Abstract
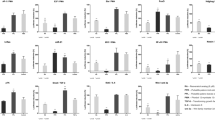
Deoxypodophyllotoxin (DPPT), a natural flavolignan, exhibits anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor activities. However, the molecular mechanism of DPPT underlying the modulation of cell cycle progression is currently unknown. In this study, we determined the effect of DPPT isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris roots on the expression of cell cycle-regulatory proteins. We observed that DPPT treatment induced the arrest of cell cycle at the G2/M phase in HeLa cervix carcinoma cells. Immunoblot experiments demonstrated that DPPT causes the phosphorylation of ERK MAPK and p21Wafl/Cipl as well as up-regulation of PLK1 and cyclinBl. This is accompanied by the activation of Cdc25C and Cdk1. These data suggest that DPPT may have a potential effect in the cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase through the activation of the Cdk1/cyclinB1 complex through Cdc25C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann KH, and Gertsch J (2007) Anticancer drugs from nature--natural products as a unique source of new microtubule-stabilizing agents. Nat Prod Rep 24, 327–357.
Bhalla K (2003) Microtubule-targeted anticancer agents and apoptosis. Oncogene 22, 9075–9086.
Dash BC and El-Deiry WS (2005) Phosphorylation of p21 in G2/M promotes cyclin B-Cdc2 kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol 25, 3364–3387.
Gallagher ^Jr B (2007) Microtubule-stabilizing natural products as promising cancer therapeutics. Curr Med Chem 14, 2959–2967.
Gautier J, Solomon MJ, Booher RN, Bazan JF, and Kirschner MW (1991) cdc25 is a specific tyrosine phosphatase that directly activates p34cdc2. Cell 67, 197–211.
Gordaliza M, Garcia PA, del Corral JM, Castro MA, and Gômez-Zurita MA (2004) Podophyllotoxin: distribution, sources, applications and new cytotoxic derivatives. Toxicon 44, 441–459.
Hamanaka R, Smith M, O’Connor P, Maloid S, Mihalic K, Spivak J, Longo D, and Ferris, D. (1995) Polo-like kinase is a cell cycle-regulated kinase activated during mitosis. J Biol Chem 270, 21086–21091.
Holloway SL, Glotzer M, King RW, and Murray AW (1993) Anaphase is initiated by proteolysis rather than by the inactivation of maturation-promoting factor. Cell 73, 1393–1402.
Ikeda R, Nagao T, Okabe H, Nakano Y, Matsunaga H, Katano M, and Mori M (1998) Antiproliferative constituents in umbelliferae plants. III. Constituents in the root and the ground part of Anthriscus sylvestris Hoffrn. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 46, 871–874.
Imbert T (1998) Discovery of podophyllotoxins. Biochimie 80, 207–222.
Jordan MA, and Wilson L (2004) Microtubules as a target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer 4, 253–265.
Kim Y, Kim SB, You YJ, and Ahn BZ (2002) Deoxypodophyllotoxin; the cytotoxic and antiangiogenic component from Pulsatilla koreana. Planta Med 68, 271–274.
Lew DJ, and Kornbluth S (1996) Regulatory roles of cyclin dependent kinase phosphorylation in cell cycle control. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8, 795–804.
Liu F, Stanton JJ, Wu Z, and Piwnica-Worms H (1997) The human Mytl kinase preferentially phosphorylates Cdc2 on threonine 14 and localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi complex. Mol Cell Biol 17, 571–583.
Loike JD, Brewer CF, Sternlicht H, Gensler WJ, and Horwitz SB (1978) Structure-activity study of the inhibition of microtubule assembly in vitro by podophyllotoxin and its congeners. Cancer Res 38, 2688–2693.
Malumbres M, and Barbacid M (2005). Mammalian cyclindependent kinases. Trends Biochem Soci 30, 630–641.
Margolis RL, and Wilson L (1998) Microtubule treadmilling: what goes around comes around. Bioessays 20, 830–836.
Masuda T, Oyama Y, Yonemori S, Takeda Y, Yamazaki Y, Mizuguchi S, Nakata M, Tanaka T, Chikahisa L, Inaba Y, and Okada Y (2002) Flow cytometric estimation on cytotoxic activity of leaf extracts from seashore plants in subtropical Japan: Isolation, quantification and cytotoxic action of (-)-deoxypodophyllotoxin. Phytother Res 16, 353–358.
McGowan CH, and Russell P (1993) Human Weel kinase inhibits cell division by phosphorylating p34cdc2 exclusively on Tyrl5. EMBO J 12, 75–85.
Muto N, Tomokuni T, Haramoto M, Tatemoto H, Nakanishi T, Inatomi Y, Murata H, and Inada A (2008) Isolation of apoptosis-and differentiation-inducing substances toward human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells from leaves of Juniperus taxifolia. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72, 477–484.
Nilsson I, and Hoffmann I (1998) Cell cycle regulation by the Cdc25 phosphatase family. Prog Cell Cycle Res 4, 107–114.
Nurse P (1990) Universal control mechanism regulating onset of M-phase. Nature 344, 503–508.
Roshak A, Capper E, Imburgia C, Fornwald J, Scott G, and Marshall L (2000) The human polo-like kinase, PLK, regulates cdc2/cyclin B through phosphorylation and activation of the cdc25C phosphatase. Cell Signal 12, 405–411.
Schmidt M, and Bastians H (2007) Mitotic drug targets and the development of novel anti-mitotic anticancer drugs. Drug Resist Updat 10, 162–181.
Shin SY, Yong Y, Kim CG, Lee YH, and Lim Y (2009) Deoxypodophyllotoxin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HeLa cells. Cancer Lett 287, 231–239.
Subrahmanyam D, Renuka B, Kumar GS, Vandana V, and Deevi DS (1999) 9-Deoxopodophyllotoxin derivatives as anti-cancer agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 9, 2131–2134.
Tamemoto H, Kadowaki T, Tobe K, Ueki K, Izumi T, Chatani Y, Kohno M, Kasuga M, Yazaki Y, and Akanuma Y (1992) Biphasic activation of two mitogenactivated protein kinases during the cell cycle in mammalian cells. J Biol Chem 267, 20293–20297.
van Leuken R, Clijsters L, and Wolthuis R (2008) To cell cycle, swing the APC/C. Biochim Biophys Acta 1786, 49–59.
Wang R, He G, Nelman-Gonzalez M, Ashorn CL, Gallick GE, Stukenberg PT, Kirschner MW, and Kuang J (2007) Regulation of Cdc25C by ERK-MAP Kinases during the G2/M Transition. Cell 128, 1119–1132.
Yong Y, Shin SY, Lee YH, and Lim Y (2009) Antitumor activity of deoxypodophyllotoxin isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris: Induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest and caspase-dependent apoptosis. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19, 4367–4371.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, S.Y., Yong, Y. & Lee, Y.H. Effect of deoxypodophyllotoxin isolated from Anthriscus sylvestris roots on the expression of cell cycle-regulatory proteins in hela cells. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 53, 304–309 (2010). https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2010.047
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3839/jksabc.2010.047