Published online Dec 26, 2019. doi: 10.4330/wjc.v11.i12.316
Peer-review started: July 23, 2019
First decision: August 2, 2019
Revised: August 13, 2019
Accepted: October 18, 2019
Article in press: October 18, 2019
Published online: December 26, 2019
Aortic arch stenting is continuously emerging as a safe and effective option to alleviate aortic arch stenosis and arterial hypertension.
We present a 15-year-old girl with aortic arch hypoplasia who had undergone implantation of an uncovered 22 mm Cheatham-Platinum stent due to severe (native) aortic arch stenosis. On follow-up seven months later, she presented a significant re-stenosis of the aortic arch. A second stent (LD Max 26 mm) was implanted and both stents were dilated up to 16 mm. After an initially unremarkable post-interventional course, the patient presented with hoarseness five days after the intervention. MRI and CT scans ruled out an intracranial pathology, as well as thoracic hematoma, arterial dissection, and aneurysm around the intervention site. Laryngoscopy confirmed left vocal fold paresis attributable to an injury to the left recurrent laryngeal nerve (LRLN) during aortic arch stenting, as the nerve loops around the aortic arch in close proximity to the area of the implanted stents. Following a non-invasive therapeutic approach entailing regular speech therapy, the patient recovered and demonstrated no residual clinical symptoms of LRLN palsy after six months.
Left recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy is a rare complication of aortic arch stenting not previously reported.
Core tip: This case report demonstrates that endovascular therapy of aortic arch hypoplasia with stent implantation in the stenosed segment may, as a rare complication of the procedure, lead to left recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy with subsequent vocal cord paresis.
- Citation: Fürniss HE, Hummel J, Stiller B, Grohmann J. Left recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy following aortic arch stenting: A case report. World J Cardiol 2019; 11(12): 316-321
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8462/full/v11/i12/316.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v11.i12.316
Hypoplasia of the aortic arch may induce arterial hypertension of the right upper body. Alleviation of aortic arch stenosis is indicated to prevent hypertension-related cardiovascular complications. Endovascular therapy including ballooning and stenting has emerged over the last decade as a safe and effective alternative to surgical reconstruction[1-4]. Acute complications of aortic arch stenting almost exclusively involve aortic wall injury, while stent compression of adjacent structures is uncommon[5,6].
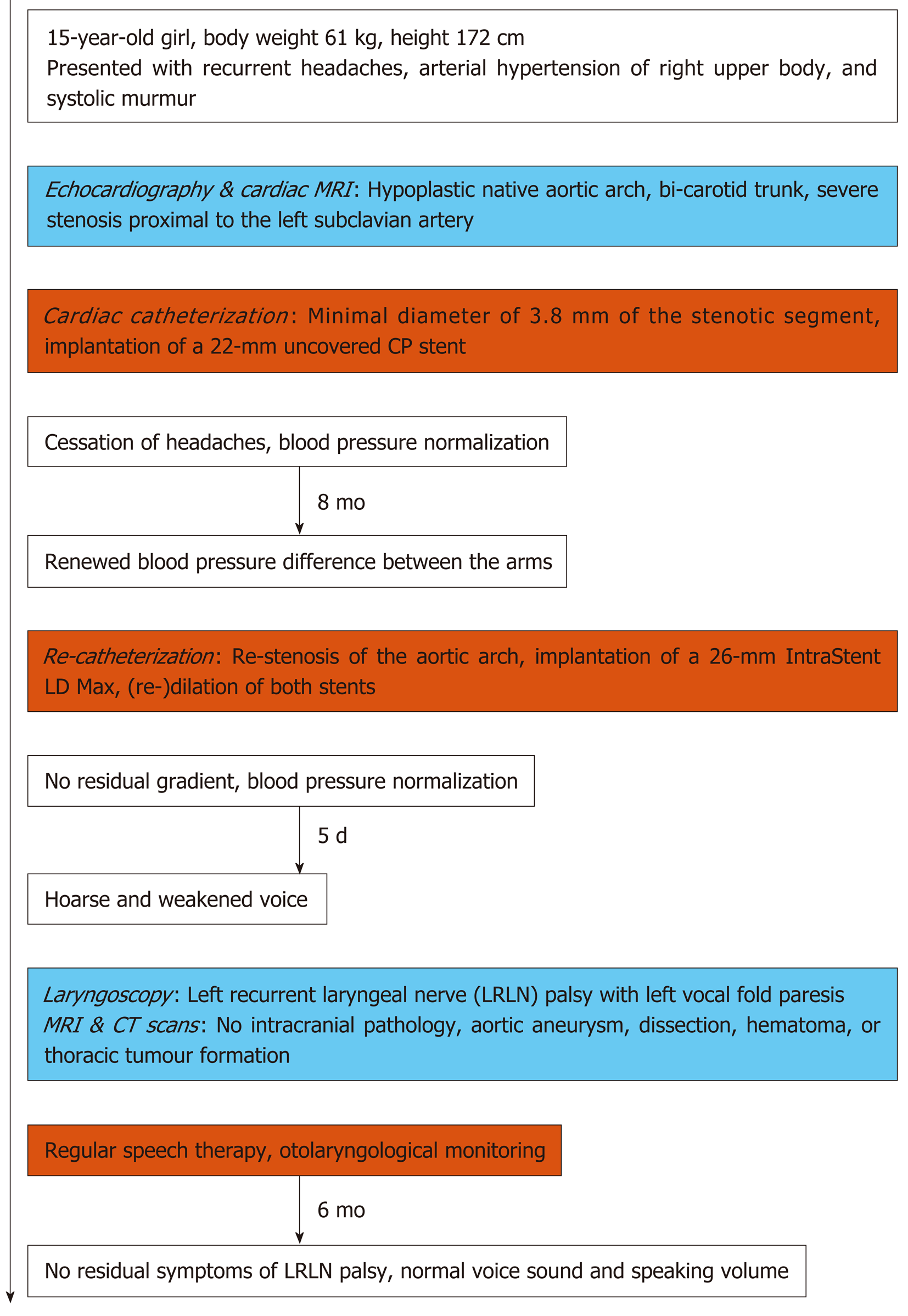
We report a 15-year-old girl who presented with recurrent headaches, arterial hypertension, and a systolic murmur.
Echocardiographic examination in a medical practice had revealed a potential coarctation of the aorta.
The patient had no history of serious illness.
There were no medically relevant aspects from the patient’s personal history. Other than arterial hypertension and coronary artery disease in the patient’s grandfather, there was no known cardiac disease within the family.
The patient presented in good general condition. Body weight was 61 kg and height were 172 cm. Her blood pressure in the right arm with 144/86 [MAP (mean arterial pressure) 110 mmHg] was significantly higher than that in the left arm [118/82 (MAP 96) mmHg] and of the right leg [118/72 (MAP 91) mmHg]. We consistently felt an unequal pulse between the right and left radial arteries (right stronger than left). A 2/6 systolic murmur was identified ventrally in the second and third left intercostal space, and, less prominently, dorsally between the shoulder blades. All other aspects of the physical examination were normal.
No laboratory examinations were done in the diagnostic work-up.
Echocardiography and cardiac MRI revealed a hypoplastic native aortic arch with a bi-carotid trunk and a segment just proximal of the left subclavian artery which was stenosed by 75% (Supplemental Figure 1A).
Our final diagnosis was a hypoplastic aortic arch with a bi-carotid trunc and severe coarctation.
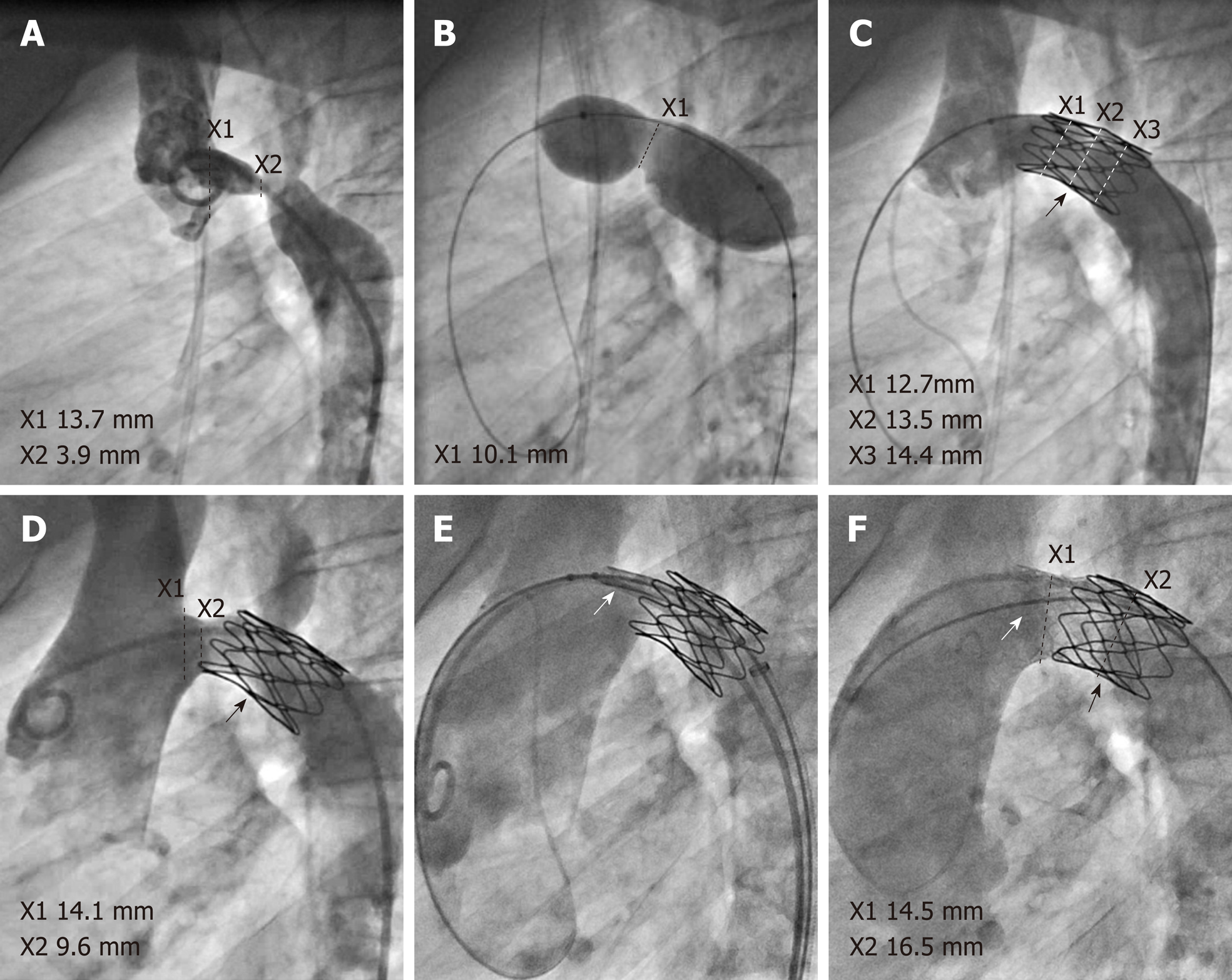
Following discussion with the family and the cardiac surgeons, we opted against surgical treatment in favor of an interventional approach to alleviate the aortic arch stenosis. Cardiac catheterization showed a minimal diameter of 3.8 mm of the stenotic segment (Figure 1A), with a relatively compliant stenosis up to 14 mm on sizing balloon interrogation with a Tyshak II balloon (NuMed, Hopkinton, NY, United States) (Figure 1B). We implanted a short 22-mm uncovered Cheatham-Platinum (CP) stent (NuMed, Hopkinton, NY, United States), which effectively resolved the pressure gradient while preserving good perfusion of the overstented left subclavian artery (Figure 1C). On follow-up seven months later, the patient demonstrated renewed blood-pressure difference between the arms. Re-catheterization revealed re-stenosis with a diameter of 9.5 mm between the brachiocephalic artery’s origin and the proximal end of the previously implanted CP stent and a systolic pressure gradient of 18 mmHg under conscious sedation, probably due to slight stent migration towards distal (Figure 1D). The re-stenosis was relieved by implantation of a 26-mm IntraStent LD Max (ev3 - Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN, United States) in telescope technique, proximal flaring of the LD Max stent with a 20-mm Cristal balloon (Balt, Montmorency, France), and (re-)dilation of both stents using a non-compliant 16-mm Atlas balloon (Bard, Tempe, AZ, United States) (Figure 1E and F).
Our interventional result was satisfactory, with a minimum aortic arch diameter of 14.5 mm (Figure 1F) and no relevant residual gradient detectable. Her immediate post-interventional course was unremarkable. However, five days after the intervention the patient presented with sudden hoarseness and a weakened voice. MRI and CT scans ruled out an aortic aneurysm or dissection, haematoma, thoracic tumour formation, and intracranial pathology such as stroke (Supplemental Figure 1B and C). Otorhinolaryngological examination including laryngoscopy confirmed paresis of the left vocal fold. Due to the anatomically proximity of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve (LRLN) to the implanted stents’ region, we attributed the vocal fold palsy to an injury to the LRLN during aortic arch stenting. After careful evaluation, we decided against medical or surgical therapy of the LRLN palsy and took a conservative approach involving regular speech therapy and close otorhino-laryngological monitoring. Fortunately, at follow-up six months later, our patient demonstrated no residual clinical symptoms of LRLN palsy with normal voice sound and speaking volume. For an overview of the time course of this case, see Figure 2.
We present a case of LRLN palsy following stent implantation in the transverse aortic arch. Vocal cord paresis is a well-known complication of surgical ligation of patent ductus arteriosus[7], and has also been described secondary to transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus and left pulmonary artery stenting[8-12]. Moreover, LRLN palsy has also occurred after surgical aortic arch reconstruction during the Norwood procedure[13]. However, to our knowledge, LRLN paralysis resulting from transverse arch stenting has not been reported in the MEDLINE database so far. We suggest that, due to the course of the LRLN as is passes underneath the aortic arch in close proximity to the pulmonary artery and the ligamentum arteriosum, stent implantation in a severely hypoplastic aortic arch may either stretch the LRLN as the transverse aortic diameter increases, or compress it between the aortic arch and the pulmonary artery, thereby leading to LRLN damage and left vocal cord paresis. Moreover, after surgical aortic stent-graft placement, additional dilation of the graft is a known independent predictor of LRLN palsy[14]. Therefore, (re-)dilation of the stents in our patient may also have played a significant role in her having developed post-intervention LRLN palsy.
Our patient recovered relatively quickly, most likely due to either nerve growth to accommodate the larger aortic diameter, or due to cessation of an inflammatory reaction or edema following either stretch or compression of the nerve. Contrary to this positive clinical course in our patient, previous reports of LRLN after endovascular therapy of patent ductus arteriosus or left pulmonary artery stenosis have documented persistent vocal cord paralysis after six months in over 50% of patients[8-12]. However, other than the case by Javois and colleagues, who described coughing after their patient drank water[12], there were no previously reported symptoms of LRLN palsy other than hoarseness after transcatheter interventions[8-11]. Presumably due to these relatively mild clinical presentations neither medical therapy nor surgical device removal was performed in any of the cases. Therefore, it remains unclear whether in the case of acute LRLN palsy after aortic arch stent implantation, the administration of medication or decompression of the nerve by surgical stent removal would lead to LRLN recovery. Indeed, further (surgical) manipulation may even aggravate symptoms. Finally, clinicians must carefully assess whether the patient’s clinical symptoms justify invasive surgical therapy.
LRLN palsy is an extremely rare complication of transverse aortic arch stenting. Interventionalists should be aware of this potential complication and inform their patients accordingly.
We thank Carole Cürten for language editing and Stefan Heinz for graphic design.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Cardiac and cardiovascular
Country of origin: Germany
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Barik R, Nurzynska D, Ueda H S-Editor: Dou Y L-Editor: A E-Editor: Zhang YL
| 1. | Zartner PA, Neudorf U, Bierbach B, Hart C, Schneider MB. First follow-up of a breakable stent for implantation in infants dedicated for a life-long stay. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2018;91:1119-1124. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 8] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Bentham J, Shettihalli N, Orchard E, Westaby S, Wilson N. Endovascular stent placement is an acceptable alternative to reoperation in selected infants with residual or recurrent aortic arch obstruction. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;76:852-859. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 11] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Holzer RJ, Chisolm JL, Hill SL, Cheatham JP. Stenting complex aortic arch obstructions. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2008;71:375-382. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 31] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Pushparajah K, Sadiq M, Brzezińska-Rajszys G, Thomson J, Rosenthal E, Qureshi SA. Endovascular stenting in transverse aortic arch hypoplasia. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;82:E491-E499. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 7] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Forbes TJ, Kim DW, Du W, Turner DR, Holzer R, Amin Z, Hijazi Z, Ghasemi A, Rome JJ, Nykanen D, Zahn E, Cowley C, Hoyer M, Waight D, Gruenstein D, Javois A, Foerster S, Kreutzer J, Sullivan N, Khan A, Owada C, Hagler D, Lim S, Canter J, Zellers T; CCISC Investigators. Comparison of surgical, stent, and balloon angioplasty treatment of native coarctation of the aorta: an observational study by the CCISC (Congenital Cardiovascular Interventional Study Consortium). J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58:2664-2674. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 200] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 152] [Article Influence: 12.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Gewillig M, Budts W, Boshoff D, Maleux G. Percutaneous interventions of the aorta. Future Cardiol. 2012;8:251-269. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 12] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Henry BM, Hsieh WC, Sanna B, Vikse J, Taterra D, Tomaszewski KA. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Comorbidities of Vocal Cord Paralysis After Surgical Closure of a Patent Ductus Arteriosus: A Meta-analysis. Pediatr Cardiol. 2019;40:116-125. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 32] [Article Influence: 6.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Assaqqat M, Siblini G, Fadley FA. Hoarseness after pulmonary arterial stenting and occlusion of the arterial duct. Cardiol Young. 2003;13:302-304. [PubMed] [Cited in This Article: ] |
| 9. | Baek SM, Chung H, Kim GB, Song MK, Bae EJ, Noh CI. Vocal Cord Palsy after Left Pulmonary Artery Stent Insertion. Chonnam Med J. 2018;54:72-73. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Kobayashi D, Turner DR, Humes RA. Left recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy secondary to left pulmonary artery stent in a child. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;80:482-484. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 4] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Liang CD, Ko SF, Huang SC, Huang CF, Niu CK. Vocal cord paralysis after transcatheter coil embolization of patent ductus arteriosus. Am Heart J. 2003;146:367-371. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 25] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Javois AJ, Patel D, Roberson D, Husayni T. Pre-existing left pulmonary artery stenosis and other anomalies associated with device occlusion of patent ductus arteriosus. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2007;70:83-89. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 5] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Pham V, Connelly D, Wei JL, Sykes KJ, O'Brien J. Vocal cord paralysis and Dysphagia after aortic arch reconstruction and Norwood procedure. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;150:827-833. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 36] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Ohta N, Kuratani T, Mori T. Vocal cord paralysis after aortic arch surgery with stent-graft placement, a contemporary method of arch surgery. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45:866. [PubMed] [DOI] [Cited in This Article: ] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in F6Publishing: 3] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |