak M, Narin I, Dogan M (1997) Trace enrichment and atomic absorption spectrometric determination of lead, copper, cadmium and nickel in drinking water samples by use of an activated carbon column. Anal Lett 30(15):2801–2810. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719708001823
Bobrowski A, Nowak K, Zarębski J (2005) Application of a bismuth film electrode to the voltammetric determination of trace iron using a Fe(III)–TEA–BrO3 – catalytic system. Anal Bioanal Chem 382(7):1691–1697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-3313-2
Ali A, Shen H, Yin X (1998) Simultaneous determination of trace amounts of nickel, copper and mercury by liquid chromatography coupled with flow-injection on-line derivatization and preconcentration. Anal Chim Acta 369(3):215–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(98)00252-9
Wang Y, Wu H, Wu WN, Li SJ, Xu ZH, Xu ZQ, Fan YC, Zhao XL, Liu BZ (2018) An AIRE active Schiff base bearing coumarin and pyrrole unit: Cu2+ detection in either solution or aggregation states. Sens Actuators B 260:106–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.201
Moro AJ, Santos M, Outis M, Mateus P, Pereira PM (2020) Selective coordination of Cu2+ and subsequent anion detection based on a naphthalimide-triazine-(DPA)2 chemosensor. Biosens (Basel) 10(9):129–139. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios10090129
Goel A, Tomer N, Ghule VD, Malhotra R (2021) A multi-responsive pyranone based Schiff base for the selective, sensitive and competent recognition of copper metal ions. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 249:119221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2020.119221
Wang S, Wang Z, Yin Y, Luo J, Kong L (2017) Coumarin-naphthol conjugated Schiff base as a “turn-on” fluorescent probe for Cu2+ via selective hydrolysis of imine and its application in live cell imaging. J Photochem Photobiol A 333:213–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2016.10.030
Jiao Y, Zhou L, He H, Yin J, Gao Q, Wei J, Duan C, Peng X (2018) A novel rhodamine B-based “off-on’’ fluorescent sensor for selective recognition of copper (II) ions. Talanta 184:143–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.01.073
Huang Q, Chen YT, Ren YW, Wang ZY, Zhu YX, Zhang Y (2018) A rapid and naked-eye visible rhodamine 6G-based chemosensor for sensitive detection of copper(ii) ions in aqueous solution. Anal Methods 10(47):5731–5737. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8ay02019a
Jiao Y, Liu X, Zhou L, He H, Zhou P, Duan C, Peng X (2018) A fluorescein derivative-based fluorescent sensor for selective recognition of copper(II) ions. J Photochem Photobiol A 355:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2017.10.058
Ranee SJ, Sivaraman G, Pushpalatha AM, Muthusubramanian S (2018) Quinoline based sensors for bivalent copper ions in living cells. Sens Actuators B 255:630–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.111
Jeong Y, Yoon J (2012) Recent progress on fluorescent chemosensors for metal ions. Inorg Chim Acta 381:2–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ica.2011.09.011
Chen X, Pradhan T, Wang F, Kim JS, Yoon J (2012) Fluorescent chemosensors based on spiroring-opening of xanthenes and related derivatives. Chem Rev 112(3):1910–1956. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200201z
Shen Y, Zheng W, Yao Y, Wang D, Lv G, Li C (2020) Phenoxazine-based near-infrared fluorescent probes for the specific detection of copper (II) ions in living cells. Chem Asian J 15(18):2864–2867. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.202000783
Aydin Z, Yan B, Wei Y, Guo M (2020) A novel near-infrared turn-on and ratiometric fluorescent probe capable of copper(ii) ion determination in living cells. Chem Commun (Camb) 56(45):6043–6046. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cc01481h
Zhu MQ, Gu Z, Zhang R, Xiang JN, Nie S (2010) A stilbene-based fluoroionophore for copper ion sensing in both reduced and oxidized environments. Talanta 81(1–2):678–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2010.01.002
Huang X, Guo Z, Zhu W, Xie Y, Tian H (2008) A colorimetric and fluorescent turn-on sensor for pyrophosphate anion based on a dicyanomethylene-4H-chromene framework. Chem Commun (Camb) 41:5143–5145. https://doi.org/10.1039/b809983a
Duan Y, Liu Y, Han H, Zhang X, Zhang M, Liao Y, Han T (2021) A donor-pi-acceptor aggregation-induced emission compound serving as a portable fluorescent sensor for detection and differentiation of methanol and ethanol in the gas phase. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 252:119515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.119515
Yang JS, Lin YD, Chang YH, Wang SS (2005) Synthesis, dual fluorescence, and fluoroionophoric behavior of dipyridylaminomethylstilbenes. J Org Chem 70(15):6066–6073. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo0509049
Arora A, Kaushal J, Kumar A, Kumar P, Kumar S (2019) Ruthenium(II)-Polypyridyl‐based sensor bearing a DPA unit for selective detection of Cu(II) ion in aqueous medium. ChemistrySelect 4(20):6140–6147. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201900682
Chang MJ, Lee MH (2018) A highly selective dual-channel fluorescent probe for the detection of Zn2+ ion and pyrophosphate in micelle. Dyes Pigm 149:915–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2017.11.057
Liu Z, Hao F, Xu H, Wang H, Wu J, Tian Y (2015) A-π-D-π-A pyridinium salts: synthesis, crystal structures, two-photon absorption properties and application to biological imaging. CrystEngComm 17(29):5562–5568. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ce00816f
Pirovano V, Marchetti M, Carbonaro J, Brambilla E, Rossi E, Ronda L, Abbiati G (2020) Synthesis and photophysical properties of isocoumarin-based D-π-A systems. Dyes Pigm 173:107917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.107917
Wu S, Wei YJ, Wang YB, Su Q, Wu L, Zhang H, Yin FP, Yuan PL (2014) Ratiometric and selective two-photon fluorescent probe based on PET-ICT for imaging Zn2+ in living cells and tissues. Chin Chem Lett 25(1):93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2013.10.005
Kumari N, Jha S, Misra SK, Bhattacharya S (2014) A probe for the selective and parts-per-billion-level detection of copper(II) and mercury(II) using a micellar medium and its utility in cell imaging. ChemPlusChem 79(7):1059–1064. https://doi.org/10.1002/cplu.201402016
Hao F, Zhang X, Tian Y, Zhou H, Li L, Wu J, Zhang S, Yang J, Jin B, Tao X, Zhou G, Jiang M (2009) Design, crystal structures and enhanced frequency-upconverted lasing efficiencies of a new series of dyes from hybrid of inorganic polymers and organic chromophores. J Mater Chem 19(48):9163–9169. https://doi.org/10.1039/b914656c
Dolomanov OV, Bourhis LJ, Gildea RJ, Howard JAK, Puschmann H (2009) OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J Appl Crystallogr 42(2):339–341. https://doi.org/10.1107/s0021889808042726
Sheldrick GM (2008) A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr A 64(Pt 1):112–122. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0108767307043930
Wu H, Chen Y, Ling X, Yuan W, Li B, Zhou Z (2021) A novel D-π-A molecule as ICT type fluorescent probe for endogenous hypochlorite imaging in living cells and zebrafishes. J Mol Liq 329:115465–115471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115465
Glover SD, Tommos C (2019) A quick and colorful method to measure low-level contaminations of paramagnetic Ni2+ in protein samples purified by immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography. Methods Enzymol 614:87–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mie.2018.08.037
Tiwari K, Kumar S, Kumar V, Kaur J, Arora S, Mahajan RK (2018) An azine based sensor for selective detection of Cu2+ ions and its copper complex for sensing of phosphate ions in physiological conditions and in living cells. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 191:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2017.09.072
Wang M, Niu X, Cao R, Zhang M, Xu H, Hao F, Liu Z (2022) An IMPLICATION-logic-based fluorescent probe for sequential detection of Cu2+ and phosphates in living cells. New J Chem 46(5):2232–2238. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1nj04992e
Shi F, Cui S, Liu H, Pu S (2020) A high selective fluorescent sensor for Cu2+ in solution and test paper strips. Dyes Pigm 173:107914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.107914
Yang XB, Yang BX, Ge JF, Xu YJ, Xu QF, Liang J, Lu J-M (2011) Benzo[a]phenoxazinium-based red-emitting chemosensor for zinc ions in biological media. Org Lett 13(10):2710–2713. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol2008022
Hu Y, Ke Q, Yan C, Xu CH, Huang XH, Hu S (2016) A new fluorescence chemosensor for selective detection of copper ion in aqueous solution. Tetrahedron Lett 57(21):2239–2243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2016.04.025
Anto PL, Anto RJ, Varghese HT, Panicker CY, Philip D, Andrade GFS, Brolo AG (2011) Spectroscopic investigations and computational study of sulfur trioxide-pyridine complex. J Raman Spectrosc 42(9):1812–1819. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2928
Shu W, Kaijun Z, Wei H, Jinming W, Zefeng Z, Qingshan L (2018) Qualitative identification of nitrate nitrogen in compound fertilizers by infrared spectroscopy. Integr Ferroelectr 188(1):18–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2018.1454755
Yang JS, Lin YD, Lin YH, Liao FL (2004) Zn(II)-induced ground-state π-deconjugation and excited-state electron transfer in N,N-Bis(2-pyridyl)amino-substituted arenes. J Org Chem 69(10):3517–3525. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo049902z
Yang JS, Lin YH, Yang CS (2002) Palladium-catalyzed synthesis of trans-4-(N,N-Bis(2-pyridyl)amino)stilbene. A new intrinsic fluoroionophore for transition metal ions. Org Lett 4(5):777–780. https://doi.org/10.1021/ol017260l
Xu Z, Pan J, Spring DR, Cui J, Yoon J (2010) Ratiometric fluorescent and colorimetric sensors for Cu2+ based on 4,5-disubstituted-1,8-naphthalimide and sensing cyanide via Cu2+ displacement approach. Tetrahedron 66(9):1678–1683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2010.01.008
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Higher Education Institutions in Anhui province (2022AH051314, KJ2021ZD0075, KJ2020A0541), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21701025), Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province (1908085MB44), the Natural Science Foundation of Fuyang Normal College (2019KYQD0019), the Training Programs of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates (S202110371026, S202110371028). The authors are also thankful to Engineering Research Centre of Biomass Conversion and Pollution Prevention Control of Anhui Provincial Department of Education, and the Anhui Province Key Laboratory for Degradation and Monitoring of Pollution of the Environment.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Rui Cao: Data curation, Writing-original draft. Mengyu Zhang: Software, Validation. Wen Tang and Meixiang Wang: Software, Investigation. Jing Wu and Xiaoxiao Niu: Validation. Zhaodi Liu: Conceptualization, Supervision. Fuying Hao: Writing-review & editing. Huajie Xu: Conceptualization, Methodology.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 758 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, R., Zhang, M., Tang, W. et al. A Novel D-π-A Type Fluorescent Probe for Cu2+ Based on Styryl-Pyridinium Salts Conjugating Di-(2-picolyl)amine (DPA) Units. J Fluoresc 33, 1565–1576 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03151-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-023-03151-0