Abstract
Background
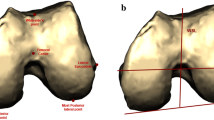
Optimal femoral component rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is crucial to establish a balanced knee reconstruction. Unbalanced knees can lead to instability, patellofemoral problems, persistent pain, stiffness, and generally poorer outcomes including early failure. Intraoperative techniques to achieve this optimal femoral component rotation include the use of the transepicondylar axis (TEA), the posterior-condylar-cut-parallel-to-the-tibial-cut (PCCPTC) technique and the anteroposterior axis technique (Whiteside’s line). The purpose of this study was to compare the PCCPTC technique to the TEA technique using computed tomography (CT) scans to assess femoral component rotational alignment.
Materials and Methods
This study used postoperative CT scans to compare the degree of femoral component rotation obtained with the use of PCCPTC technique and the TEA. The femoral component rotation of 30 TKA was measured on postoperative CT scans the angle of deviation between the two lines radiographic trans-epicondylar axis (rTEA) and femoral prosthesis posterior condylar line (FPPCL) was determined. This angle represented the rotation of the femoral component relative to the true rTEA.
Results
The degree of rotation measured 2.67 ± 1.11 degrees in the PCCPTC group and 5.60 ± 1.64 degrees in the TEA group.
Conclusion
The use of the TEA technique for determining rotational alignment in TKR results in excessive external rotation of the femoral component compared to the PCCPTC technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anouchi YS, Whiteside LA, Kaiser AD, Milliano MT. The effects of axial rotational alignment of the femoral component on knee stability and patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty demonstrated on autopsy specimens. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;287:170–7.
Insall JN. Surgery of the knee. 2nd ed. New York: Churchil Livingstone; 1993.
Moreland JR. Mechanisms of failure in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1988;226:49–64.
Barrack RL, Schrader T, Bertot AJ, Wolfe MW, Myers L. Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2001;392:46–55.
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE. Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1998;356:144–53.
Fehring TK. Rotational malalignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2000;380:72–9.
Insall JN, Scuderi GR, Komistek RD, Math K, Dennis DA, Anderson DT. Correlation between condylar lift-off and femoral component alignment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002;403:143–52.
Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, Urabe K, Hirata G, Iwamoto Y. Effect of femoral and tibial component position on patellar tracking following total knee arthroplasty: 10-year followup of Miller-Galante I knees. Am J Knee Surg 2001;14:152–6.
Romero J, Stähelin T, Wyss T, Hofmann S. Significance of axial rotation alignment of components of knee prostheses. Orthopade 2003;32:461–8.
Scuderi GR, Komistek RD, Dennis DA, Insall JN. The impact of femoral component rotational alignment on condylar lift-off. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2003;410:148–54.
Berger RA, Rubash HE, Seel MJ, Thompson WH, Crossett LS. Determining the rotational alignment of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty using the epicondylar axis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;286:40–7.
Scuderi Gr IJ. The posterior stabilised knee prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg 1989;74A:980–6.
Stiehl JB, Cherveny PM. Femoral rotational alignment using the tibial shaft axis in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1996;331:47–55.
Olcott CW Scott RD. The Ranawat Award. Femoral component rotation during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999;367:39–42.
Whiteside LA, Arima J. The anteroposterior axis for femoral rotational alignment in valgus total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1995;321:168–72.
Bland JM. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between 2 methods of clinical agreement. Lancet 1986; 1:307–10.
Matsuda S, Miura H, Nagamine R, Urabe K, Harimaya K, Matsunobu T, et al. Changes in knee alignment after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 1999;14:566–70.
Windsor RE SG, Moran MC, Insall JN. Mechanism of failure of the femoral and tibial component in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 1989;248:15–9.
Figgie HE 3rd, Goldberg VM, Figgie MP, Inglis AE, Kelly M, Sobel M. The effect of alignment of implant on fracture of patella after condylar total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 1989;71A: 1031–9.
Mochizuki RM. Patellar complications following total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 1979;61A: 879–83.
Rhoads DD, Noble PC, Reuben JD, Tullos HS. The effect of femoral component position on the kinematics of total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;286:122–9.
Hungerford DS, Krackow KA. Total joint arthroplasty of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1985;192:23–33.
Hollister AM, Jatana S, Singh AK, Sullivan WW, Lupichuk AG. The axes of rotation of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;290:259–68.
Kim BS, Reitman RD, Schai PA, Scott RD. Selective patellar non resurfacing in total knee arthroplasty: 10 year results. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999;367:81–8.
Katz MA, Beck TD, Silber JS, Seldes RM, Lotke PA. Determining femoral rotational alignment in total knee arthroplasty: Reliability of techniques. J Arthroplasty 2001;16:301–5.
Yau WP, Chiu KY, Tang WM. How precise is the determination of rotational alignment of the femoral prosthesis in total knee arthroplasty: An in vivo study. J Arthroplasty 2007;22:1042–8.
Yan CH, Yau WP, Ng TP, Lie WH, Chiu KY, Tang WM. Interand intra-observer errors in identifying the transepicondylar axis and Whiteside’s line. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2008;16:316–20.
Churchill Dl IS, Johnson CC, Beynnon BD. The transepicondylar axis approximates the optimal flexion axis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1998;356:111–8.
Arima J, Whiteside LA, McCarthy DS, White SE. Femoral rotational alignment, based on the anteroposterior axis, in total knee arthroplasty in a valgus knee. A technical note. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77:1331–4.
Yoshino N, Takai S, Ohtsuki Y, Hirasawa Y. Computed tomography measurement of the surgical and clinical transepicondylar axis of the distal femur in osteoarthritic knees. J Arthroplasty 2001;16:493–497.
Winemaker MJ. Perfect balance in total knee arthroplasty: The elusive compromise. J Arthroplasty 2002;17:2–10.
Stiehl JB, Abbott BD. Morphology of the transepicondylar axis and its application in primary and revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 1995;10:785–9.
Berger RA, Seel MJ, Schleiden M, Britton CA, Crossett LS, Rubash HE. Determination of femoral component rotation in total knee arthroplasty using computed tomography. Orthop Trans 1993;17:1174.
Jazrawi LM, Birdzell L, Kummer FJ, Di Cesare PE. The use of computed tomography for determining femoral and tibial total knee arthroplasty component rotation. Proceedings of the sixth annual meeting of American academy of orthopedic surgeons, Rosemont, IL. 1999.
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1989;248:13–4.
Berger RA, Crossett LS. Determining the rotation of the femoral and tibial components in total knee arthroplasty: A computer tomography technique. Oper Tech Orthop 1998;8:128–33.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaidya, S.V., Gadhiya, R.M., Bagaria, V. et al. Computed tomographic evaluation of femoral component rotation in total knee arthroplasty. IJOO 47, 40–44 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.106898
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.106898