Abstract
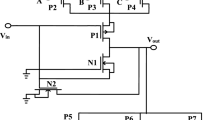
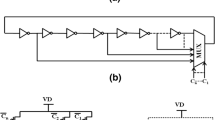
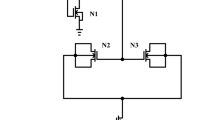
This paper presents a three-bit digital controlled oscillator (DCO) with three-stage ring topology. The proposed DCO circuit has been realized in TSMC 0.18-μm CMOS technology. DCO circuit has been designed with NAND gate based inverter delay cell for low power consumption and a digitally controlled load element is added at the output node of inverter to control the tuning range of proposed DCO circuit. Load element of DCO circuit has been implemented using three IMOS varactors to provide a better frequency tuning capability at low supply voltage (Vdd). The digital control bit varies the driving current across the load element that causes to change the oscillation frequency of proposed DCO. A tunable range of frequency from 0.818 to 0.872 GHz has been obtained with different combination of digital control bit with Vdd of 1.8 V. Effect of Vdd variations has also been observed. For control bits CBA = ‘000’ the proposed DCO operates from 0.711 to 1.278 GHz with Vdd variations from 1.6 to 3 V. Further, at control bits CBA = ‘111’, DCO oscillates form 0.755 to 1.296 GHz with Vdd variation. The proposed DCO shows a phase noise of − 101.24 dBc/Hz at an offset of 1 MHz from carrier frequency with 0.248 mW power consumption at 0.872 GHz operating frequency. Figure of merit for the proposed DCO circuit is 166.10 dBc/Hz.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hwang, I., Lee, S., Lee, S., & Kim, S. (2000). A digitally controlled phase-locked loop with fast locking scheme for clock synthesis application. In IEEE solid-state circuits conference digest of technical papers (ISSCC) (pp. 168–169).
Boerstler, D. W. (1999). A low-jitter PLL clock generator for microprocessors with lock range of 340-612 MHz. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 34(4), 513–519.
Teh, Y. K., Mohd-Yasin, F., Choong, F., Reaz, M. I., & Kordesch, A. V. (2009). Design and analysis of UHF micropower CMOS DTMOST rectifiers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 56(2), 122–126.
Catli, B., & Hella, M. M. (2008). A 0.5-V 3.6/5.2 GHz CMOS multi-band LC VCO for ultra low-voltage wireless applications. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (pp. 996–999).
Chen, Y. J., & du Plessis, M. (2006). An integrated 0.35 μm CMOS optical receiver with clock and data recovery circuit. Microelectronics Journal, 37(9), 985–992.
De Paula, L. S., Susin, A. A., & Bampi, S. (2008). A wide band CMOS differential voltage-controlled ring oscillator. In Proceedings of the 21st annual symposium on Integrated circuits and system design (pp. 85–89).
Fong, N. H., Plouchart, J. O., Zamdmer, N., Liu, D., Wagner, L. F., Plett, C., et al. (2003). Design of wide-band CMOS VCO for multiband wireless LAN applications. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(8), 1333–1342.
Luo, Y., Ma, C., Gan, Y., Qian, M., & Ye, T. (2015). A dual-band CMOS LC-VCO with highly linear frequency tuning characteristics. Microelectronics Journal, 46(12), 1420–1425.
Samori, C., Levantino, S., & Boccuzzi, V. (2001). A-94 dBc/Hz@ 100 kHz, fully-integrated, 5-GHz, CMOS VCO with 18% tuning range for Bluetooth applications. In IEEE Conference on Custom Integrated Circuits (pp. 201–204).
Maget, J., Tiebout, M., & Kraus, R. (2002). Influence of novel MOS varactors on the performance of a fully integrated UMTS VCO in standard 0.25-µm CMOS technology. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37(7), 953–958.
Chung, C. C., & Lee, C. Y. (2003). An all-digital phase-locked loop for high-speed clock generation. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(2), 347–351.
Staszewski, R. B., & Balsara, P. T. (2005). Phase-domain all-digital phase-locked loop. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 52(3), 159–163.
Raha, P., Randall, S., Jennings, R., Helmick, B., Amerasekera, A., & Haroun, B. (2002).A robust digital delay line architecture in a 0.13-µm CMOS technology node for reduced design and process sensitivities. In IEEE international symposium on quality electronic design (pp. 148–153).
Zhao, J., & Kim, Y. B. (2008). A 12-bit digitally controlled oscillator with low power consumption. In IEEE midwest symposium on circuits and systems (pp. 370–373).
Staszewski, R. B., Muhammad, K., Leipold, D., Hung, C. M., Ho, Y. C., Wallberg, J. L., et al. (2004). All-digital TX frequency synthesizer and discrete-time receiver for Bluetooth radio in 130-nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 39(12), 2278–2291.
Muhammad, K., Ho, Y. C., Mayhugh, T. L., Hung, C. M., Jung, T., Elahi, I., et al. (2006). The first fully integrated quad-band GSM/GPRS receiver in a 90-nm digital CMOS process. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41(8), 1772–1783.
Ahrens, T. I., Hajimiri, A., & Lee, T. H. (1997). A 1.6 GHz 0.5 mW CMOS LC low phase noise VCO using bond wire inductance. In 1st International workshop design of mixed-mode integrated circuits and applications (pp. 69–71).
Kral, A., Behbahani, F., &Abidi, A. A. (1998). RF-CMOS oscillators with switched tuning. In IEEE custom integrated circuits conference (pp. 555–558).
Ahrens, T. I., & Lee, T. H. (1998). A 1.4-GHz 3-mW CMOS LC low phase noise VCO using tapped bond wire inductances. In IEEE international symposium on low power electronics and design (pp. 16–19).
Andreani, P., & Mattisson, S. (2000). On the use of MOS varactors in RF VCOs. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 35(6), 905–910.
Kumar, M., Arya, S., & Pandey, S. (2015). Ring VCO design with variable capacitance XNOR delay cell. Journal of the Institution of Engineers (India): Series B, 96(4), 371–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-014-0154-4.
Panigrahi JK, & Acharya DP (2010). Performance analysis and design of wideband CMOS voltage controlled ring oscillator. In 5th IEEE international conference on industrial and information systems (pp. 234–238).
Chen, Z. Z., & Lee, T. C. (2011). The design and analysis of dual-delay-path ring oscillators. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 58(3), 470–478.
Xuemei, L., Zhigong, W., & Lianfeng, S. (2013). Design and analysis of a three-stage voltage-controlled ring oscillator. Journal of Semiconductors, 34(11), 115003.
Lee, S. Y., & Hsieh, J. Y. (2008). Analysis and implementation of a 0.9-V voltage-controlled oscillator with low phase noise and low power dissipation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 55(7), 624–627.
Tomar, A., Pokharel, R. K., Nizhnik, O., Kanaya, H., & Yoshida, K. (2007). Design of 1.1 GHz highly linear digitally-controlled ring oscillator with wide tuning range. In IEEE international workshop on radio-frequency integration technology (pp. 82–85).
Staszewski, R. B., Hung, C. M., Barton, N., Lee, M. C., & Leipold, D. (2005). Adigitally controlled oscillator in a 90-nm digital CMOS process for mobile phones. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40(11), 2203–2211.
Pokharel, R. K., Uchida, K., Tomar, A., Kanaya, H., & Yoshida, K. (2009). Low phase noise 10 bit 5 GHz DCO using on-chip CPW resonator in 0.18 µm CMOS technology. In IEEE 1st Asian Himalayas international conference on internet (pp. 1–4).
Hajimiri, A., Limotyrakis, S., & Lee, T. H. (1998). Phase noise in multi-gigahertz CMOS ring oscillators. In IEEE Proceedings of custom integrated circuits conference (pp. 49–52).
Grozing, M., Phillip, B., & Berroth, M. (2003). CMOS ring oscillator with quadrature outputs and 100 MHz to 3.5 GHz tuning range. In IEEE Proceedings of solid-state circuits conference (pp. 679–682).
Pokharel, R. K., Tomar, A., Kanaya, H., & Yoshida, K. (2008). Design of highly linear, 1 GHz 8-bit digitally controlled ring oscillator with wide tuning range in 0.18-um CMOS process. Microwave Conference, 2008, 623–626.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, D., Kumar, M. Design of a 3-bit digital control oscillator (DCO) using IMOS varactor tuning. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 100, 613–620 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01506-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-019-01506-x