

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 1231.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190713
收稿日期:2019-12-25
出版日期:2020-06-10
发布日期:2020-03-06
通讯作者:
孙新园,欧阳健明
E-mail:sunxinyuan1985@163.com;toyjm@jnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LIU Hong1,ZOU Guojun1,SUN Xinyuan2,*( ),OUYANG Jianming1,*(
),OUYANG Jianming1,*( )
)
Received:2019-12-25
Online:2020-06-10
Published:2020-03-06
Contact:
Xinyuan SUN,Jianming OUYANG
E-mail:sunxinyuan1985@163.com;toyjm@jnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
研究了不同草酸/钙(Ox/Ca)摩尔比对CaOx晶体在损伤前后的人肾近曲小管上皮细胞(HK-2)表面的生长差异及形成的晶体对细胞的毒性差异. 实验结果表明, CaOx过饱和溶液对正常细胞和损伤细胞均会产生进一步的损伤, 导致细胞活力、 溶酶体的完整性和线粒体膜电位降低, 而细胞内活性氧(ROS)、 细胞骨架的紊乱程度、 磷酯酰丝氨酸(PS)外翻比例和骨桥蛋白(OPN)表达量均增加; 且随着过饱和溶液中Ox/Ca摩尔比的增加而损伤加重. 正常细胞主要诱导二水草酸钙(COD)晶体形成, 且COD的含量与Ox/Ca摩尔比成正相关. 损伤细胞表面主要生成一水草酸钙(COM), 且晶体的数量和聚集程度与Ox/Ca摩尔比成正相关. 相比于正常细胞, 损伤细胞诱导的晶体棱角更加尖锐, 其对细胞的损伤大于棱角圆钝的晶体. 实验结果还表明, 降低CaOx的过饱和度、 减小Ox/Ca摩尔比和修复受损伤的肾上皮细胞均有利于抑制CaOx结石形成.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
刘虹,邹国均,孙新园,欧阳健明. 不同草酸/钙摩尔比条件下草酸钙晶体的生长及对HK-2细胞的毒性. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6): 1231.
LIU Hong,ZOU Guojun,SUN Xinyuan,OUYANG Jianming. Differences of Growth and Cytotoxicity of Calcium Oxalate Crystals Formed on HK-2 Cells Under Different Oxalic Acid/Calcium Ratios †. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1231.
| Group | c(Ca2+)/(mmol·L-1) | c(Ox2-)/(mmol·L-1) | Ox/Ca molar ratio | Labeling | RS* of CaOx |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1.00×0.25 | 9.27 |
| Ⅱ | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.50×0.50 | 9.27 |
| Ⅲ | 0.25 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 0.25×1.00 | 9.27 |
Table 1 Composition and labeling of CaOx supersaturated solution with different Ox/Ca molar ratios
| Group | c(Ca2+)/(mmol·L-1) | c(Ox2-)/(mmol·L-1) | Ox/Ca molar ratio | Labeling | RS* of CaOx |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 1.00×0.25 | 9.27 |
| Ⅱ | 0.50 | 0.50 | 1.00 | 0.50×0.50 | 9.27 |
| Ⅲ | 0.25 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 0.25×1.00 | 9.27 |
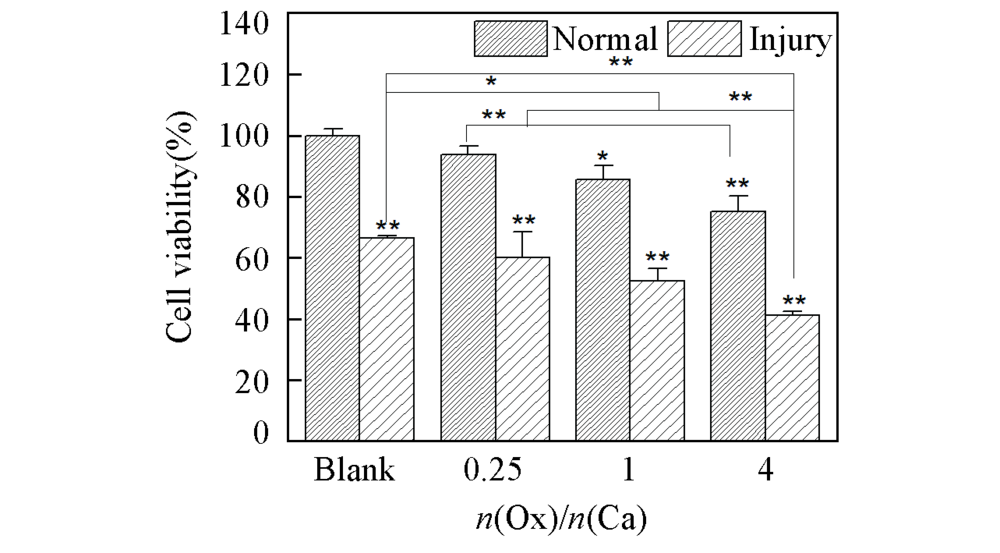
Fig.1 Cell viability of HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solutions with various Ox/Ca molar ratios Action time: 12 h; ** P<0.01, * P<0.05 vs. normal blank group.
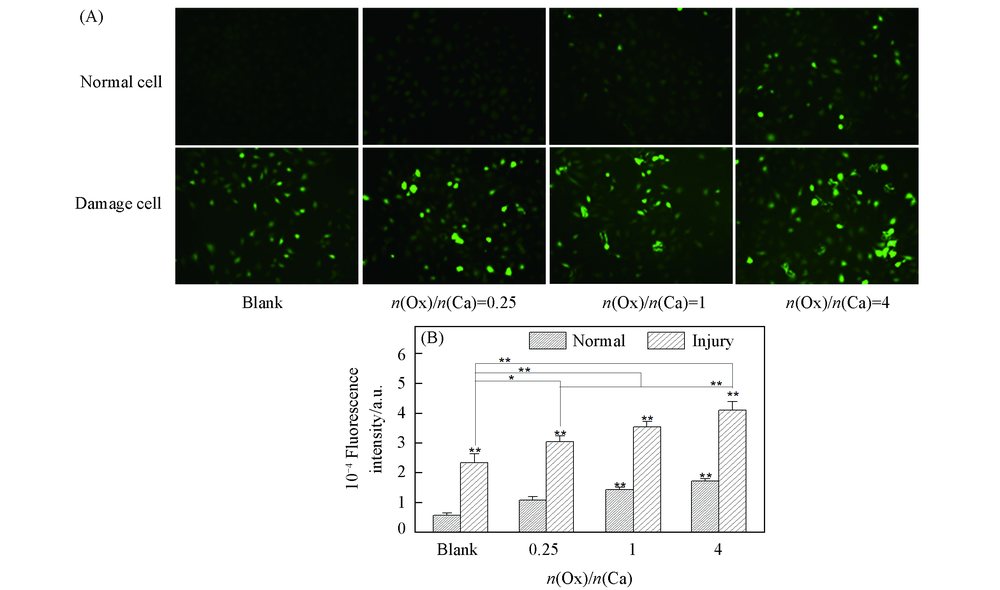
Fig.2 Intracellular ROS level of HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solutions with various Ox/Ca molar ratios (A) Fluorescence microscopy images of ROS; (B) quantitative fluorescence intensity.Action time: 12 h; ** p<0.01, * p<0.05 vs. normal blank group.
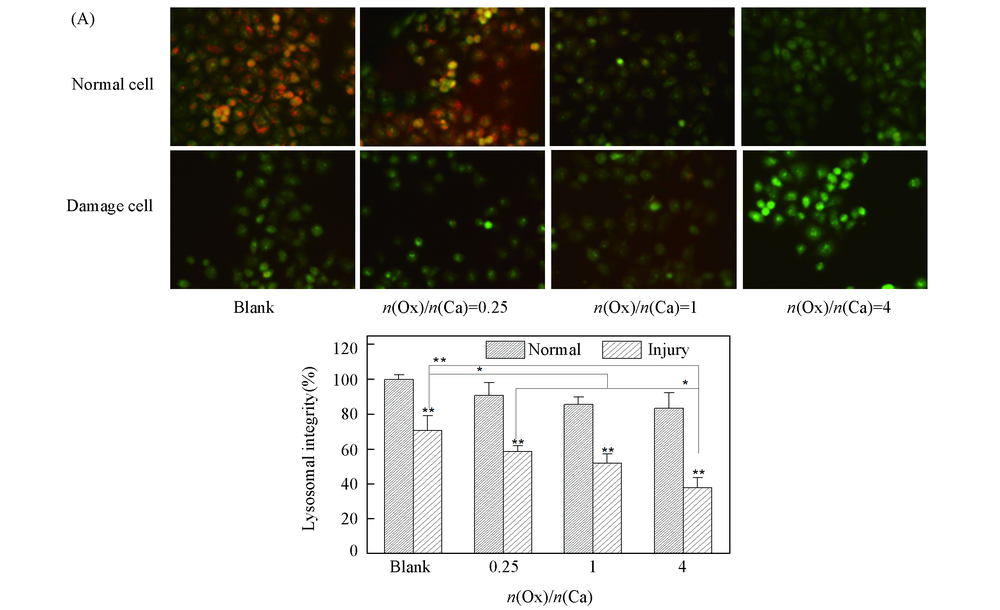
Fig.3 Lysosomal integrity observation of HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solution with various Ox/Ca molar ratios (A) Fluorescence microscopy images; (B) quantitative fluorescence intensity.Action time: 12 h; ** P<0.01, * P<0.05 vs. normal blank group.
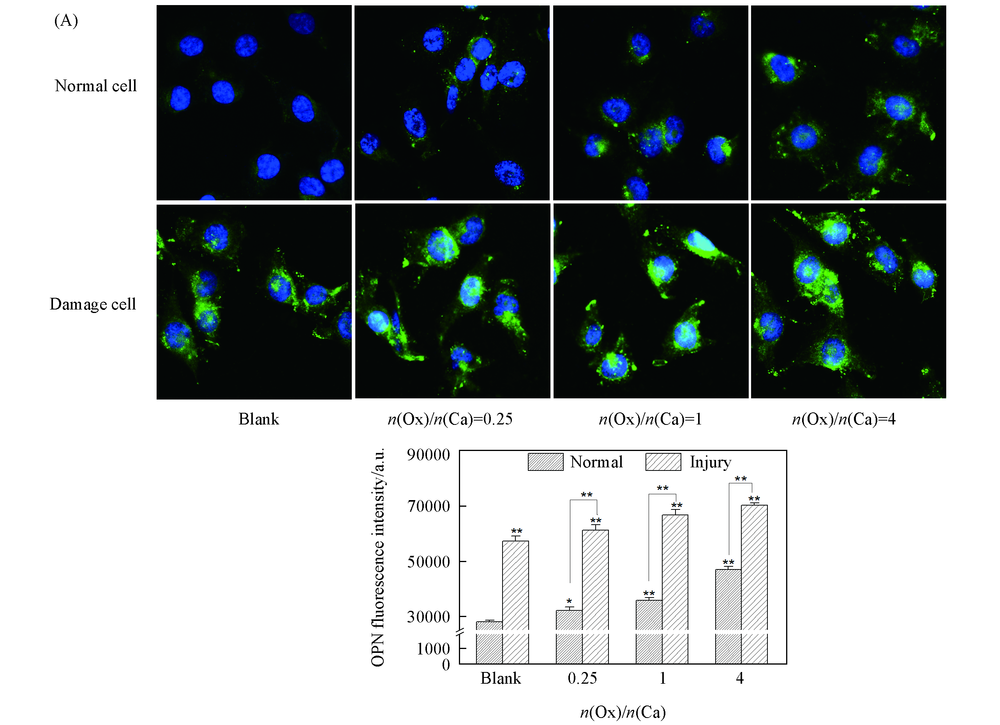
Fig.4 OPN expression of HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solutions with various Ox/Ca molar ratios (A) Fluorescence microscopy images; (B) quantitative results of OPN expression. Nucleus: blue;OPN: green. Action time: 12 h; ** P<0.01, * P<0.05 vs. normal blank group.
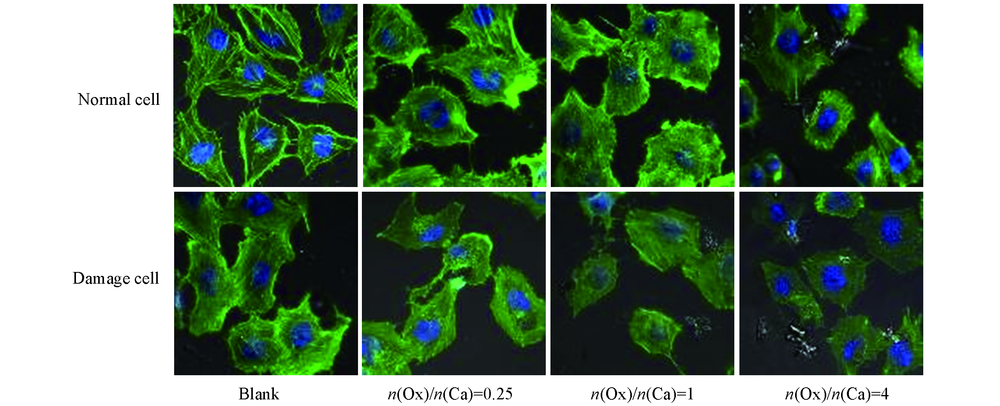
Fig.5 Confocal observation images of cytoskeleton in HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solutions with various Ox/Ca molar ratios Actin: green; nuclei: blue; action time: 12 h.
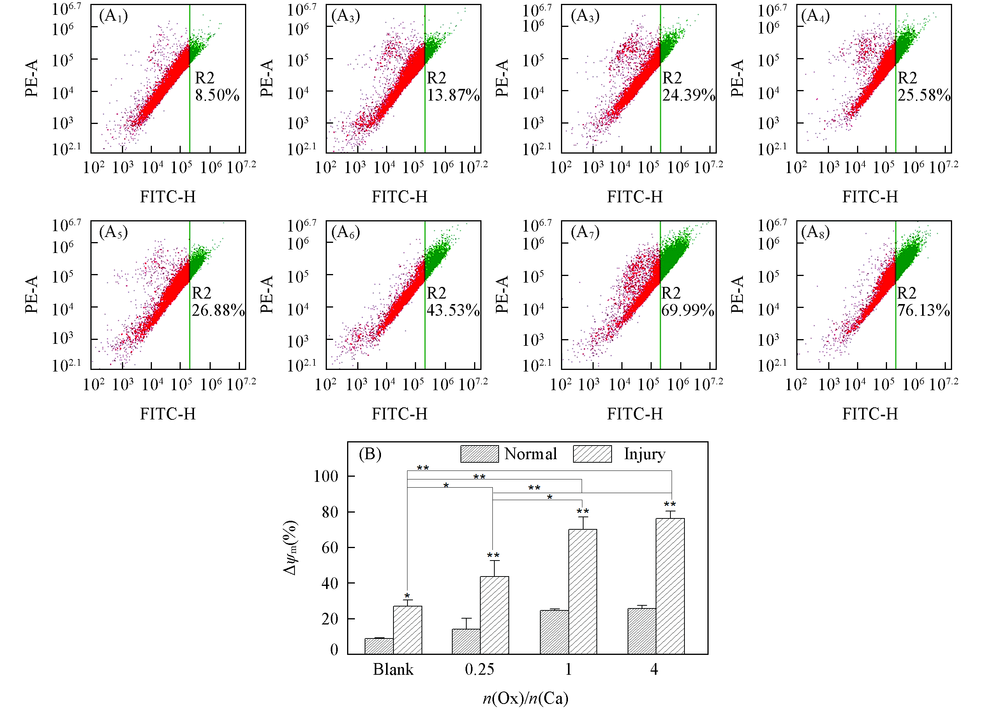
Fig.6 Mitochondrial membrane potential detection(Δψm) of HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solutions with various Ox/Ca molar ratios (A1—A8) Flow cytometric data of mitochondrial membrane potential(Δψm), green R2 value represents decreasing membrane potential; (A1)—(A4) normal cell; (A5)—(A8): damage cell; (A1), (A5) blank; n(Ox)/n(Ca): (A2), (A6) 0.25; (A3), (A7) 1; (A4), (A8) 4. (B) Quantitative histogram of Δψm. Action time: 12 h; ** P<0.01, * P<0.05 vs. normal blank group.
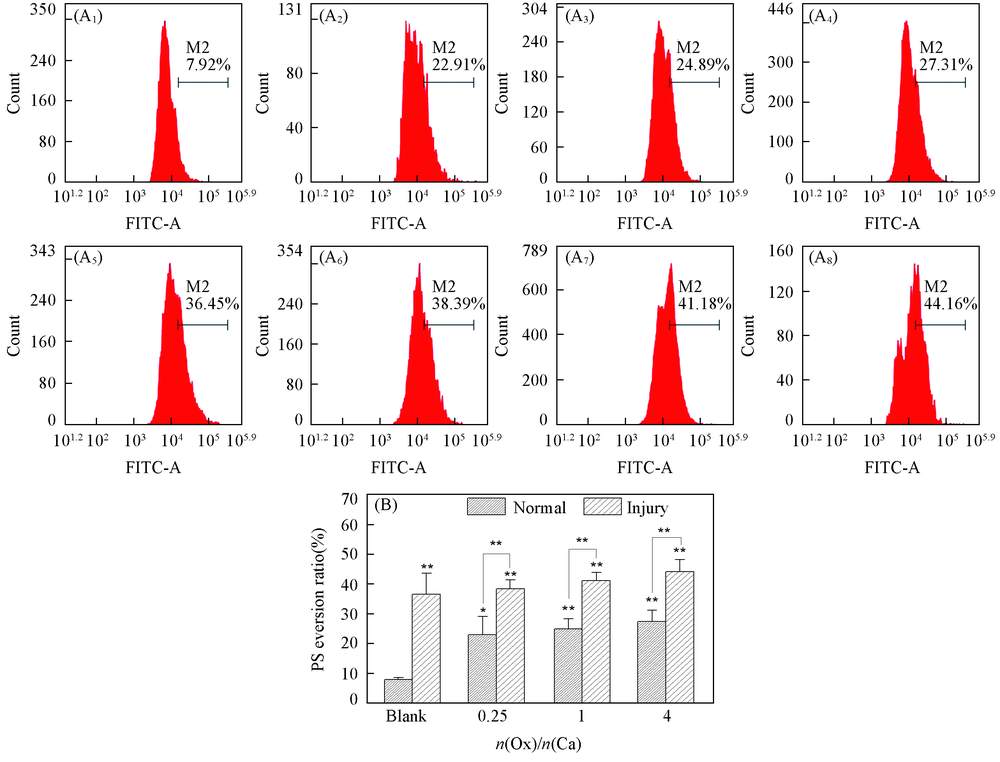
Fig.7 Flow cytometry analysis of PS eversion in HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solutions with various Ox/Ca molar ratios (A1—A8) Histogram of the percentage of PS eversion; abscissa: the fluorescence intensity; ordinate: the number of cells; (A1)—(A4) normal cell; (A5)—(A8): damage cell; (A1), (A5) blank; n(Ox)/n(Ca): (A2), (A6) 0.25; (A3), (A7) 1; (A4), (A8) 4. (B) Quantitative histogram. Action time: 12 h; ** P<0.01, * P<0.05 vs. normal blank group.
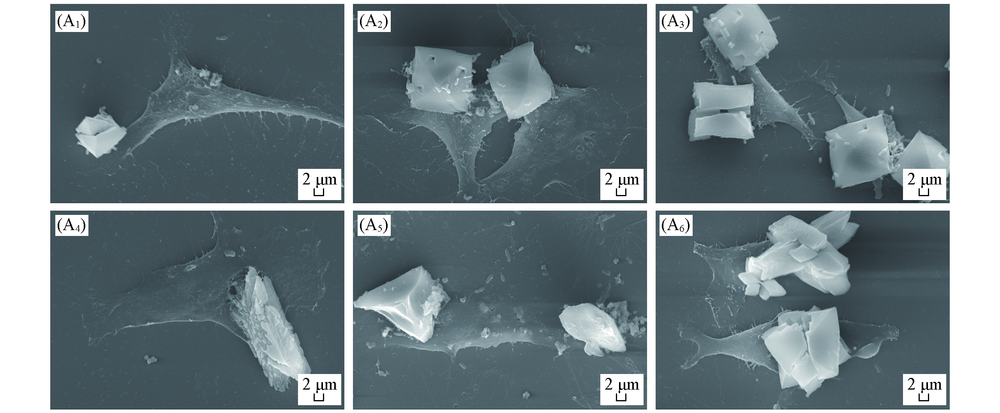
Fig.9 SEM images of CaOx crystals on HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solutions with various Ox/Ca molar ratios (A1)—(A3) Normal cells; (A4)—(A6) damage cell; n(Ox)/n(Ca): (A1), (A4) 0.25;(A2), (A5) 1; (A3), (A7) 4. Action time: 12 h.
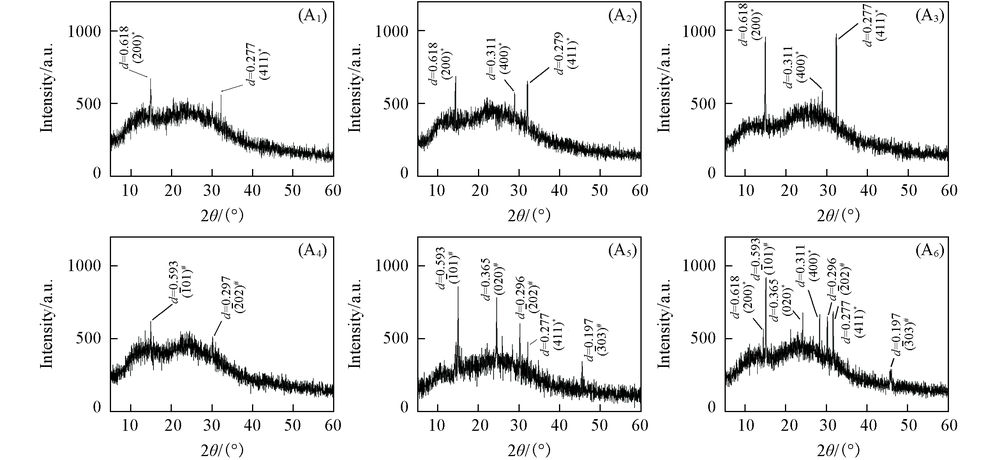
Fig.10 XRD patterns of CaOx crystals on HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solutions with various Ox/Ca molar ratios * COD; # COM. (A1)—(A3) normal cell; (A4)—(A6) damage cell; n(Ox)/n(Ca): (A1), (A4) 0.25; (A2), (A5) 1; (A3), (A6) 4. Action time: 12 h.
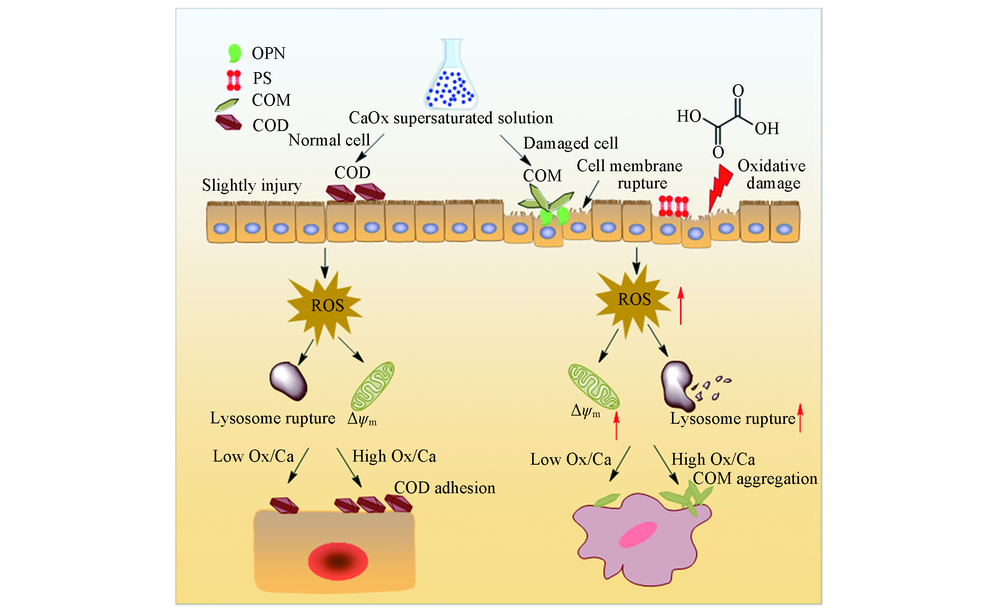
Fig.11 Mechanism diagram of cytotoxic difference and CaOx crystal difference induced by HK-2 cells before and after injury with CaOx supersaturated solutions with various Ox/Ca molar ratios
| [1] | Daudon M., Jungers P., Bazin D., Bazin D., Williams J. C. Jr., Urolithiasis, 2018, 46(5), 459—470 |
| [2] | Khan A., Int. Urol. Nephrol., 2018, 50(5), 799—806 |
| [3] | Yuen J. W. M., Gohel M. D. I., Poon N., Shum D. K., Tam P. C., Au D. W., Clin. Chim. Acta, 2010, 411, 1018—1026 |
| [4] | Yao X. Q., Deng S. P., Ouyang J. M. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities 2011, 32(2), 236—240 |
| ( 姚秀琼, 邓穗平, 欧阳健明 . 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(2) 236—240) | |
| [5] | Rimer J. D., Kolbach-Mandel A. M., Ward M. D., Wesson J. A., Urolithiasis, 2017, 45(1), 57—74 |
| [6] | Zuo J., Khan A., Glenton P. A., Khan S. R., Nephrol. Dial. Transplant., 2011, 26(6), 1785—1796 |
| [7] | Gan Q. Z., Sun X. Y., Yao X. Q., Ouyang J. M. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities 2016, 37(6), 1050—1058 |
| ( 甘琼枝, 孙新园, 姚秀琼, 欧阳健明 . 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6) 1050—1058) | |
| [8] | Zhang S., Yang R. E., Ouyang J. M. , Acta Chimica Sinica 2011, 3, 284—290 |
| ( 张生, 杨如娥, 欧阳健明 化学学报, 2011, 3, 284—290) | |
| [9] | Chai W., Liebman M., Kynast-Gales S., Massey L., Am. J. Kidney Dis., 2004, 44(6), 1060—1069 |
| [10] | Guerra A., Allegri F., Meschi T., Adorni G., Prati B., Nouvenne A., Novarini A., Maggiore U., Fiaccadori E., Borghi L., Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. , 2005, 43(6), 585—589 |
| [11] | Bretherton T., Rodgers A., Cryst. Growth., 1998, 192, 448—455 |
| [12] | Jung T., Kim W. S., Choi C. K., Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2004, 24, 31—33 |
| [13] | Seeger H., Kaelin A., Ferraro P. M., Weber D., Jaeger P., Ambuehl P., Robertson W., Unwin R., Wagner C. R., Mohebbi N., BMC Nephrol., 2017, 18(1), 349 |
| [14] | Mitchell T., Kumar P., Reddy T., Wood K. D., Knight J., Assimos D. J., Holmes R. P., Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol., 2019, 316(3), F409—F413 |
| [15] | Borghi L., Guerra A., Meschi T., Briganti A., Schianchi T., Allegri F., Novarini A., Kidney Int., 1999, 55(3), 1041—1050 |
| [16] | Carvalho M., Vieira M. A., Int. Braz. J. Urol., 2004, 30(3), 205—209 |
| [17] | Schepers M. S. J., Van Ballegooijen E. S., Bangma C. H., Verkoelen C. F., Kidney Int., 2005, 68(4), 1660—1669 |
| [18] | Grohe B., Taller A., Vincent P. L., Tieu L. D., Rogers K. A., Heiss A., Sørensen E. S., Mittler S., Goldberg H. A., Hunter G. K., Langmuir, 2009, 25(19), 11635—11646 |
| [19] | King M., Mcclure W. F., Andrews L. C., International Center for Diffraction Data: Newtown Square, PA, 1992 |
| [20] | Ouyang J. M., Yao X. Q., Tan J., Wang F. X., J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 2011, 16(3), 405—416 |
| [21] | Yao X. Q., Ouyang J. M., Peng H., Zhu W. Y., Chen H. Q., Carbohydr. Polym., 2012, 90(1), 392—398 |
| [22] | Yuen J. W. M., Gohel M. D. I., Poon N. W., Shum D. K. Y., Tam P. C., Au D. W. T., Clin. Chim. Acta, 2010, 411, 1018—1026 |
| [23] |
Lieske J. C., Toback F. G., Deganello S., Kidney Int., 1998, 54(3), 796—803
doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00058.x URL |
| [24] | Ouyang J. M., Yao X. Q., Su Z. X., Cui F. Z ., Science in China Series B: Chemistry, 2003, 1, 14—20 |
| ( 欧阳健明, 姚秀琼, 苏泽轩, 崔福斋 中国科学B辑, 2003, 1, 14—20) | |
| [25] | Lieske J. C., Toback F. G., Deganello S., Calcif. Tissue Int., 1996, 58, 195—200 |
| [26] | Scheid C. R., Cao L. C., Honeyman T., Jonassen J. A., Front Biosci., 2004, 9(797), 797—808 |
| [27] | Deng S. P., Ouyang J. M., Cryst. Growth Des., 2008, 9(1), 82—87 |
| [28] | Zhang S., Su Z. X., Yao X. Q., Peng H., Deng S. P., Ouyang J. M., Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2012, 32(4), 840—847 |
| [29] | Yao X. Q., Peng H., Tan J., Ouyang J. M., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2012, 28(3), 459—464 |
| [30] | Rodgers A., J. Am. Soc. Nephrology: JASN, 1999, 10, S351—S354 |
| [31] | Robertson W. G., Peacock M., Nephron, 1980, 26(3), 105—110 |
| [32] | Ebisuno S., Umehara M., Kohjimoto Y., Ohkawa T., BJU Int, l999, 84(1), 118—122 |
| [33] | Zorov D. B., Juhaszova M., Sollott S. J., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2006, 1757, 509—517 |
| [34] | Sun X. Y., Yao X. Q., Yu K., Ouyang J. M. , Chinese J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 32(5), 818—826 |
| ( 孙新园, 姚秀琼, 余凯, 欧阳健明 . 无机化学学报, 2016, 32(5) 818—826) | |
| [35] | Sun X. Y., Xu M., Ouyang J. M., ACS Omega, 2017, 2(9), 6039—6052 |
| [1] | 甘琼枝, 孙新园, 姚秀琼, 欧阳健明. 肾上皮细胞损伤使草酸钙晶体黏附增强的分子机制[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6): 1050. |
| [2] | 罗泽伟, 王益民, 刘坤平, 魏福静, 李玉, 段忆翔. 功能化石墨烯的制备及抗癌药物递送载体的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(10): 1900. |
| [3] | 张江华, 吕英, 贾红亮, 宋银银, 孙晓霞, 柴敦宵, 王兰英. 吲哚二甲川菁的合成、 晶体结构、光谱性质及生物应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(10): 1924. |
| [4] | 郑永标, 庞海月, 王继峰, 陈丹霞, 施国伟, 黄建忠. 从细脚拟青霉分离的新环二肽与新十元环内酯[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(8): 1665. |
| [5] | 曾莉, 胡俊, 魏俊超. 聚乳酸-乙醇酸/纳米氧化锌复合电纺纤维装载亲疏水药物的控释及体外细胞毒性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(8): 1788. |
| [6] | 王海, 张超, 张琳华, 刘兰霞, 郑义, 朱敦皖. 载紫杉醇星型M-PLA-TPGS纳米颗粒的合成及其用于前列腺癌治疗药物载体的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(10): 2239. |
| [7] | 徐玉东, 张正勇, 孔继烈, 李国栋, 熊焕明. 聚甲基丙烯酰胺包覆的ZnO发光量子点及其在细胞成像中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(7): 1565. |
| [8] | 李晓东, 杨淑敏, 徐红, 马於光. 一种光功能有机纳米粒子的制备及细胞毒性评价[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(01): 210. |
| [9] | 杨宝春, 姜耀东, 秦雪娟, 陈志良, 任非. 抗肿瘤药物在金属有机骨架中的装载及体外释放[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(01): 26. |
| [10] | 郭玲香, 高秋端. 赖氨酸修饰聚酰胺-胺树枝状高分子的制备及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(01): 176. |
| [11] | 姚秀琼 邓穗平 欧阳健明. HKC细胞损伤对草酸钙晶体成核和聚集的促进作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(2): 236. |
| [12] | 李非凡, 田华雨, 陈磊, 夏加亮, 陈学思, 景遐斌. 六氯环三磷腈交联寡聚乙烯亚胺的制备及基因载体应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(9): 1896. |
| [13] | 时美, 范雪梅 , 李雪 , 王铮 , 王义明 , 罗国安. cDNA基因芯片技术分析三聚氰胺肾毒性的相关基因表达[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(4): 684. |
| [14] | 殷跃凡, 李艳梅, 资彦楠, 周轶平, 毕韵梅. 聚[(甲氧基乙氧基乙氧基)1.0(乙氧基吡咯烷酮)1.0]膦腈的合成及性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(6): 1245. |
| [15] | 陈素芸, 孙国明, 姜磊, 李楠, 李培勇, 朱新远. 细胞内转运载体超支化聚砜胺及其生物相容性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(4): 825. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||