Abstract
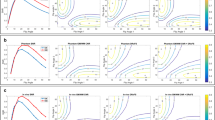
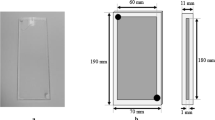
In this study, we compared the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and the geometric accuracy between conventional-bore and wide-bore 3-T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) by using both balanced fast field echo (bFFE) and turbo spin-echo (TSE) pulse sequences with a large field of view (FOV). A large-diameter phantom was scanned using clinical 60-cm conventional-bore and 70-cm wide-bore scanners. The signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) of both the bFFE and the TSE pulse sequences were calculated for each MR scanner for various acceleration factors (AFs). The diameter of the phantom was measured in four directions to evaluate the geometric accuracy. The SNR values were found to increase as the FOV increased for both the conventional- and the wide-bore scanners. No statistically significant differences in the SNR and the geometric accuracy were observed in either sequences between the two bores (p > 0.05), although the image noise tended to increase as the AF of both bores increased. Wide-bore MRI using a large FOV can provide a SNR and a geometric accuracy comparable to those of conventional-bore MRI, despite the increase in the image noise as the AF of both bores is increased.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. H. Hunt et al., Clin. Neuroradiol. 21, 141 (2011).
C. Bangard et al., Eur. J. Radiol. 64, 152 (2007).
J. Stattaus et al., Eur. Radiol. 18, 2865 (2008).
G. Koch et al., J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 29, 285 (2018).
T. Torfeh et al., Magn. Reson. Imaging 33, 939 (2015).
S. Saito, K. Tanaka and T. Hashido, Radiol. Phys. Technol. 9, 154 (2016).
G. P. Liney et al., Br. J. Radiol. 86, 20130150 (2013).
H. Nakazawa et al., J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 58, 595 (2014).
R. G. Price et al., J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 18, 51 (2017).
N. Schieda et al., Magn. Reson. Imaging 45, 11 (2017).
O. Bieri and K. J. Scheffler, Magn. Reson. Imaging 38, 2 (2013).
D. C. Zhu and R. D. Penn, Magn. Reson. Med. 54, 725 (2005).
H. Lu et al., J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 22, 13 (2005).
S. S. Kaushik et al., J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 45, 51 (2017).
F. L. Goerner and G. D. Clarke, Med. Phys. 38, 5049 (2011).
R. R. Price et al., Med. Phys. 17, 287 (1990).
Z. Wang et al., IEEE. T. Image Process 13, 600 (2004).
T. Yoshida et al., Br. J. Radiol. 89, 20160512 (2016).
G. B. Chavhan et al., Radiographics 28, 1147 (2008).
D. Wang et al., Magn. Reson. Imaging 22, 211 (2004).
C. P. Karger et al., Phys. Med. Biol. 51, 253 (2006).
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a Korea University Graduate School Junior Fellow Research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, JS., Lee, HB., Lee, KB. et al. Comparison of the Signal-to-Noise Ratio and the Geometric Accuracy between Conventional-Magnetic Bore and Wide-Magnetic Bore 3-T Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 76, 59–65 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.76.59
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3938/jkps.76.59