| [1]Wai IH, Ui Gani N,Yaseen M, et al. Operative management of distal tibial extra-articalar fractures-intramedul lary nail versus minmally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil. 2017;19(6):537-541.[2]Vaienti E, Schiavi P, Ceccarelli F, et al. Treatment of distal tibial fractures: prospective comparative study evaluating two surgical procedures with investigation for predictive factors of unfavourable outcome. Int Orthop. 2019;43(1):201-207. [3]Daolagupu AK, Mudgal A, Agarwala V, et al. A Comparative study of intramedullary interlocking nailling and minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis inextra articular distal tibial fractures. Indian J Orthop. 2017;51(3):292-298.[4]Maredza M, Petrou S, Dritsaki M, et al. Acomparison of the cost-effectiveness of in tramedullary nail fixation and locking plate ication in the treatment of adult patients with anextra-articular fracture of the dital tibia. Bone Joint J. 2018;100B(5):624-633.[5]Costa ML, Achten J, Griffin J, et al. Effect of locking plate fixations vs intramedullary nail fixation on 6-month disability among adult with displaced fracture of the distal tibia the UK FixDT randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;318(18): 1767-1776. [6]钟华,朱智敏,刘立华.MIPPO技术下LCP锁定和加压固定后应力遮挡的有限元研究[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(3): 213-216.[7]李赞罡,陈为坚,李贵涛.不同运动步态下锁定加压钢板固定胫骨干骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4): 612-619.[8]刘易军,宫赫,刘百奇,等.胫骨上端外部形状及内部结构的模拟[J].中国生物医学工程学,2006,25(5):563-579.[9]Sitthiseripratip K, Van Oosterwyck H, Vander Sloten J, et al. Finite element study of trochanteric gamma nail for trochanteric fracture. Med Eng Phys. 2003;25(2):99-106.[10]李维新,袁斌云.跟骨骨折锁定钢板内固定与普通钢板内固定的有限元分析[J].中医正骨,2013,25(4):10-11.[11]Galloway F, Kahnt M, Ramm H, et al. A Large scale finite element study of a cementless ossointegrated tibial tray. J Biomech. 2013;46(11):1900-1906.[12]Wong C, Mikkelsen P, Hansen LB, et al. Finite element analysis of tibial fractures. Dan Med Ball. 2010;57(5):A4148.[13]Chen FC, Huang XW, Ya YS, et al. Finite element analysis of intramedullary nailing and double locking plate for treating extra-articular proximal tibial fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):2-8.[14]Atmaca H, Ozkan A, Matla I, et al. The effect of proximal tibial corrective osteotomy on menisci tibia and tarsal bones: a finit element model study of tibia vara. Int J Med Robot. 2014; 10(1):93-97.[15]Sawatari T, Tsamura H, Iesaka K, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty the influence of tibial component inclination. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(3):541-554.[16]Sowmianarayanan S, Chandrasekaran A, Kumar RK. Finite element analysis of a subtrochanteric fractured femur with dynamic hip screw, dynamic condylar screw, and proximal femur nail implants a comparative study. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(1):117-127.[17]马童,蔡珉巍,涂意辉,等.经皮微创钢板固定技术Meta接骨板治疗胫骨远端干骺端骨折[J].生物骨科材料与临床研究,2011,8(3): 30-34. [18]赵勇,申才佳,李勇,等.胫骨远端前外侧解剖型钢板治疗不稳定性Pilon骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2013,15(6):666-667. [19]Kuo LT, Chi CC, Chuang CH. Surgical interventions for treating distal tibial metaphyseal fractures in adultes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;(3):CD010261.[20]Beytemur O, Barl A, Albay C, et al. Comparison of intramedullary nailing and minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis in the treatment of simple intra-articular fractures of the distal tibia (AO-OTA type43C1-C2). Acta orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017;51(1):12-16.[21]Guo C, Ma J, Ma X, et al. Comparing intramedullary nailing and plate fixation for treating distal tibail fractures: ameta-analysis of randomizedcontroll edtrials. Int J Surg. 2018;53:5-11. [22]Lai TC, Fleming JJ. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis for distal tibia fractures. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2018;35(2): 223-232.[23]Redfern DJ, Syed SU, Davies SJ. Fractures of the distal tibia:minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 2004; 35(6):615-620.[24]Park KC, Oh CW, Kim JW, et al. Minimally invasive plate augmentation in the treatment of long bone non unions. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2017;137(11):8-18.[25]Nork SE, Schwartz AK, Agel J, et al. Intramedullary nailing of distal meta physeal tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87(6):1213-1221.[26]Shukla R, Jain N, Jain RK, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using locking plates for AO 43-type fractures lessons learnt from a prospective study. Foot Ankle Spec. 2018;11(3):1-5.[27]Bisaccia M, Cappiello A, Meccariello L, et al. Nail orplate in the management of distal extra-articular tibial fracture, what is better? Valutation of out comes. SICOT J. 2018;4:2.[28]Guo C, Ma J, Ma X, et al. Comparing intramedullary nailing and plate fixation for treating distal tibail fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Surg. 2018;53:5-11.[29]Wang Z, Cheng Y, Xin D, et al. Expert tibial nails for treating distal tibial fractures with soft tissue damage: apatient series. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(6):1232-1235.[30]Oken OF, Yildirim AO, Asilturk M, et al. Finite element analysis of the stability of AO/OTA 43-C1 type distal tibial fractures treated with distal tibia medial anatomic plate versus anterolateral anatomic plate. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2017;51(5):1-5.[31]Garg S, Khanna V, Goyal MP, et al. Comparative prospective study between medial and lateral distal tibial locking compression plates for distal third tibia fractures. Chin J Traumatol. 2017;20(3):151-154.[32]Choudhari P, Padia D. Minimally invasive osteosynthesis of distal tibia fractures using anterolateral locking plate. Malays Orthop J. 2018;12(3):38-42.[33]Muzaffar N, Bhat R, Yasin M. Complications of minmally invasive percutaneous plating for distal tibail fractures. Trauma Mon. 2016;21(3):e22131.[34]Akra GA, Lazarides S, Nanu AM. Early results of minimally invasive percutaneou splate osteosynthesis for fractures of the distal tibia; aretrospective case series and review of the literature. Clin Med Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;10:1179544117701724.[35]Kim JW, Kim HU, Oh CW, et al. A prospective randomized study on operative treatment for simple distal tibial fractures-minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis versus minimal open reduction and inter nail fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32(1):e19-e24. |
.jpg)
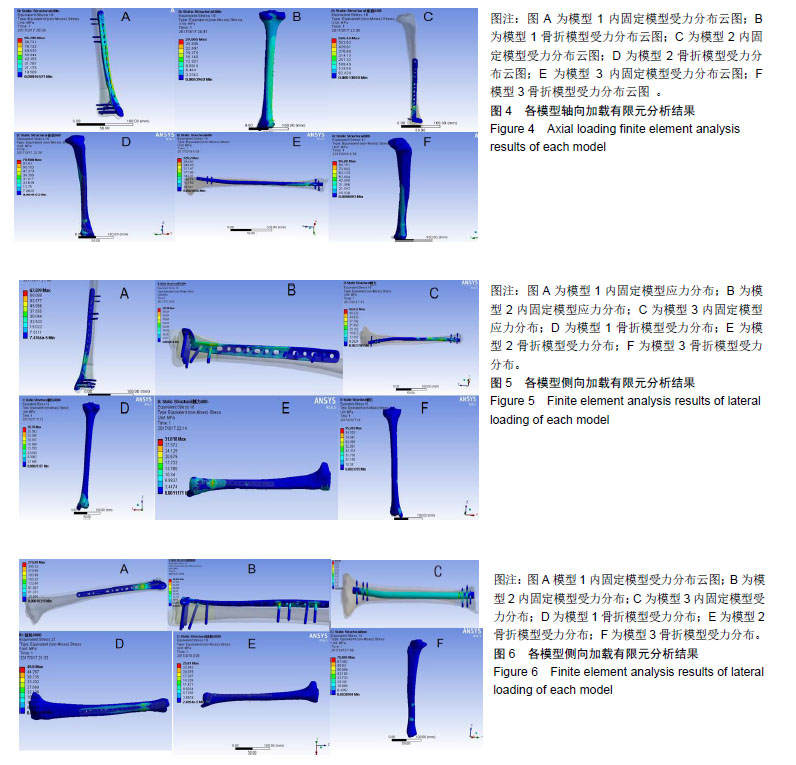
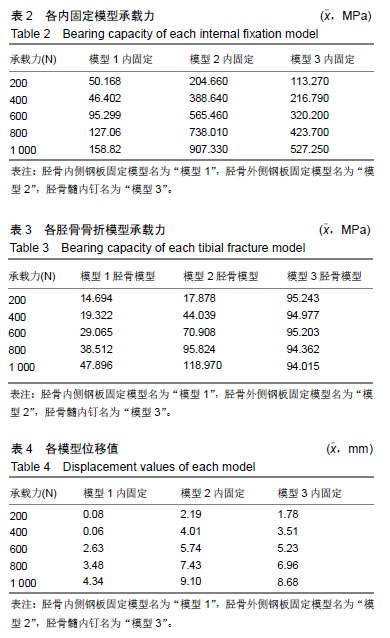

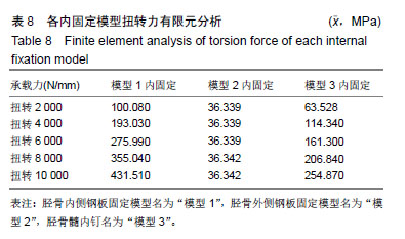

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)