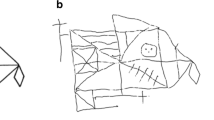
Abstract
Neuropsychological evidence suggests that visuospatial memory is subserved by two separable processing systems, with dorsal underpinnings for global form and ventral underpinnings for the integration of part elements. Previous drawing studies have explored the effects of Gestalt organisation upon memory for hierarchical stimuli, and we here present an exploratory study of an apraxic dorsal stream patient’s (MH) performance. We presented MH with a stimulus set (previously reported by Riddoch et al., Cognitive Neuropsychology, 20(7), 641-671, 2003) and devised a novel quantitative scoring system to obtain a finer grain of insight into performance. Stimuli possessed either good or poor Gestalt qualities and were reproduced in a copy condition and two visual memory conditions (with unlimited viewing before the model was removed, or with 3 s viewing). MH’s copying performance was impaired in comparison to younger adult and age-matched older adult controls, with a variety of errors at the local level but relatively few at the global level. However, his performance in the visual memory conditions revealed impairments at the global level. For all participants, drawing errors were modulated by the Gestalt qualities of the stimuli, with accuracy at the global and local levels being lesser for poor global stimuli in all conditions. These data extend previous observations of this patient, and support theories that posit interaction between dorsal and ventral streams in the representation of hierarchical stimuli. We discuss the implications of these findings for our understanding of visuospatial memory in neurological patients, and also evaluate the application of quantitative metrics to the interpretation of drawings.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akshoomoff, N. A., Feroleto, C. C., Doyle, R. E., & Stiles, J. (2002). The impact of early unilateral brain injury on perceptual organization and visual memory. Neuropsychologia, 40(5), 539–561.
Alvarez, G. A., & Cavanagh, P. (2004). The capacity of visual short-term memory is set both by visual information load and by number of objects. Psychological Science, 15, 106–111.
Atkinson, J., King, J., Braddick, O., Nokes, L., Anker, S., & Braddick, F. (1997). A specific deficit of dorsal stream function in Williams’ syndrome. Neuroreport, 8(8), 1919–1922.
Ayzenberg, V., & Behrmann, M. (2022). The dorsal visual pathway represents object-centered spatial relations for object recognition. Journal of Neuroscience, 42(23), 4693–4710.
Broderick, P., & Laszlo, J. I. (1987). The drawing of squares and diamonds: A perceptual-motor task analysis. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 43(1), 44–61.
Carson, L., Filipowicz, A., Anderson, B., & Danckert, J. (2019). Representational drawing following brain injury. Neuropsychologia, 133,
Cohen, L. L., Feinstein, A., Masuda, A., & Vowles, K. E. (2014). Single-case research design in pediatric psychology: Considerations regarding data analysis. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 39(2), 124–137.
Crawford, J. R., Garthwaite, P. H., & Porter, S. (2010). Point and interval estimates of effect sizes for the case-controls design in neuropsychology: Rationale, methods, implementations, and proposed reporting standards. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 27, 245–260.
Crawford, J. R., & Garthwaite, P. H. (2012). Single-case research in neuropsychology: a comparison of five forms of t-test for comparing a case to controls. Cortex, 48(8), 1009–1016.
Elkins, R. J., Filley, J. L., & Roeltgen, R. C. (1992). Drawing ability in apraxia: a comparison of the diagnostic utility of three scoring systems. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 14(6), 991–1005.
Etherton, J. L., & Axelrod, B. N. (2013). Do administration instructions alter optimal neuropsychological test performance? Data from healthy volunteers. Applied Neuropsychology: Adult, 20(1), 15–19.
Fornara, G. A., Di Cristofori, A., Bertani, G. A., Carrabba, G., & Zarino, B. (2018). Constructional apraxia in older patients with brain tumors: Considerations with an up-to-date review of the literature. World Neurosurgery, 114, e1130–e1137.
Gagnon, M., Awad, N., Mertens, V. B., & Messier, C. (2003). Comparing the Rey and Taylor complex figures: A test-retest study in young and older adults. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 25(6), 878–890.
Gainotti, G., D’Erme, P., & Diodato, S. (1985). Are drawing errors different in right-sided and left-sided constructional apraxics? Italian Journal of Neurological Sciences, 6, 495–501.
Gainotti, G., & Trojano, L. (2018). Constructional apraxia. Handbook of clinical neurology, 151, 331–348.
Georgiou-Karistianis, N., Tang, J., Mehmedbegovic, F., Farrow, M., Bradshaw, J., & Sheppard, D. (2006). Age-related differences in cognitive function using a global local hierarchical paradigm. Brain research, 1124(1), 86–95.
Goodale, M. A., Meenan, J. P., Bülthoff, H. H., Nicolle, D. A., Murphy, K. J., & Racicot, C. I. (1994). Separate neural pathways for the visual analysis of object shape in perception and prehension. Current Biology, 4(7), 604–610.
Goodale, M. A., Milner, A. D., Jakobson, L. S., & Carey, D. P. (1991). A neurological dissociation
between perceiving objects and grasping them. Nature, 349, 154–156.
Greene, J. D. W. (2005). Apraxia, agnosias, and higher visual function abnormalities. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 76(suppl 5), v25–v34.
Halligan, P. W., & Marshall, J. C. (1993). The history and clinical presentation of neglect. In: Robertson IH, C. Marshall JC, editors. Unilateral neglect: clinical and experimental studies. Hove: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, pp. 3-25.
Hartman, M., & Potter, G. (1998). Sources of age differences on the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure test. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 12(4), 513–524.
Harvey, R. M., & Schatz, J. D. (2000). Apraxia of drawing in a patient with a right parietal lesion. Brain, 123(9), 1832–1848.
Hebart, M. N., & Hesselmann, G. (2012). What visual information is processed in the human dorsal stream? The Journal of Neuroscience, 32(24), 8107–8109.
Hécaen, H., & Assal, G. (1970). A comparison of constructive deficit following right and left hemispheric lesions. Neuropsychologia, 8, 289–303.
Helmes, E. (2013). Cognitive screening of older adults: the utility of pentagon drawing. International psychogeriatrics, 25(3), 413–419.
Humphreys, G. W. (1999). Integrative agnosia. Case studies in vision, 41-58.
Humphreys, G. W., & Riddoch, M. J. (2006). Features, objects, action: The cognitive neuropsychology of visual object processing, 1984–2004. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 23(1), 156–183.
Humphreys, G. W., & Riddoch, M. J. (2013). To see but not to see: A case study of visual agnosia. Psychology Press.
Kessels, R. P. (2019). Improving precision in neuropsychological assessment: Bridging the gap between classic paper-and-pencil tests and paradigms from cognitive neuroscience. The Clinical Neuropsychologist, 33(2), 357–368.
Kobourov, S. G., Mchedlidze, T., & Vonessen, L. (2015, September). Gestalt principles in graph drawing. In International Symposium on Graph Drawing (pp. 558-560). Springer, Cham.
Lamb, M. R., Robertson, L. C., & Knight, R. T. (1989). Attention and interference in the processing of global and local information: Effects of unilateral temporal-parietal junction lesions. Neuropsychologia, 27(4), 471–483.
Ledford, J. R., Lane, J. D., & Severini, K. E. (2017). Systematic use of visual analysis for assessing outcomes in single case design studies. Brain Impairment, 19(1), 4–17.
Leek, E. C., Rapp, B. C., & Turnbull, O. H. (2000). The analysis of drawing from memory performance in brain-damaged patients. Brain and Cognition, 43, 310–315.
Lehky, S. R., & Sereno, A. B. (2007). Comparison of shape encoding in primate dorsal and ventral visual pathways. Journal of Neurophysiology, 97(1), 307–319.
Lezak, M. D. (1995). Neuropsychological assessment (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press.
McConley, R., Martin, R., Banos, J., Blanton, P., & Faught, E. (2006). Global/local scoring modifications for the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure: Relation to unilateral temporal lobe epilepsy patients. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 12(3), 383–390.
McIntosh, R. D., & Brooks, J. L. (2011). Current tests and trends in single-case neuropsychology. Cortex, 47(10), 1151–1159.
Meyers, J. E., Volbrecht, M., Axelrod, B. N., & Reinsch-Boothby, L. (2011). Embedded symptom validity tests and overall neuropsychological test performance. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 26(1), 8–15.
Milner, A. D., & Goodale, M. A. (1995). The visual brain in action. Oxford University Press.
Mitchell, K. J., Johnson, M. K., Raye, C. L., & D’Esposito, M. (2000). fMRI evidence of age-related hippocampal dysfunction in feature binding in working memory. Cognitive Brain Research, 10, 197–206.
Montse, A., Pere, V., Carme, J., Francesc, V., & Eduardo, T. (2001). Visuospatial deficits in Parkinson’s disease assessed by judgment of line orientation test: Error analyses and practice effects. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 23(5), 592–598.
Osterrieth, P. A. (1944). Le test de copie d’une figure complexe. Archives of Psychology, 30, 206–356.
Papagno, C. (2002). Progressive impairment of constructional abilities: a visuospatial sketchpad deficit? Neuropsychologia, 40(12), 1858–1867.
Park, D. C., Polk, T. A., Mikels, J. A., Taylor, S. F., & Marshuetz, C. (2022). Cerebral aging: Integration of brain and behavioral models of cognitive function. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 3(3), 151–165.
Pellicano, E., Gibson, L., Maybery, M., Durkin, K., & Badcock, D. R. (2005). Abnormal global processing along the dorsal visual pathway in autism: a possible mechanism for weak visuospatial coherence? Neuropsychologia, 43(7), 1044–1053.
Rentz, D. M., Papp, K. V., Mayblyum, D. V., Sanchez, J. S., Klein, H., Souillard-Mandar, W., Sperling, R. A., & Johnson, K. A. (2021). Associations of digit clock drawing with PET amyloid and tau pathology in normal older adults. Neurology, 96(14), e1844–e1854.
Richardson, H. E., & Glass, J. N. (2002). A comparison of scoring protocols on the Clock Drawing Test in relation to ease of use, diagnostic group, and correlations with Mini-Mental State Examination. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 50(1), 169–173.
Riddoch, M. J., & Humphreys, G. W. (1987). A case of integrative visual agnosia. Brain, 110(6), 1431–1462.
Riddoch, M. J., Humphreys, G. W., Blott, W., Hardy, E., & Smith, A. D. (2003). Visual and spatial short-term memory in integrative agnosia. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 20(7), 641–671.
Riddoch, M. J., Humphreys, G. W., Jacobson, S., Pluck, G., Bateman, A., & Edwards, M. (2004). Impaired orientation discrimination and localisation following parietal damage: On the interplay between dorsal and ventral processes in visual perception. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 21(6), 597–623.
Robens, S., Heymann, P., Gienger, R., Hett, A., Müller, S., Laske, C., ... & Elbing, U. (2019). The digital tree drawing test for screening of early dementia: an explorative study comparing healthy controls, patients with mild cognitive impairment, and patients with early dementia of the Alzheimer type. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, 68(4), 1561-1574.
Roncato, S., Sartori, G., Masterson, J., & Rumiati, R. (1987). Constructional apraxia: An information processing analysis. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 4, 113–129.
Russell, C., Deidda, C., Malhotra, P., Crinion, J. T., Merola, S., & Husain, M. (2010). A deficit of spatial remapping in constructional apraxia after right-hemisphere stroke. Brain, 133(4), 1239–1251.
Schurgin, M. W. (2018). Visual memory, the long and the short of it: A review of visual working memory and long-term memory. Attention, Perception, & Psychophysics, 80(5), 1035–1056.
Shin, M. S., Park, S. Y., Park, S. R., Seol, S. H., & Kwon, J. S. (2006). Clinical and empirical applications of the Rey-Osterrieth complex figure test. Nature protocols, 1(2), 892–899.
SPSS (25). (2019). IBM SPSS statistics for Windows, Version 25.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.
Smith, A. D. (2009). On the use of drawing tasks in neuropsychological assessment. Neuropsychology, 23(2), 231.
Smith, A. D., & Gilchrist, I. D. (2005). Within-object and between-object coding deficits in drawing production. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 22(5), 523–537.
Smith, A. D., & Gilchrist, I. D. (2005). Drawing from childhood experience: constructional apraxia and the production of oblique lines. Cortex, 41(2), 195–204.
Smith, A. D., Gilchrist, I. D., Butler, S., & Harvey, M. (2006). Around the clock surveillance: Simple graphic disturbance in hemispatial neglect carries implications for the clock-drawing task. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 77, 407–409.
Smith, A. D., Gilchrist, I. D., Butler, S., Muir, K., Bone, I., Reeves, I., & Harvey, M. (2007). Non-lateralized deficits of drawing production in hemispatial neglect. Brain and Cognition, 64, 150–157.
Smith, A. D., Kenny, L., Rudnicka, A., Briscoe, J., & Pellicano, E. (2016). Drawing firmer conclusions: Autistic children show no evidence of a local processing bias in a controlled copying task. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 46, 3481–3492.
Stiles, J., Akshoomoff, N., & Haist, F. (2013). The Development of Visuospatial Processing. In: RUBENSTEIN J. L. R. and RAKIC P. (ed.) Comprehensive Developmental Neuroscience: Neural Circuit Development and Function in the Brain, volume 3, pp. 271-296 Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Streiner, D. L. (2003). Starting at the beginning: an introduction to coefficient alpha and internal consistency. Journal of personality assessment, 80(1), 99–103.
Trojano, L., & Gainotti, G. (2016). Drawing disorders in Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 53(1), 31–52.
Trojano, L., & Grossi, D. (1998). “Pure” constructional apraxia-a cognitive analysis of a single case. Behavioural Neurology, 11(1), 43–49.
Trojano, L., Grossi, D., & Flash, T. (2009). Cognitive neuroscience of drawing: Contributions of neuropsychological, experimental and neurofunctional studies. Cortex, 3(45), 269–277.
Umegaki, H., Suzuki, Y., Yamada, Y., Komiya, H., Watanabe, K., Nagae, M., & Kuzuya, M. (2020). Association of the qualitative clock drawing test with progression to dementia in non-demented older adults. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 9(9), 2850.
Ungerleider, L. G., & Mishkin, M. (1982). Two cortical visual systems. In J. Ingle, M. A. Goodale, &
R. J. W. Mansfield (Eds.), Analysis of visual behavior (pp. 549–586). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Van der Stigchel, S., De Bresser, J., Heinen, R., Koek, H. L., Reijmer, Y. D., Biessels, G. J., & Van Den Berg, E. (2018). Parietal involvement in constructional apraxia as measured using the pentagon copying task. Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders, 46(1–2), 50–59.
Vasquez, B., & Danckert, J. (2008). Direction specific costs to spatial working memory from saccadic and spatial remapping. Neuropsychologia, 46(9), 2344–2354.
van Sommers, P. (1984). Drawing and cognition. Cambridge University Press.
van Sommers, P. (1989). A system for drawing and drawing-related neuropsychology. Cognitive Neuropsychology, 6, 117–164.
Vinter, A. (1994). Hierarchy among graphic production rules: a developmental approach. In: C. Faure, P. Keuss, G. Lorette & A. Vinter (Eds.) Advances in handwriting and drawing: a multidiscipliniary approach. Paris: Europia.
Warrington, E. K., James, M., & Kinsbourne, M. (1966). Drawing disability in relation to laterality of cerebral lesion. Brain, 89, 53–92.
Willems, A. M., Biessels, G. J., & Riddoch, M. J. (2008). Drawing ability in normal aging. Neuropsychology, Development, and Cognition. Section B, Aging, Neuropsychology and Cognition, 15(1), 38-47.
Williams, C. C., Henderson, J. M., & Zacks, F. (2005). Incidental visual memory for targets and distractors in visual search. Perception & psychophysics, 67(5), 816–827.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank MH and the healthy volunteers that offered their time and their drawings, as well as Samuel Alcock and Keanu Toomer, who spent even more time scoring them.
Open practices statement
Since this was an exploratory investigation, it was not preregistered, and ethical approval was not awarded on the basis of data being publicly available.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Salo, S.K., Harries, C.A., Riddoch, M.J. et al. Visuospatial memory in apraxia: Exploring quantitative drawing metrics to assess the representation of local and global information. Mem Cogn (2024). https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-024-01531-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3758/s13421-024-01531-w