Article contents
Multiplication Formulas and Canonical Bases for Quantum Affine gln
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 20 November 2018
Abstract
We will give a representation-theoretic proof for the multiplication formula in the Ringel-Hall algebra  $\mathfrak{H}\vartriangle \,(n)$
of a cyclic quiver
$\mathfrak{H}\vartriangle \,(n)$
of a cyclic quiver  $\Delta \,(n)$. As a first application, we see immediately the existence of Hall polynomials for cyclic quivers, a fact established by J. Y. Guo and C. M. Ringel, and derive a recursive formula to compute them. We will further use the formula and the construction of a monomial basis for
$\Delta \,(n)$. As a first application, we see immediately the existence of Hall polynomials for cyclic quivers, a fact established by J. Y. Guo and C. M. Ringel, and derive a recursive formula to compute them. We will further use the formula and the construction of a monomial basis for  $\mathfrak{H}\vartriangle \,(n)$ given by Deng, Du, and Xiao together with the double Ringel-Hall algebra realisation of the quantum loop algebra
$\mathfrak{H}\vartriangle \,(n)$ given by Deng, Du, and Xiao together with the double Ringel-Hall algebra realisation of the quantum loop algebra 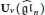 ${{U}_{v}}({{\widehat{\mathfrak{g}\mathfrak{l}}}_{n}})$ given by Deng, Du, and Fu to develop some algorithms and to compute the canonical basis for
${{U}_{v}}({{\widehat{\mathfrak{g}\mathfrak{l}}}_{n}})$ given by Deng, Du, and Fu to develop some algorithms and to compute the canonical basis for 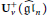 $U_{v}^{+}({{\widehat{\mathfrak{g}\mathfrak{l}}}_{n}})$. As examples, we will show explicitly the part of the canonical basis associated with modules of Lowey length at most 2 for the quantum group
$U_{v}^{+}({{\widehat{\mathfrak{g}\mathfrak{l}}}_{n}})$. As examples, we will show explicitly the part of the canonical basis associated with modules of Lowey length at most 2 for the quantum group  ${{U}_{v}}({{\widehat{\mathfrak{g}\mathfrak{l}}}_{2}})$.
${{U}_{v}}({{\widehat{\mathfrak{g}\mathfrak{l}}}_{2}})$.
- Type
- Research Article
- Information
- Copyright
- Copyright © Canadian Mathematical Society 2018
References
- 2
- Cited by




