Export citation and abstract BibTeX RIS
We have detected the  line of A-species methanol at 2502.784 MHz (Heuvel & Dymanus 1973; Xu & Lovas 1997) using the Nançay Radio Telescope,6
toward Sgr B2. The elliptic beam from this large telescope has HPBWs of 2
line of A-species methanol at 2502.784 MHz (Heuvel & Dymanus 1973; Xu & Lovas 1997) using the Nançay Radio Telescope,6
toward Sgr B2. The elliptic beam from this large telescope has HPBWs of 2 2 × 11'—the major axis being aligned with the local vertical—which was large enough to include all the (M), (S), and (N) substructures of the source (Benson & Johnston 1984). The measurements were conducted in a sequence of 1 hr observations around local source transit in 2016 July/August and 2017 April using a sky symmetric position switching scheme where the observation is timed so that the on- and off-positions are observed along the same azimuth/elevation track in the local sky. The off position used was located approximately 21.3 arcminutes east of Sgr B2 and some tests were done with different throws to try to eliminate the possibility of off-beam contamination. A set of overlapping pointings were done in order to estimate the source size along the R.A. coordinate, see Figure 1.
2 × 11'—the major axis being aligned with the local vertical—which was large enough to include all the (M), (S), and (N) substructures of the source (Benson & Johnston 1984). The measurements were conducted in a sequence of 1 hr observations around local source transit in 2016 July/August and 2017 April using a sky symmetric position switching scheme where the observation is timed so that the on- and off-positions are observed along the same azimuth/elevation track in the local sky. The off position used was located approximately 21.3 arcminutes east of Sgr B2 and some tests were done with different throws to try to eliminate the possibility of off-beam contamination. A set of overlapping pointings were done in order to estimate the source size along the R.A. coordinate, see Figure 1.
Figure 1. Integrated intensities along a strip of five positions with half-beam spacing centered on Sgr B2. The superimposed fit shows that the distribution is consistent with a Gaussian source considerably smaller than the beam size of 132 arcseconds. The vertical errors include baseline noise and an adopted 10% calibration uncertainty. The horizontal bars correspond to the estimated pointing error. The center spectrum at the top has  as spectral axis and is resampled to 1 km s−1 channel−1. It was observed at the equatorial coordinates 17h47m20
as spectral axis and is resampled to 1 km s−1 channel−1. It was observed at the equatorial coordinates 17h47m20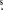 5, −28°23'06
5, −28°23'06 0 (J2000). Third order polynomial baselines were subtracted in the velocity range −245 to +125 km s−1. Note that the flux density numbers pertain to the noise weighted average of two circular polarization components.
0 (J2000). Third order polynomial baselines were subtracted in the velocity range −245 to +125 km s−1. Note that the flux density numbers pertain to the noise weighted average of two circular polarization components.
Download figure:
Standard image High-resolution imageOur search for this line was motivated by the fact that the lower sibling transition at 834 MHz (Radford 1972) had only been detected in the Milky Way center sources Sgr B2 and Sgr A* (Ball et al. 1970), and that there was a detection of the higher related transition,7 near 5 GHz, reported by Robinson et al. (1974) and Mezger & Smith (1976) in Sgr B2. To our knowledge, observations of the 2.5 GHz line have not been reported before.
Analysis of the results will appear in a later publication but we note here that the source appears rather compact as compared to what is suggested by the 834 MHz map by Gottlieb et al. (1979). The line profile properties are similar to the 834 MHz line, and it also shows a remarkable likeness—in an inverted sense—to the absorption line at 12.2 GHz (Whiteoak et al. 1988).
A search for this line was also conducted toward Orion-KL where narrower lines can be expected and thus a possibility to resolve the hyperfine structure of these lines existed. The effort did not yield any detection down to a 1σ level of about 20 mJy (at 1 km s−1 resolution).
We thank Université d'Orléans for the funding contribution to AOHO's site visit, and the Paris Observatory for facilitating an internship for LB as well as a temporary affiliation for AOHO. We are also grateful to observatory staff J-M Martin, P Colomb, and E Gérard for technical advice.
Footnotes
- 6
http://nrt.obspm.fr/, affiliated with l'Observatoire de Paris.
- 7






