Abstract
Introduction
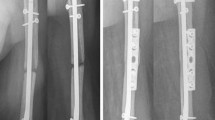
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the results achieved after the use of lateral minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in oligotrophic humerus nonunions resulting from failed intramedullary nailing (IM).
Method
We evaluated nine patients with humerus nonunion after failed locked intramedullary nailing, all treated using 3.5-mm locked compression plates (LCP) placed through lateral minimally invasive approaches, between 2010 and 2016. Patient’s age averaged 39.7 years. All nonunions were diaphyseal and oligotrophic. All nonunions had previous surgical treatment with static locked nails (seven antegrade and two retrograde). The IM nails were all well inserted in the humerus (none of them protruded or had rotator cuff lesions associated). Pre-operative Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) score averaged 25.5 points. Pre-operative Constant’s score averaged 80.2. Pre-operative visual analog scale of pain averaged 2.4 points.
Results
Follow-up averaged 17.7 months. Time between initial surgery and revision procedure averaged 11.7 months. Union was achieved in all cases, after an average of 4.8 months. DASH score at last follow-up averaged 5.1 points, and final Constant’s score averaged 93.7 points. The analog scale of pain averaged 0.7 points. Time from definitive surgery to work return averaged 3.9 months. Long 3.5-mm LCPs were used (plate length averaged 16.9 screw holes). In two cases, a third 4-cm incision at the nonunion site was performed and cancellous autologous iliac crest bone graft was associated.
Conclusion
In our series of nine patients, we achieved union and good objective and subjective results, with high patient satisfaction, using a lateral MIPO technique and placing long 3.5-mm LCPs in selected oligotrophic humerus nonunions after failed IM nailing.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinker MR, O’Connor DP (2007) Exchange nailing of ununited fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:177–188
Ouyang H, Xiong J, Xiang P et al (2013) Plate versus intramedullary nail fixation in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures: an updated meta-analysis. J Shoulder Elb Surg 22:387–395
Kurup H, Hossain M, Andrew JG (2011) Dynamic compression plating versus locked intramedullary nailing for humeral shaft fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (6): CD005959
Gessmann J, Konigshausen M, Coulibaly MO et al (2016) Anterior augmentation plating of aseptic humeral shaft nonunions after intramedullary nailing. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136:631–638
Emmerson KP, Sher JL (1998) A method of treatment of nonunion of humeral shaft fractures following treatment by locked intramedullary nail: a report of three cases. Injury 29:550–552
Gerber A, Marti R, Jupiter J (2003) Surgical management of diaphyseal humerus nonunion after intramedullary nailing: wave-plate fixation and autologous bone grafting without nail removal. J Shoulder Elb Surg 12:309–313
Ring D, Jupiter J (2004) Humerus nonunion after intramedullary rod fixation. Locking compression plate without removing the nail. Tech Orthop 18:356–359
Nadkarni B, Srivastav SH, Mittal V, Agarwal SH (2008) Use of locking compression plates for long bone nonunions without removing existing intramedullary nail: review of literature and our experience. J Trauma 65:482–486
Allende C, Paz A, Altube G et al (2014) Revision with plates of humerus nonunions secondary to failed intramedullary nailing. Int Orthop 38:899–903
Vilaca PR, Uezumi MK (2012) Anterior minimally invasive bridge-plate technique for treatment of humeral shaft nonunion. J Orthopaed Traumatol 13:211–216
Weber BG, Pseudoarthrosis CO (1976) Pathophysiology, biomechanics, therapy, results. Huber, Bern
Lammens J, Bauduin G, Driesen R et al (1998) Treatment of nonunion of the humerus using the Ilizarov external fixator. Clin Orthop Relat Res 353:223–230
Patel VR, Menon DK, Pool RD, Simonis RB (2000) Nonunion of the humerus after failure of surgical treatment. Management using the Ilizarov circular fixator. J Bone Joint Surg Br 82:977–983
McKee MD, Miranda MA, Riemer BL (1996) Management of humeral nonunion after the failure of locking intramedullary nails. J Orthop Trauma 10:492–499
Dujardin FH, Mazirt N, Tobenas AC et al (2000) Failure of locked centro-medullary nailing in pseudarthrosis of the humeral diaphysis. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 86:773–780
Ji F, Tong D, Tang H et al (2009) Minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) technique applied in the treatment of humeral shaft distal fractures through a lateral approach. Int Orthop 33:543–547
Rancan M, Dietrich M, Lamdark T et al (2010) Minimal invasive long Philos plate ostheosynthesis in methaphyseal fractures of the proximal humerus. Injury 41:1277–1283
Wu CC (1996) Humeral shaft nonunion treated by a Seidel interlocking nail with a supplementary staple. Clin Orthop 326:203–208
Flinkkila T, Ristiniemi J, Hamalainen M (2001) Nonunion after intramedullary nailing of humeral shaft fractures. J Trauma 50:540–544
Anglen JO, Archdeacon MT, Cannada LK et al (2009) Avoiding complications in the treatment of humeral fractures. Instr Course Lect 58:3–11
Rommens PM, Kuechle R, Bord T et al (2008) Humeral nailing revisited. Injury 39:1319–1328
Reed AA, Joyner CJ, Brownlow HC, Simpson AH (2002) Human atrophic fracture non-unions are not avascular. J Orthop Res 20:593–599
Ramoutar DN, Rodrigues J, Quah C et al (2011) Decortication and compression plate fixation of long bone non-union: is bone graft necessary? Injury 42:24–1434
Funding
There is no funding source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allende, C., Vanoli, F., Gentile, L. et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis in humerus nonunion after intramedullary nailing. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 42, 2685–2689 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3911-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3911-1