Abstract.
Objective
CCX CKR is a decoy chemokine receptor that specifically binds the chemokines CCL19, CCL25 and CCL21. CCL19 was previously found to be upregulated in pulmonary sarcoidosis. We have, therefore, investigated CCX CKR expression in this inflammatory disease.
Methods and results
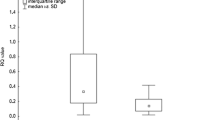
CCX CKR mRNA was semiquantitated using RT-PCR in unseparated bronchoalveolar (BAL) cells from sarcoidosis patients (S, n = 29) and healthy control subjects (C, n = 9). CCX CKR transcripts were upregulated in patients (mean ± SEM); S, 0.82 ± 0.10; C, 0.44 ± 0.04; p = 0.01; this upregulation paralleled the disease course as assessed by the chest radiographic stage (p < 0.02). Immunocytochemistry localised the CCX CKR protein to ciliated bronchial cells. Flow cytometric fluorescent ligand uptake assay showed that these cells are able to internalize its ligand.
Conclusion
These observations implicate CCX CKR in the modulation of the inflammatory response in sarcoidosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 2 February 2006; returned for revision 24 April 2006; accepted by M. Parnham and J. Skotnicki 9 May 2006
E. Kriegova, A. Tsyrulnyk, and A. Arakelyan contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kriegova, E., Tsyrulnyk, A., Arakelyan, A. et al. Expression of CCX CKR in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Inflamm. res. 55, 441–445 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-006-6019-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-006-6019-9