Abstract
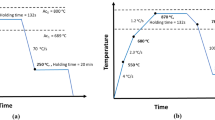
The effect of aging temperature on martensite reversion and mechanical behavior of a 2304-lean duplex stainless steel (LDSS) was analyzed after cold rolling to 74% reduction and aging at 400–600 °C for 1800 s. Strain-induced martensite (SIM) formation results from cold rolling. After cold rolling, the results revealed a Nishiyama–Wasser (N–W) relationship between the ∝ '-martensite laths and the metastable austenite. Increasing the aging temperature led to a rise in the steel strength, resulting in very low ductility, but with high yield and tensile strength of the specimens. The SIM reversion started between 500 and 550 °C for 1800 s soaking time. At temperatures between 400 and 500 °C, substantial embrittlement occurred. Precipitation of the ∝ + ∝ ′ (spinodal decomposition) in solid solution in ferrite was not observed. Hence, it is not the cause of the steel embrittlement. The mechanisms involved in the increase of strength and embrittlement were the aging of the austenite phase due to the formation of a substructure with ultrafine or nano-deformation twins, stacking faults, and shear bands in a lamellar array, and possibly Suzuki effect mechanism occurrence.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also form part of an ongoing study.
References
Schweitzer PA (2003) Metallic materials: physical, mechanical, and corrosion properties. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York, p 710
Mesquita TJ, Chauveau E, Mantel M, Kinsman N, Roche V, Nogueira RP (2012) Lean duplex stainless steels. The role of molybdenum in pitting corrosion of concrete reinforcement studied with industrial and laboratory castings. Mater Chem Phys 132:967–972
Breda M, Pezzato L, Pizzo M, Calliari I (2014) Effect of cold rolling on pitting resistance in duplex stainless steels. La Metall Ital 6:15–19
Guo Y, Hu J, Li J, Jiang L, Liu T, Wu Y (2014) Effect of annealing temperature on the mechanical and corrosion behavior of a newly developed novel lean duplex stainless steel. Materials 7:6604–6619
Gunn RN (1997) Duplex stainless steels: microstructure, properties, and applications. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, 219 pp
Zhang Z, Han D, Jiang Y, Shi C, Li J (2012) Microstructural evolution and pitting resistance of annealed lean duplex stainless steel UNS S32304. Nucl Eng Des 243:56–62
Zhang L, Zhang W, Jiang Y, Deng B, Sun D, Li J (2009) Influence of annealing treatment on the corrosion resistance of lean duplex stainless steel 2101. Electrochem Acta 54:5387–5392
G. Krauss (2015) Steels: processing, structure, and performance. ASM Int., Ohio, 715 pp
Jinlong L, Tongxiang L, Chen W, Limin D (2016) Effect of ultrafine grain on tensile behaviour and corrosion resistance of the duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng C 62:558–563
Jiménez JA, Frommeyer G, Carsí M, Ruano OA (2001) Superplastic properties of a δ/γ stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A 307:134–142
Bhadak B, Zaid M, Bhattacharjee PP (2014) Effect of warm rolling on the evolution of microstructure, microtexture and mechanical properties of commercial grade duplex steel. Proc Mater Sci 5:855–862
C.L. Beech (1989) Effect of temperature and strain rate on the mechanical properties and deformation behavior of a duplex stainless steel, M.S. Thesis, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, CO, pp. 158
Maria GGB, Dias CAD, Rodrigues DG, Santos DB (2018) Strain-induced martensite and reverse transformation in 2304 lean duplex stainless steel and its influence on mechanical behavior. Steel Res Int 90(3):1800437
Ran Q, Xu Y, Li J, Wan J, Xiao X, Yu H et al (2014) Effect of heat treatment on transformation-induced plasticity of economical Cr19 duplex stainless steel. Mater Des 56:959–965
Saenarjhan N, Kang J-H, Lee SC, Kim S-J (2017) Influence of annealing temperature on deformation behavior of 329LA lean duplex stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A 679:531–537
Yen HW, Ooi SW, Eizadjou M, Breen A, Huang CY, Bhadeshia HK et al (2015) Role of stress-assisted martensite in the design of strong ultrafine-grained duplex steels. Acta Mater 82:100–114
Gauzzi F, Montanari R, Principi G, Tata ME (2006) AISI, 304 steel: anomalous evolution of martensitic phase following heat treatments at 400 °C. Mater Sci Eng A 438–440:202–206
Mangonon PL, Thomas G (1970) Structure and properties of thermal-mechanically treated 304 stainless. Metall Trans 1:1587–1594
Chukhleb AN, Martynov VP (1960) Change in the phase composition of steels of type 18–8 in dependence on the temperature and the degree of deformation. Met Sci Heat Treat 1:43–45
Mukhopadhyay CK, Jayakumar T, Kasiviswanathan KV, Raj B (1995) Study of aging-induced ∝′-martensite formation in cold worked AISI, type 304 stainless steel using an acoustic emission technique. J Mater Sci 30:4556–4560
Rathbun RW, Matlock DK, Speer JG (2000) Strain aging behavior of austenitic stainless steels containing strain-induced martensite. Scr Mater 42:887–891
Fujita M, Kaneko Y, Nohara A, Saka H, Zauter R, Mughrabi H (1994) Temperature dependence of the dissociation width of dislocations in a commercial 304L stainless steel. ISIJ Int 34:697–703
Vignal V, Zhang H, Delrue O, Heintz O, Popa I, Peultier J (2011) Influence of long-term aging in solution containing chloride ions on the passivity and the corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steels. Corros Sci 53:894–903
Keichel J, Foct J, Gottstein G (2003) Deformation and annealing behavior of nitrogen alloyed duplex stainless steels. Part II Annealing ISIJ Int 43:1788–1794
Reick W, Pohl M, Padilha AF (1998) Recrystallization-transformation combined reactions during annealing of a cold rolled ferritic-austenitic duplex stainless steel. ISIJ Int 38:567–571
Breda M, Brunelli K, Grazzi F, Scherillo A, Calliari I (2015) Effects of cold rolling and strain-induced martensite formation in a SAF 2205 duplex stainless steel. Metall Mater Trans A 46:577–586
Moallemi M, Zarei-Hanzaki A, Baghbadorani HS (2017) Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties in a cold deformed nitrogen bearing TRIP-assisted duplex stainless steel after reversion annealing. Mater Sci Eng A 683:83–89
Tomimura K, Takaki T, Tokunaga Y (1991) Reversion austenite mechanism from deformation induced martensite in metastable austenitic stainless steels. ISIJ Int 31:1431–1437
Tavares SS, Pardal JM, Silva MR, de Oliveira CA (2014) Martensitic transformation induced by cold deformation of lean duplex stainless steel UNS S32304. Mater Res 17:381–385
Sandim MJR, Souza Filho IR, Mota CFGS, Zilnyk KD, Sandim HRZ (2021) Microstructural and magnetic characterization of a lean duplex steel: strain-induced martensite formation and austenite reversion. J Mag Magn Mater 517:167–370
Kurc-Lisiecka A, Ozgowicz W, Ratuszek W, Chruściel K (2012) Texture and structure evolution during cold rolling of austenitic stainless steel. J Achiev Mater Manuf Eng 52:22–30
Somani MC, Juntunen P, Karjalainen LP, Misra RDK, Kyröläinen A (2009) Enhanced mechanical properties through reversion in metastable austenitic stainless steels. Metall Mater Trans A 40:729–744
Järvenpää A, Jaskari M, Kisko A, Karjalainen P (2020) Processing and properties of reversion-treated austenitic stainless steels. Metals 10(281):1–43
Panov D, Kudryavtsev E, Chernichenko R, Smirnov A, Stepanov N, Simonov Y et al (2021) Mechanisms of the reverse martensite-to-austenite transformation in a metastable austenitic stainless steel. Metals 11:1–13
Takaki S, Tomimura K, Ueda S (1994) Effect of pre-cold-working on diffusional reversion of deformation induced martensitic in metastable austenitic stainless steel. ISIJ Int 34:522–527
Malta PO, Dias FL, de Souza ACM, Santos DB (2018) Microstructure and texture evolution of duplex stainless steels with different molybdenum contents. Mater Charact 142:406–421
Humphreys FJ, Hatherly M (1995) Recrystallisation and related annealing phenomena. Pergamom, Oxford
Belyakov A, Kimura Y, Tsuzaki K (2006) Microstructure evolution in dual-phase stainless steel during severe deformation. Acta Mater 54:2521–2532
Guo Y, Hu J, Li J, Jiang L, Liu T, Wu Y (2014) Effect of annealing temperature on the mechanical and corrosion behavior of a newly developed novel lean duplex stainless steel. Mater 7:6604–6619
Mahajan S, Pande CS, Imam MA, Rath BB (1997) Formation of annealing twins in f.c.c. crystals. Acta Mater. 45:2633–2638
Fargas G, Akdut N, Anglada M, Mateo A (2008) Microstructural evolution during industrial rolling of a duplex stainless steel. ISIJ Int 48:1596–1602
Duprez L, De Cooman BC, Akdut N (2002) Deformation behaviour of duplex stainless steel during industrial hot rolling. Steel Res Int 73:531–538
Zhang W, Hu J (2013) Effect of annealing temperature on transformation induced plasticity effect of a lean duplex stainless steel. Mater Charact 79:37–42
Martin S, Wolf S, Martin U, Krüger L, Rafaja D (2016) Deformation mechanisms in austenitic TRIP/TWIP steel as a function of temperature. Metall Mater Trans A 47:49–58
Singh J (1985) Influence of deformation on the transformation of austenitic stainless steels. J Mater Sci 20:3157–3166
Chiba A, Kim MS (2001) Suzuki segregation and dislocation locking in supersaturated Co–Ni-based alloy. Mater Trans 42:2112–7
Jeong SW, Kang UG, Choi JY, Nam WJ (2012) Comparative study of hardening mechanisms during aging of a 304 stainless steel containing ∝′-martensite. J Mater Eng Perform 21:1937–1942
Miura H, Kobayashi KM, Todaka Y, Watanabe C, Aoyagi Y, Sugiura N (2017) Heterogeneous nanostructure developed in heavily cold-rolled stainless steels and the specific mechanical properties. Scr Mater 133:33–36
Yan FK, Tao NR, Archie F, Gutierrez-Urrutia I, Raabe D, Lu K (2014) Deformation mechanisms in an austenitic single-phase duplex microstructured steel with nano-twinned grains. Acta Mater 81:487–500
Pramanik S, Bera S, Ghosh SK (2014) Influence of cold rolling on microstructural evolution in 2205 duplex stainless steel. Steel Res Int 85(5):776–783
Sokura LA, Nevedomskiy VN, Bert NA (2018) The features of Moiré pattern on electron-microscope images of free-standing quantum dots containing dislocations. IOP Conf Ser J Phys Conf Ser 1124:022028
Misra RDK, Nayak S, Mali SA, Shah JS, Somani MC, Karjalainen LP (2009) Microstructure and deformation behavior of phase-reversion-induced nanograined/ultrafine-grained austenitic stainless steel. Metall Mater Trans A 40A:2498–2509
Lee SH, Choi JY, Nam WJ (2009) Hardening behavior of a 304 stainless steel containing deformation-induced martensite during static strain aging. Mater Trans 50:926–929
Guy KB, Butler EP, West DRF (1983) Reversion of bcc ∝′ martensite in Fe–Cr–Ni austenitic stainless steels. Metal Sci 17:167–176
Mota CFGS, Aota LS, Sandim HRZ, Zilnyk KD, Sandim MJR (2023) Austenite reversion in lean duplex steel: microstructural, dilatometric and magnetic characterization. Mater Charac 195(112509):1–12
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to FAPEMIG, CAPES-PROEX, and CNPq for the research fellowships made available to students and for their financial support. Thanks to UFMG Microscopy Center and CIT SENAI for providing excellent scientific support. We also thank Aperam South America company for the samples supply.
Funding
The funding was provided by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, 403570/2021-2, Dagoberto Brandão Santos.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Catalin Croitoru.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Assumpção, R.F., Santos, R.M., de Sousa, M.L.O. et al. Effect of low aging temperature and the reversion of martensite on the mechanical behavior of a 2304 lean duplex stainless steel. J Mater Sci 58, 5970–5988 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08401-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-023-08401-x