Multisystemic Sarcoidosis Presenting With Leg Ulcers, Pancytopenia, and Polyserositis Was Successfully Treated With Glucocorticoids: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang, China
Introduction: Sarcoidosis is a chronic granulomatous disease of unknown etiology. A variety of studies have pointed out that almost every part of the body can be affected, but it most often affected the lungs and intrathoracic lymph nodes. However, cases of sarcoidosis involving multiple organs in one patient are rarely reported. We describe a unique case of sarcoidosis, which was characterized by multiorgan involvement, including leg ulcers, splenomegaly, pancytopenia, and polyserositis. Glucocorticoids were effective during the treatment of the above lesions. This case highlights the diversity of clinical manifestations of sarcoidosis and emphasizes the importance of its differential diagnosis and the periodical follow-up. These are crucial to physicians in the diagnosis and treatment of sarcoidosis.
Main Symptoms and Important Clinical Findings: A 30-year-old male complained about intermittent fever 3 years ago. A computed tomographic scan of the chest showed lymphadenopathy in the mediastinum and hilar regions. Routine blood tests showed leukopenia and mild anemia. The pathologic result of mediastinal lymph node biopsy was granulomatous lesions; thus, the patient was diagnosed with type II sarcoidosis without glucocorticoid therapy. In the following 2 years, the patient suffered from intermittent fever accompanied by dyspnea, fatigue, occasional cough, less sputum, and apparent weight loss. Abnormal physical examinations included leg ulcers and splenomegaly. Laboratory and physical tests revealed pancytopenia, polyserositis, and enlargement of lymph nodes. The pathological findings of leg ulceration, pleura, and left supraclavicular lymph node all suggested granulomas.
Diagnosis, Interventions, and Outcomes: It strongly suggested sarcoidosis since tuberculosis, lymphoma, and connective tissue disease were all excluded. Due to severe conditions and multiorgan involvement, we tried to provide methylprednisolone for this patient. After 9 months of oral glucocorticoids therapy, his subjective symptoms as well as hematological and radiological findings were all improved. His leg skin ulceration and scab were also completely disappeared.
Conclusion: Sarcoidosis has diverse clinical presentations, and many patients present with atypical symptoms. It needs to be timely identified by the clinician and carefully differentiated from other diseases with similar findings so as to make an accurate diagnosis. In this case, the patient had a poor clinical response to glucocorticoids in the early stage of treatment due to the severe condition and multi-organ involvement. It is worth noting that the patient had improved significantly after 9 months of treatment of corticosteroids, which suggested that follow-up is critical.
Introduction
Sarcoidosis results from non-caseating granuloma formation due to ongoing inflammation, the latter of which causes the accumulation of activated T cells and macrophages. There are three criteria for the diagnosis of sarcoidosis: (1) a compatible clinical and radiologic presentation, (2) pathological evidence of non-caseating granulomas, and (3) exclusion of other diseases with similar findings such as infections (e.g., tuberculosis) and malignancy (e.g., lymphoma). Almost all organs can be affected by sarcoidosis, including the lung, eyes, lymph nodes, skin, spleen, liver, kidney, abdomen, heart, and bone marrow (1, 2). Monitoring extrapulmonary organs is essential because early recognition and treatment may prevent irreversible or life-threatening complications. Treatment with glucocorticoids should be considered for patients who have significant symptoms or are at progressive stage II or III of pulmonary disease or has a severe extrapulmonary disease. Second- and third-line therapies for pulmonary sarcoidosis, including immunosuppressants and biological agents, are reserved for patients with the corticosteroid-refractory disease, intolerable adverse effects, or corticosteroid toxicity (3).
To date, as far as we know, our case is extremely rare. First, the patient presented with splenomegaly, pancytopenia, and immune impairment, which were not clinically helpful to distinguish between benign and malignant. Second, massive pleural effusion and abdominal effusion were distinctly unusual in sarcoidosis. Third, the patient's liver and gallbladder may have been involved in sarcoidosis. Fourth, there was a poor clinical response to glucocorticoids at the early stage of treatment. Notably, long-term follow-up showed improvements in his symptoms, hematological deficits, polyserositis, and reduced nodule size up to 9 months after glucocorticoid treatment. The diagnosis of sarcoidosis was confirmed after the effective treatment response to glucocorticoids.
Case Report
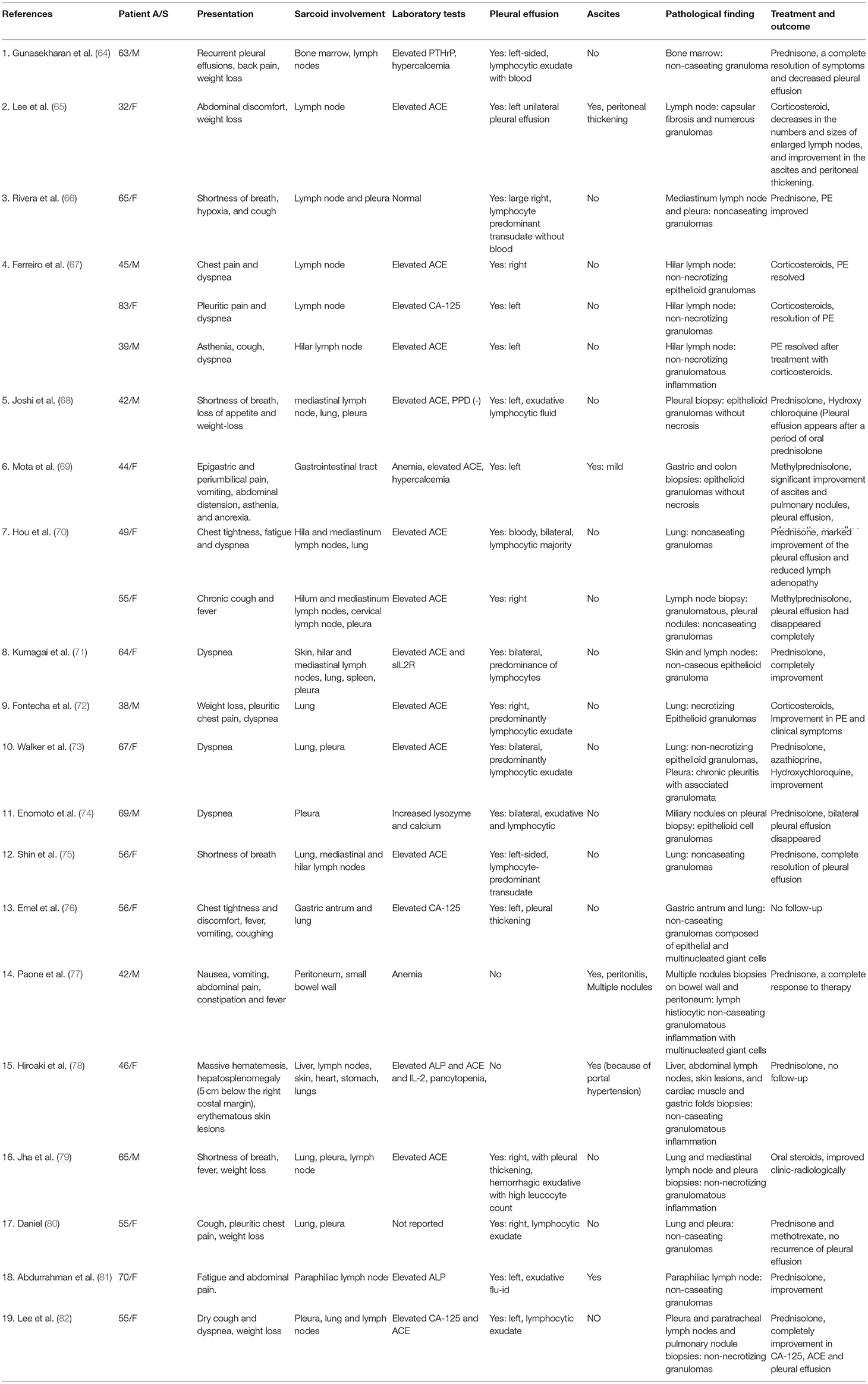
A 30-year-old male suffered an intermittent fever with a maximum temperature of 39°C since July 2017. He had a history of type 1 diabetes mellitus for 8 years. He was admitted to a local hospital and received cephalosporin therapy for a week, and then his temperature returned to normal. A CT scan of the chest showed lymphadenopathy in the mediastinum and hilar regions and multiple small nodules in both lungs. His white blood cell count was 2.9 × 109/L with severe lymphopenia of 0.5 × 109/L, and hemoglobin was 107 g/L, while the platelet count was average at 331 × 109/L. He received a positron emission tomography-CT scan to identify whether it was benign or malignant, which revealed multiple enlarged lymph nodes with hypermetabolism in the bilateral hilum, mediastinum, axilla, and clavicle, and lymphoma could not be excluded (Figure 1). Subsequently, the patient underwent a biopsy of mediastinal lymph nodes performed by thoracoscopy, and the pathologic result was granulomatous lesions; thus, type II sarcoidosis was diagnosed. However, he did not receive glucocorticoid therapy with the consideration of his diabetes history and the early stage of sarcoidosis, and then he was told to recheck every 6 months. In the following 2 years, the patient suffered from intermittent fever (T max 37.7°C), which could be alleviated by oral antibiotics, accompanied by dyspnoea, fatigue, occasional cough, less sputum, and significant weight loss (lost 50 pounds). It is unfortunate that the patient was not regularly rechecked as prescribed. Last month, he complained that he had experienced progressive abdominal distention and dyspnoea, so he came to our hospital. The patient was sane without nausea and vomiting, and no positive signs were found on neurological examination. Abnormal physical findings consisted of a few scattered skin ulcers on the legs and splenomegaly extending 5 cm below the left costal margin. Abdominal ultrasonography revealed enhanced hepatic parenchyma echo, gallbladder (8.13 × 3.29 cm) and spleen enlargement (17.29 × 5.48 cm), and peritoneal effusion (depth of ~7.34 cm). An abdominal contrast-enhanced CT scan also revealed multiple retroperitoneal lymph nodes. A CT scan of the chest showed lymphadenopathy in the mediastinum and hilar regions with multiple nodules, patchy shadows, ground-glass opacities, and emerging bilateral pleural effusion as well as right atelectasis. Cardiac ultrasound reported that there were no abnormalities in cardiac structure, blood flow, or left ventricular systolic function, with an ejection fraction of 69%. No abnormal finding was seen in ECG. Ophthalmic tests including vision and fundus oculi were both normal. Superior lymph node ultrasound revealed enlargement throughout the left supraclavicular lymph nodes, bilateral inguinal nodes, popliteal lymph nodes, left neck lymph nodes, and bilateral axillary lymph nodes (Grade 3). Blood cell count was a remarkable abnormality with marked leucopenia and anemia. The liver function test suggested liver damage and hypoproteinemia. In addition, the patient also had severely impaired immune function. Laboratory test results are shown in Table 1.
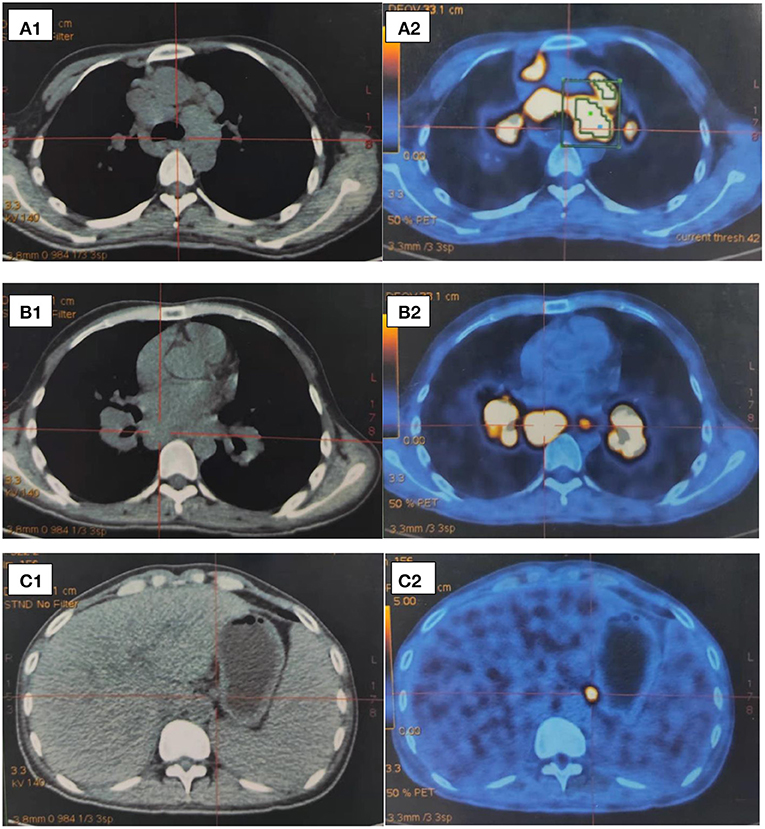
Figure 1. (A–C) Partial images of positron emission tomography-CT scan in 2017. (A) Mediastinal lymph nodes enlargement (tracheal carina) SUV max = 18.39; (aortopulmonary window) SUV max = 18.93. (B) Hilar lymph nodes enlargement. (C) Markedly enlarged spleen.
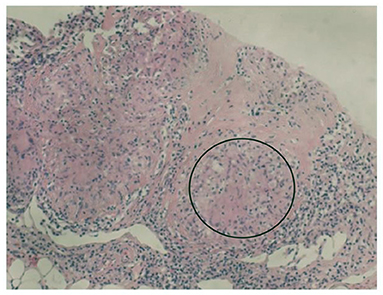
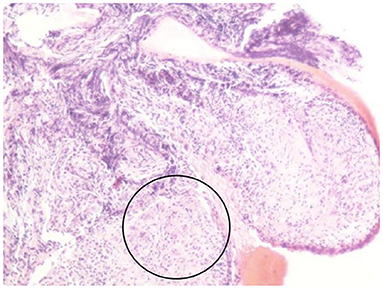
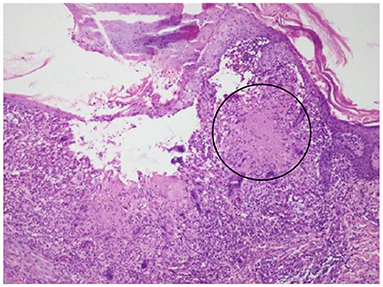
In summary, the patient had multiple organ involvement, and the disease progressed rapidly during these 2 years. During hospitalization, he took thoracentesis. As shown in Table 2, the pleural effusion was a yellow exudate. Cytopathologic examination of the pleural fluid was negative for malignant cells. In addition, both M. tuberculosis strains (acid-fast) and tuberculosis RT-PCR were negative. Subsequently, a biopsy of the left supraclavicular lymph node revealed the non-caseating granulomas with negative results for acid-fast staining and tuberculosis PCR. This result was in accordance with sarcoidosis (Figure 2). Histological analysis of the pleura obtained by thoracoscopy also revealed granulomas (Figure 3). A bone marrow aspirate and biopsy showed partial hypoplasia and no evidence of a lymphoproliferative disorder was found. In addition, a biopsy was taken from the left leg ulceration also revealed granulomas with a negative mycobacterium genetic test and culture results of fungi and bacteria (Figure 4). Abdominocentesis was not performed due to intestinal bloating and fewer ascites. Based on the above pathological results, the diagnosis of sarcoidosis was strongly suspected. Because of severe conditions and multiorgan involvement, 40 mg methylprednisolone was given intravenously once daily for seven consecutive days, followed by oral methylprednisolone 24 mg once daily.
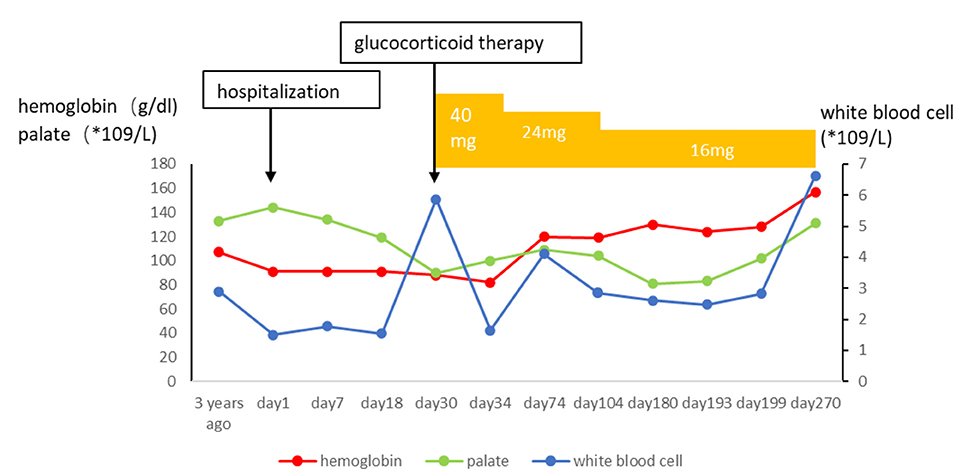
After 1 month of methylprednisolone therapy for 24 mg once daily, there was no reduction in pleural effusion on high-resolution CT (HRCT), and the spleen was larger than before; thus, we continued to maintain the current dosage (24 mg once daily). After another months' treatment, the right pleural effusion was decreased slightly, then the dose of methylprednisolone was reduced to 16 mg once daily. Six months later, a follow-up HRCT showed that the bilateral pleural effusion was significantly less than before (Figure 5). Hepatic function (Figure 6) and superficial lymph nodes and spleen were reduced. After methylprednisolone administration (the dosage was still 16 mg/day) for 9 months, the patient became asymptomatic with a normal blood cell count (Figure 7), and the CD4+ T cell count increased from 82 to 162. Ascites were negative, and the spleen and gallbladder were both reduced. In addition, the leg skin ulcers and scabs completely disappeared (Figure 8). We then focused on the patient's side effects of glucocorticoids. The patient had no psychiatric symptoms or gastrointestinal discomfort. Blood glucose levels were reasonably controlled by subcutaneous injection of insulin (fasting blood glucose and postprandial blood glucose levels were maintained at 6–8 and 8–10 mmol/l, respectively).
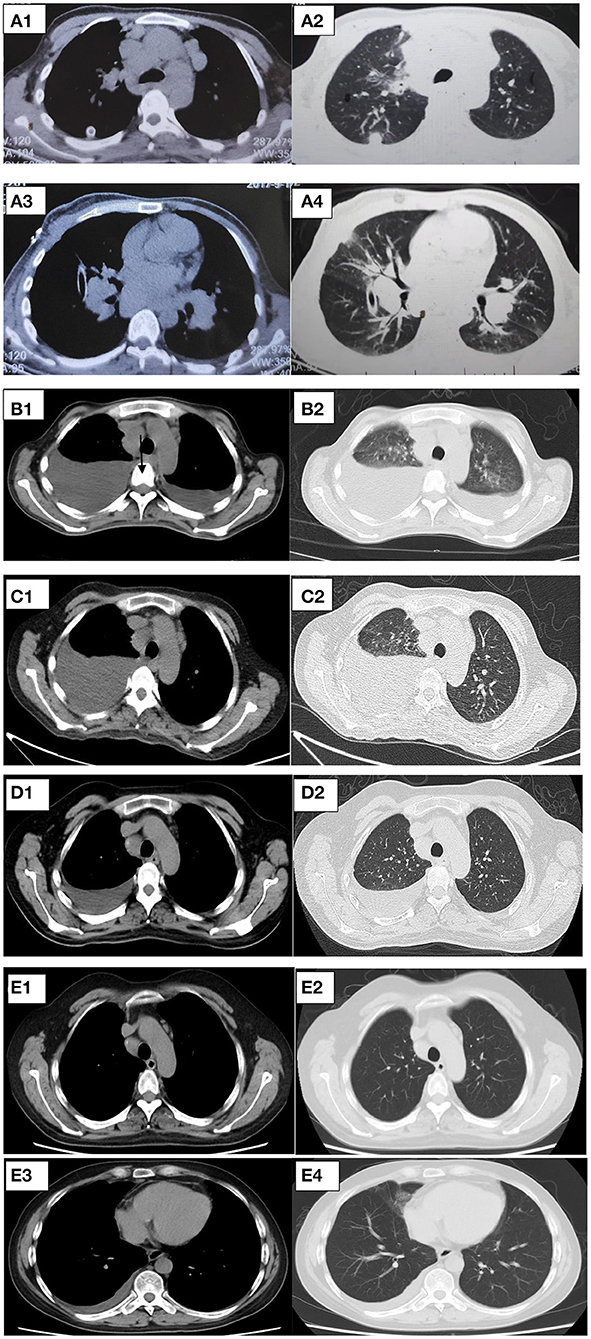
Figure 5. (A–D) Representative CT cuts of the thorax during the course of the disease. (A) Chest CT in 2017. (B) Pre-glucocorticoid therapy (September 29, 2020, chest CT). (C) One month after glucocorticoid therapy (November 25, 2020, HRCT). (D) Six months after glucocorticoid therapy (March 20, 2021, HRCT). (E) Nine months after glucocorticoid therapy (June 30, 2021, chest contrast-enhanced CT). CT, computed tomography; HRCT, high resolution computed tomography.
Figure 6. (A–C) The change of hepatic function (ALP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, gamma glutamate transpeptidase; ALB, albumin; ALT, alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate transaminase).
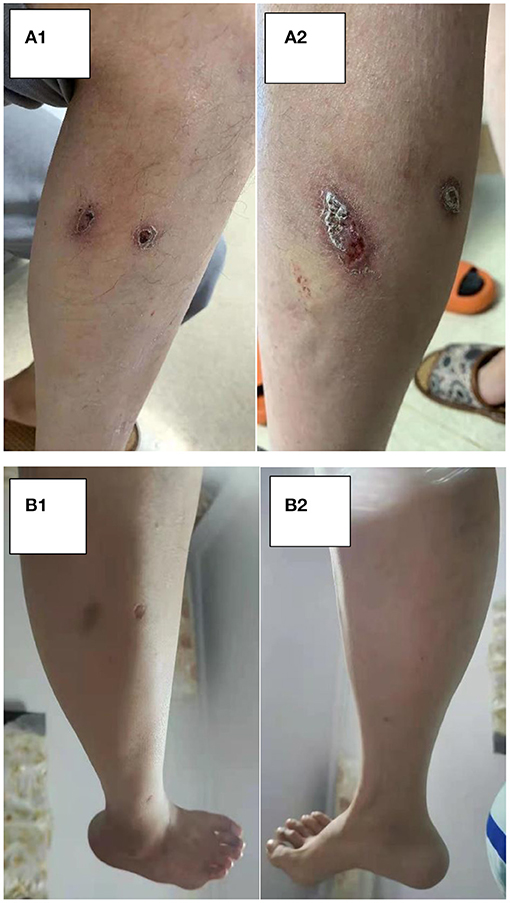
Figure 8. (A,B) The change in leg skin. (A) Pre-glucocorticoid therapy (September 13, 2020). (B) Nine months after glucocorticoid therapy (June 30, 2021).
Discussion and Conclusion
The strength of our study is that it is the first case of sarcoidosis with systematic manifestations, including skin, spleen, pleura, lymph node, and abdomen manifestations, which were probably sensitive to glucocorticoid therapy. However, our study also had a limitation. We lack pathological evidence of abdominal organ involvement, such as the peritoneum, spleen, liver, and bladder. Furthermore, there was no significant improvement in splenomegaly, which may be related to the insufficient courses of treatment or the overlapping presentations. Glucocorticoids have been reported to be the first-line treatment for sarcoidosis. But our patient is at high risk of side effects with glucocorticoid therapy because of diabetes history. Conventional and biological immunosuppressive drugs such as methotrexate and tocilizumab have been studied for their glucocorticoid-sparing properties to reduce glucocorticoid exposure and maintain remission (4). Therefore, we may first consider glucocorticoid-sparing therapy in patients with high-risk factors for glucocorticoid complications. Finally, given the patient's splenomegaly, systemic lymphadenopathy, and reduced immune function, although there is currently no pathological support for the diagnosis of lymphoma, it can occur 2–8 years after the sarcoidosis diagnosis most of the time, preferentially in patients with a chronic course of the disease (5). The patient requires a more extended period of treatment and consequent follow-up clinic.
Pulmonary involvement can be seen in more than 90% of patients with sarcoidosis. Almost all organs can be affected by sarcoidoses, such as the spleen, liver, kidney, abdomen, heart, and bone marrow. However, the eyes, lymph nodes, and skin are the most commonly involved organs (6–8). Our study provides a systematic literature review of the patient's several unusual extrapulmonary manifestations in the following report.
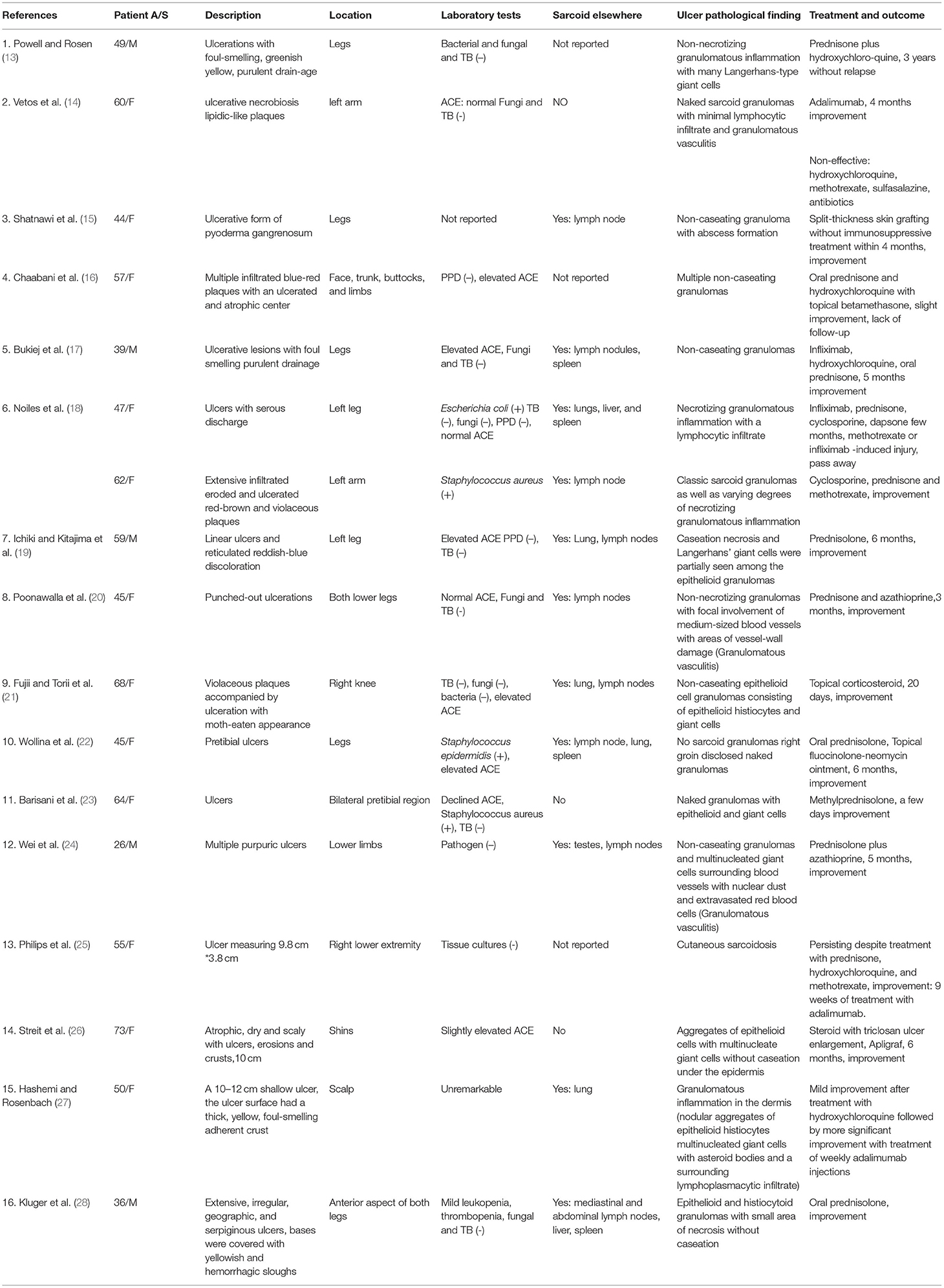
Cutaneous involvement occurs in nearly one-third of sarcoidosis patients (9), and the lesions can exhibit many different manifestations, which are divided into two categories: “specific,” where histological examination shows typical non-caseating granulomas, and “non-specific,” where there is a lack of the former feature (10). The specific lesions include lupus pernio, infiltrated plaques, maculopapular eruptions, subcutaneous nodules, and scars, whereas a variety of unusual forms include erythrodermic, ichthyosiform, psoriasiform, verrucous, or ulcerated sarcoidosis (11). Although ulcerative sarcoidosis remains rare, it has been increasingly reported in the last few decades. A previous review (12) of 147 patients with cutaneous sarcoidosis found ulceration in 4.8% of patients, which is consistent with Powell's study (13). We reviewed 17 cases with full text from the English-language literature based on a PubMed search using the terms ulcerative sarcoidosis and case report for the last 20 years (13–28). They are presented in Table 3. We found a female to male ratio of 2.4–1, and the average age of presentation was 52 years (age range, 26–73 years). Approximately 76% (13/17) of cases presented with involvement of the legs. Additionally, ulcers were generally solitary or sporadic lesions with necrotic yellow, blue, or red plaques accompanied by a foul smell and discharge. Upon histologic examination of ulcerative sarcoidosis, 11 of the ulcerative sarcoidosis in our review were described as either epithelioid granulomas or non-caseating granulomas. However, several cases also showed atypical features, including caseation necrosis and granulomatous vasculitis, including our case, which did not generally seem to be compatible with sarcoidosis. The histologic difference in these cases may primarily include an infection aspect. Moreover, extensive workup needs to be done in these patients to ensure that it was not only an infection. The lesions should also be distinguished from other granulomatous disorders, such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA), eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA), and lymphomatous granulomatosis (29). In terms of laboratory tests, only five patients presented with elevated ACE, while one declined in our review. Although elevated ACE levels have been seen in patients with sarcoidosis, the ACE level lacks specificity, and it has large interindividual variability, which limits its clinical utility (30).
Corticosteroids have been reported to improve the symptoms of sarcoidosis in all organs. Our patient showed a good response to methylprednisolone therapy for his skin ulcers. In our review of ulcerative sarcoidosis, many types of treatments have been reported, such as skin grafts, antimalarials (chloroquine or hydroxychloroquine), topical corticosteroids, anti-ulcer cream, immunosuppressive drugs (azathioprine or cyclosporine), and biologic agents (adalimumab or infliximab). However, failures and side effects were also accompanied by the above treatments, including corticosteroid-induced hyperglycaemia and methotrexate- or infliximab-induced organ injury. Therefore, it is essential for us to pay attention to the response and the side effects of drug treatment depending on the patients' conditions.
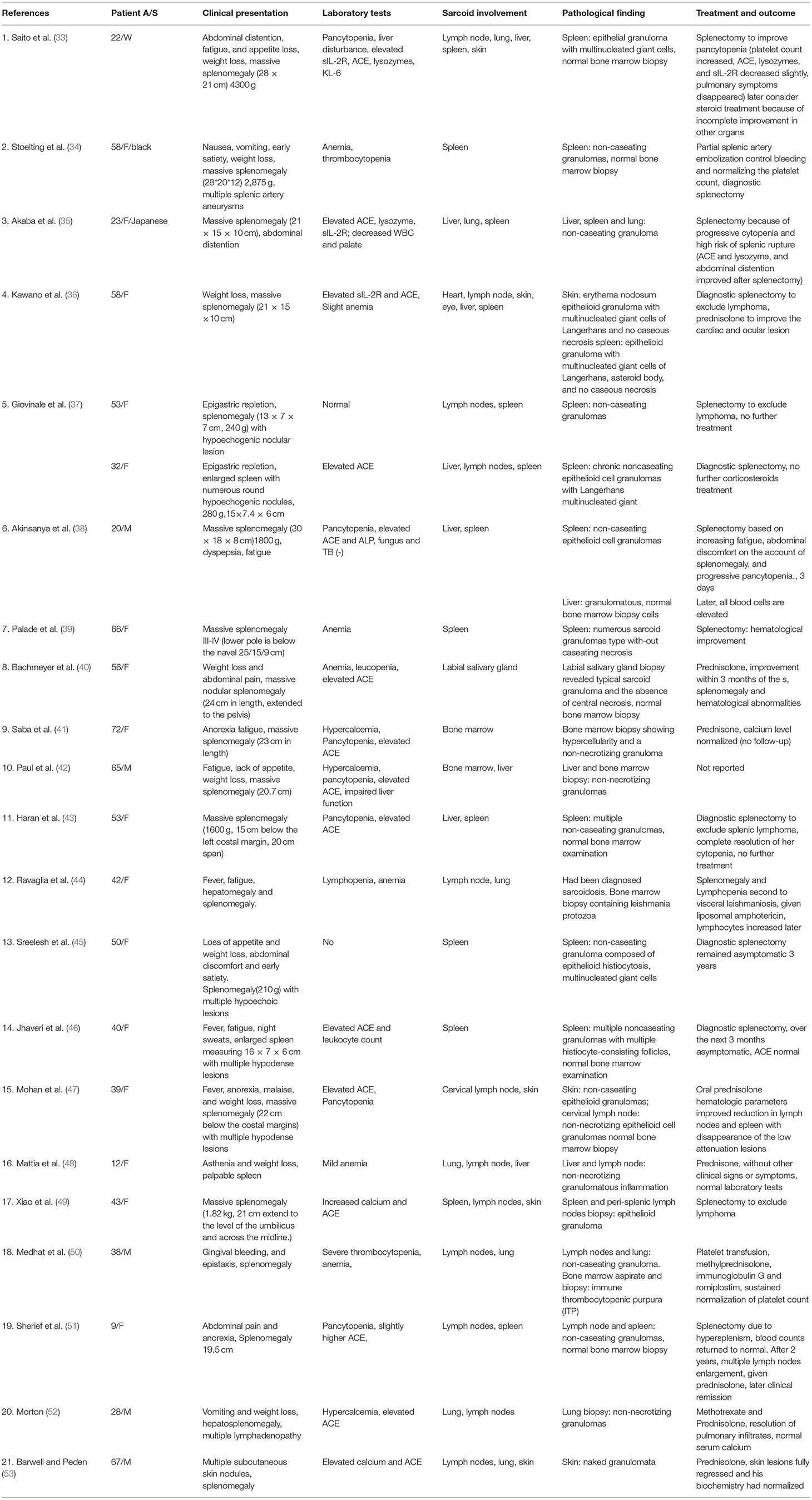
Previous studies have reported that splenomegaly was present in 5.6–50.0% of sarcoidosis cases (31, 32). We described 22 cases presenting splenomegaly and sarcoidosis with histological proof in the last 20 years, as shown in Table 4 (33–53). In the spleen, massive splenomegaly is the most common presentation, followed by multiple splenic lesions (54). Massive splenomegaly [defined when it extends into the pelvis, when it has crossed the midline of the abdomen, or when it has a weight over 1,000-1,500 g or the largest dimension >20 cm (42)] was clinically perceptible in 12 patients. There were six patients who presented with an in-homogeneously enlarged spleen with hypoechoic nodular lesions. The more frequent clinical features were digestive symptoms (including abdominal distention, appetite loss, nausea, vomiting, early satiety, dyspepsia, abdominal pain in 13 cases) and constitutional symptoms (fever N = 3; fatigue N = 7; weight loss N = 9). Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and serum calcium levels were elevated in 68 and 23% of cases, respectively. In addition, sIL-2R and liver enzymes were elevated in several patients. Therefore, measurement of the above marker levels, even though not diagnostic, may be helpful to monitor activities and evaluate the therapeutic effect. Moreover, of the 23 cases, including our patient, 16 cases had haematologic abnormalities (pancytopenia N = 8; bicytopenia N = 5; solely anemia N = 3). Several putative mechanisms may explain haematologic abnormalities in sarcoidosis: hypersplenism, bone marrow involvement, and autoimmune destruction, such as immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) and lymphoma (55), which represent a diagnostic challenge. Therefore, we emphasize that biopsies of bone marrow, spleen, and lymph nodes may be necessary to identify the cause. Pancytopenia was presented in two patients with bone marrow involvement, and thrombocytopenia was present in one patient with ITP. It is worth mentioning that a case of splenomegaly and abnormal blood cell counts were secondary to bone marrow infection with Leishmania protozoa, which needs our attention to exclude parasitic infection. The coexistence of sarcoidosis and opportunistic infection, even in the absence of any immunosuppressive therapy, has previously been documented (56).
No treatment is required when splenomegaly is asymptomatic. When disabling, treatment relies on oral corticosteroids, which were also highly effective in our patients. In our review, hematological abnormalities improved after splenectomy or glucocorticoid therapy in six and three patients, respectively. Splenectomy is necessary for patients who fail to respond to pharmacotherapy, massive splenomegaly with pressure-related symptoms, prophylaxis for splenic rupture, treatment for refractory cytopenia, or diagnostic exclusion of malignancy, especially splenic marginal zone lymphoma (42, 54). However, splenectomy could develop life-threatening infection postoperatively, and patients are at an increased risk of vascular complications, including pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and portal and splenic vein thrombosis (57). The exacerbation of DPB has been reported in the literature after splenectomy (35). Likewise, the risks of glucocorticoid therapy also need to be weighed against the potential benefits.
Another feature of this patient's illness was bilateral pleural effusions and ascites, which have been thought to be unusual in sarcoidosis. In a study of 181 outpatients with sarcoidosis, 2.8% had pleural effusions, and only 1.1% had sarcoid pleural involvement (58). The mechanism of pleural effusion formation in sarcoidosis could be attributed to the following five points: (1) pleural involvement, (2) superior vena cava obstruction (59), (3) bronchial stenosis and lobar atelectasis resulting from endobronchial sarcoidosis (60), (4) trapped lung (61), and (5) chylothorax leading to lymphatic disruption (62). Ascites are also rare manifestations of sarcoidosis. It may appear as a result of portal hypertension-related to liver involvement or severe pulmonary involvement with a serum ascites albumin gradient (SAAG) higher than 1.1 g/dl and peritoneal involvement with a SAAG lower than 1.1 g/dl. Very few cases presented both pleural effusion and ascites (63). As shown in Table 5, of the 22 patients with pleural effusion or ascites from 2010 to 2021 (64–82), there was an increased incidence in women (14/22), 17 (77%) had pleural effusion, two (9%) patients had ascites and three (17%) patients had both. In 21 cases with pleural effusion, including our case, 10 cases had biopsy-proven pleural involvement. Sarcoid pleural effusions are more commonly left-sided (48%, 10/21) and less frequently bilateral (24%, 5/21), and they are often exudative and lymphocytic. The etiology of pleural effusion in sarcoidosis requires us to rule out some possible diseases, such as connective tissue diseases, tuberculosis, carcinoma, lymphoma, and chronic heart failure. In our patient, we performed a detailed differential diagnosis. Given that pleural effusion was an exudate and there were no abnormalities in brain sodium peptide, renal function, or rheumatism-related antibodies, we could temporarily rule out heart failure hypoproteinemia, nephrotic syndrome, and rheumatic disease (such as lupus). Moreover, acid-fast staining, tuberculosis PCR, and malignant cells were all negative in pleural fluid. The most powerful point was that the histopathology of pleural demonstrated granulomas consistent with sarcoidosis. Similarly, in six cases with ascites, including our case, one case had peritoneal involvement, one case had gastrointestinal involvement, and one case was because of portal hypertension. The most commonly reported manifestations were abdominal pain, abdominal distention, nausea, vomiting, and fever. The most commonly reported manifestations were colicky abdominal pain, chills, and feverishness. Several diseases should routinely be investigated and ruled out in patients with ascites, including inflammatory, infectious, and neoplastic diseases. An abdominal laparotomy or laparoscopy is sometimes required to reveal the involvement of granulomatous disease in the viscera and peritoneum. In addition, elevated ACE levels were seen in almost 73% (16/22) of cases. CA-125 can also be elevated in three cases, and one patient had normalization of CA-125 levels after treatment with prednisolone. However, the diagnostic significance of these biomarkers in sarcoidosis remains uncertain.
Above all, sarcoidosis has diverse clinical presentations, and many patients present with atypical symptoms. Thus, it needs to be timely identified by the clinician, and carefully differentiated from other diseases with similar findings, so as to make an accurate diagnosis. In this case, the patient had a poor clinical response to glucocorticoids in the early stage of treatment due to a severe condition and multiorgan involvement. It is worth noting that the patient had improved significantly after 9 months of treatment with corticosteroids, which suggests that multisystemic sarcoidosis requires a long treatment course and a regular follow-up clinic.
Patient Perspective
The patient believed that our diagnosis and treatment for his disorder were reasonable. Most importantly, his clinical manifestations and laboratory examination results were significantly improved. During the process of glucocorticoid therapy, blood glucose and blood pressure were well controlled, and there was no gastrointestinal discomfort. The only thing that confused him was occasionally depression. The patient indicated that he would continue to comply with our treatment and undergo regular rechecks and feedback.
Data Availability Statement
All data sets generated for this study are included in the article.
Ethics Statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author Contributions
XQ and SH drafted the case report. AA, YY, and W-yL performed the biopsy and language modifying. JK, YY, and Q-yW revised the report. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Clinical Key Specialty Project Foundation (Project Number: 2016YFC 1304103 and 2016YFC 1304500).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank the patient who contributed to this report.
References
1. Statement on Sarcoidosis. Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS), and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) adopted by the ATS Board of Directors and by the ERS Executive Committee, February 1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (1999) 160:736–55. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.160.2.ats4-99
3. Soto-Gomez N, Peters JI, Nambiar AM. Diagnosis and management of sarcoidosis. Am Fam Physician. (2016) 93:840–8
4. Hellmich B, Águeda AF, Monti S, Luqmani R. Treatment of giant cell arteritis and takayasu arteritis-current and future. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2020) 22:84. doi: 10.1007/s11926-020-00964-x
5. Brincker H. The sarcoidosis-lymphoma syndrome. Br J Cancer. (1986) 54:467–73. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.199
6. Gezer NS, Başara I, Altay C, Harman M, Rocher L, Karabulut N, et al. Abdominal sarcoidosis: cross-sectional imaging findings. Diagn Interv Radiol. (2015) 21:111–7. doi: 10.5152/dir.2014.14210
7. Thomas J, Charles D, Kachare N. Isolated splenic sarcoidosis with hypersplenism. J Clin Rheumatol. (2020) 26:e103–4. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000000966
8. Sugai M, Murata O, Oikawa H, Katagiri H, Matsumoto A, Nagashima H, et al. A case of bone marrow involvement in sarcoidosis with crescentic glomerular lesions. Respir Med Case Rep. (2020) 31:101202. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101202
9. Caplan A, Rosenbach M, Imadojemu S. Cutaneous sarcoidosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. (2020) 41:689–99. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2015.08.010
10. English JC. 3rd, Patel PJ, Greer KE. Sarcoidosis. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2001) 44:725–43. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2001.114596
11. Ball NJ, Kho GT, Martinka M. The histologic spectrum of cutaneous sarcoidosis: a study of twenty-eight cases. J Cutan Pathol. (2004) 31:160–8. doi: 10.1111/j.0303-6987.2004.00157.x
12. Yoo SS, Mimouni D, Nikolskaia OV, Kouba DJ, Sauder DN, Nousari CH. Clinicopathologic features of ulcerative-atrophic sarcoidosis. Int J Dermatol. (2004) 43:108–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.01896.x
13. Powell E, Rosen T. Ulcerative sarcoidosis: a prototypical presentation and review. Cutis. (2017) 100:312–6
14. Vetos D, Wu DJ, Downing MB, Rajpara A. Adalimumab for treatment of severe ulcerative sarcoidosis. Dermatol Online J. (2021) 27:undefined. doi: 10.5070/D327654058
15. Shatnawi NJ, Al-Zoubi NA, Al-Bakkar LA, Gharaibeh LM, Hamouri S. Nonhealing leg ulcer as the presentation of sarcoidosis: a case report. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. (2021) 2021:15347346211037850. doi: 10.1177/15347346211037850
16. Chaabani M, Hafsi W, Alaoui F, Sassi W, Mokni M. Generalized ulcerative cutaneous sarcoidosis: an unusual presentation of the disease. Int J Dermatol. (2021). doi: 10.1111/ijd.15846. [Epub ahead of print].
17. Bukiej A, Wu J, Sequeira W. Ulcerative cutaneous sarcoidosis successfully treated with infliximab. Clin Rheumatol. (2021) 40:4349–54. doi: 10.1007/s10067-021-05689-5
18. Noiles K, Beleznay K, Crawford RI, Au S. Sarcoidosis can present with necrotizing granulomas histologically: two cases of ulcerated sarcoidosis and review of the literature. J Cutan Med Surg. (2013) 17:377–83. doi: 10.2310/7750.2013.13035
19. Ichiki Y, Kitajima Y. Ulcerative sarcoidosis: case report and review of the Japanese literature. Acta Derm Venereol. (2008) 88:526–8. doi: 10.2340/00015555-0525
20. Poonawalla T, Colome-Grimmer MI, Kelly B. Ulcerative sarcoidosis in the legs with granulomatous vasculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. (2008) 33:282–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2007.02643.x
21. Fujii H, Torii H. Case of sarcoidosis with seasonal cutaneous ulceration. J Dermatol. (2017) 44:1331–2. doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.13682
22. Wollina U, Baunacke A, Hansel G. Multisystemic sarcoidosis presenting as pretibial leg ulcers. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. (2016) 15:263–6. doi: 10.1177/1534734616652553
23. Barisani A, Negosanti M, La Placa M, Infusino SD, Misciali C, Sorci M, et al. Erythematous patches and pretibial ulcers: an uncommon presentation of cutaneous sarcoidosis. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. (2016) 14:295–7. doi: 10.1111/ddg.12753
24. Wei CH, Huang YH, Shih YC, Tseng FW, Yang CH. Sarcoidosis with cutaneous granulomatous vasculitis. Australas J Dermatol. (2010) 51:198–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-0960.2010.00630.x
25. Philips MA, Lynch J, Azmi FH. Ulcerative cutaneous sarcoidosis responding to adalimumab. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2005) 53:917. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2005.02.023
26. Streit M, Böhlen LM, Braathen LR. Ulcerative sarcoidosis successfully treated with apligraf. Dermatology. (2001) 202:367–70. doi: 10.1159/000051685
27. Hashemi DA, Rosenbach M. Ulcerative sarcoidosis. JAMA Dermatol. (2019) 155:238. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2018.3597
28. Kluger N, Girard C, Durand L, Bessis D, Guillot B. Leg ulcers revealing systemic sarcoidosis with splenomegaly and thrombocytopenia. Int J Dermatol. (2013) 52:1425–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05210.x
29. McKee PH, Calonje E, Granter SR. Pathology of the Skin With Clinical Correlations. Vol. 1, 3rd edn. London: Elsevier (2005).
30. Studdy PR, Bird R. Serum angiotensin converting enzyme in sarcoidosis—its value in present clinical practice. Ann Clin Biochem. (1989) 1989:13–8. doi: 10.1177/000456328902600102
31. Sato H, Nagai S, du Bois RM, Handa T, Suginoshita Y, Ohta K, et al. HLA-DQB1 0602 allele is associated with splenomegaly in Japanese sarcoidosis. J Intern Med. (2007) 262:449–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2007.01829.x
32. Kurosaki F, Bando M, Nakayama M, Mato N, Yamasawa H, Higashizawa T, et al. A patient with sarcoidosis who developed heterochronic involvements in different organs from initial organs during 7 years. Respir Investig. (2014) 52:71–4. doi: 10.1016/j.resinv.2013.05.003
33. Saito S, Kodama K, Kogiso T, Yamanashi Y, Taniai M, Ariizumi S, et al. Atypical sarcoidosis diagnosed by massive splenomegaly. Intern Med. (2020) 59:641–8. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.3646-19
34. Stoelting A, Esperti S, Balanchivadze N, Piacentino V, Mangano A. Sarcoidosis presenting as massive splenomegaly and severe epistaxis, case report. Ann Med Surg. (2020) 54:6–9. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2020.03.007
35. Akaba T, Takeyama K, Kondo M, Kobayashi F, Okabayashi A, Sawada T, et al. Coexistence of diffuse panbronchiolitis and sarcoidosis revealed during splenectomy: a case report. BMC Pulm Med. (2020) 20:77. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-1117-y
36. Kawano S, Kato J, Kawano N, Yoshimura Y, Masuyama H, Fukunaga T, et al. Sarcoidosis manifesting as cardiac sarcoidosis and massive splenomegaly. Intern Med. (2012) 51:65–9. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.51.5247
37. Giovinale M, Fonnesu C, Soriano A, Cerquaglia C, Curigliano V, Verrecchia E, et al. Atypical sarcoidosis: case reports and review of the literature. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2009) 13:37–44. doi: 10.1097/00000441-200605000-00009
38. Akinsanya L, Hussain I, Awoniyi D, Usman K. Leucopenia as presentation of sarcoidosis. Int J Health Sci. (2008) 2:109–12.
39. Palade R, Voiculescu D, Suliman E, Simion G. Splenic sarcoidosis—a case report. Chirurgia. (2012) 107:670–4.
40. Bachmeyer C, Fayand A, Georgin-Lavialle S, Fedida B, Naccache JM, Lionnet F, et al. Massive splenomegaly indicating sarcoidosis. Am J Med. (2017) 130:e141–2. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2016.11.033
41. Saba R, Khreis M, Francisque F, Saleem N. Rare case of sarcoidosis presenting with pancytopenia, acute renal failure and hypercalcaemia. BMJ Case Rep. (2016) 2016:bcr2016214840. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2016-214840
42. Paul S, Gupta V, Gonsalves WI, Kochuparambil ST, Gangat N. Sarcoidosis presenting with pancytopenia. Am J Med. (2014) 127:e9–10. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.05.031
43. Haran MZ, Feldberg E, Miller G, Berrebi A. Sarcoidosis presenting as massive splenomegaly and bicytopenia. Am J Hematol. (2000) 63:232–3. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8652(200004)63:4<232::aid-ajh15>3.0.co;2-v
44. Ravaglia C, Gurioli C, Casoni GL, Asioli S, Poletti V. Fever, splenomegaly and lymphopenia in sarcoidosis. Visceral leishmaniasis Thorax. (2013) 68:496–7. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-201408
45. Sreelesh KP, Kumar ML, Anoop TM. Primary splenic sarcoidosis. Proc Bayl Univ Med Cent. (2014) 27:344–5. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2014.11929154
46. Jhaveri K, Vakil A, Surani SR. Sarcoidosis and its splenic wonder: a rare case of isolated splenic sarcoidosis. Case Rep Med. (2018) 2018:4628439. doi: 10.1155/2018/4628439
47. Mohan A, Sood R, Shariff N, Gulati MS, Gupta SD, Dutta AK. Sarcoidosis manifesting as massive splenomegaly: a rare occurrence. Am J Med Sci. (2004) 328:170–2. doi: 10.1097/00000441-200409000-00007
48. Mattia G, Michele L, Giovanna F, Anna MB, Gabriele S, de Martino M, et al. Common symptoms for a rare disease in a girl with sarcoidosis: a case report. Ital J Pediatr. (2018) 44:74. doi: 10.1186/s13052-018-0517-6
49. Xiao GQ, Zinberg JM, Unger PD. Asymptomatic sarcoidosis presenting as massive splenomegaly. Am J Med. (2002) 113:698–9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01295-0
50. Medhat BM, Behiry ME, Fateen M, El-Ghobashy N, Fouda R, Embaby A, et al. Sarcoidosis beyond pulmonary involvement: a case series of unusual presentations. Respir Med Case Rep. (2021) 34:101495. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2021.101495
51. Sherief LM, Amer OT, Mokhtar WA, Kamal NM, Ibrahim HM. Pediatric sarcoidosis presenting as huge splenomegaly. Pediatr Int. (2017) 59:366–7. doi: 10.1111/ped.13219
52. Morton A. A young man with weight loss and lymphadenopathy—a case study. Aust Fam Phys. (2013) 42:575–6
53. Barwell ND, Peden NR. A trout fisherman with hypercalcaemia and skin lesions. Scott Med J. (2011) 56:181. doi: 10.1258/smj.2011.011121
54. Baughman RP, Iannuzzi MC. Diagnosis of sarcoidosis: when is a peek good enough? Chest. (2000) 117:931–2. doi: 10.1378/chest.117.4.931
55. Papanikolaou IC, Sharma OP. The relationship between sarcoidosis and lymphoma. Eur Respir J. (2010) 36:1207–9. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00043010
56. Baughman RP, Lower EE. Fungal infections as a complication of therapy for sarcoidosis. QJM. (2005) 98:451–6. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hci073
57. Crary SE, Buchanan GR. Vascular complications after splenectomy for hematologic disorders. Blood. (2009) 114:5404. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-210112
58. Huggins JT, Doelken P, Sahn SA, King L, Judson MA. Pleural effusions in a series of 181 outpatients with sarcoidosis. Chest. (2006) 129:1599–604. doi: 10.1378/chest.129.6.1599
59. Gordonson J, Trachtenberg S, Sargent EN. Superior vena cava obstruction due to sarcoidosis. Chest. (1973) 63:292–3. doi: 10.1378/chest.63.2.292
60. Poe RH. Middle-lobe atelectasis due to sarcoidosis with pleural effusion. N Y State J Med. (1978) 78:2095–7.
61. Heidecker JT, Judson MA. Pleural effusion caused by a trapped lung. South Med J. (2003) 96:510–1. doi: 10.1097/01.SMJ.0000047745.99481.C3
62. Aberg H, Bah M, Waters AW. Sarcoidosis: complicated by chylothorax. Minn Med. (1966) 49:1065–70.
63. Iyer S, Afshar K, Sharma OP. Peritoneal and pleural sarcoidosis: an unusual as-sociation—review and clinical report. Curr Opin Pulm Med. (2008) 14:481–7. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e328304ae43
64. Gunasekharan A, Thekekara J, Kwon Y, Irani F. Recurrent pleural effusions and elevated PTHrP: an unusual case of sarcoidosis. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. (2020) 10:594–6. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2020.1816275
65. Lee SW, Lee MH, Lee JE, Choi SY Yi BH, Jung JM. Peritoneal sarcoidosis: a case report. Medicine. (2019) 98:e16001. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016001
66. Rivera E, Gesthalter Y, Vardelaan P, Chee A, Majid A. Sarcoidosis with pleural effusion as the presenting symptom. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. (2018) 25:148–51. doi: 10.1097/LBR.0000000000000453
67. Ferreiro L, San José E, González-Barcala FJ, Suárez-Antelo J, Toubes ME, Valdés L. Pleural effusion and sarcoidosis: an unusual combination. Arch Bronconeumol. (2014) 50:554–6. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2013.07.020
68. Joshi S, Periwal P, Dogra V, Talwar D. Sarcoidosis as unusual cause of massive pleural effusion. Respir Med Case Rep. (2015) 16:143–5. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2015.09.011
69. Mota C, Ferreira C, Oliveira ME, Santos JM, Victorino RMM. Multisystemic sarcoidosis with early gastrointestinal symptoms. GE Port J Gastroenterol. (2017) 24:137–41. doi: 10.1159/000450899
70. Hou G, Wang W, Zhao YB, Su XM, Wang QY Li ZH, et al. Bloody pleural effusion—a rare manifestation of sarcoidosis. Intern Med. (2013) 52:1211–5. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.52.9507
71. Kumagai T, Tomita Y, Inoue T, Uchida J, Nishino K, Imamura F. Pleural sarcoidosis diagnosed on the basis of an increased CD4/CD8 lymphocyte ratio in pleural effusion fluid: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2015) 9:170. doi: 10.1186/s13256-015-0656-y
72. Fontecha Ortega M, Rodríguez Álvarez SJ, García Satué JL. Pleural effusion: a rare manifestation of sarcoidosis. Arch Bronconeumol. (2017) 53:170–1. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2016.07.006
73. Walker S, Adamali H, Bhatt N, Maskell N, Barratt SL. Pleuroparenchymal sarcoidosis—a recognized but rare manifestation of disease. Respir Med Case Rep. (2018) 23:110–4. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2018.01.007
74. Enomoto Y, Yokomura K, Suda T. Bilateral pleural effusion associated with miliary sarcoidosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2015) 191:474–5. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201411-2022IM
75. Shin KH, Kim KU, Lee G, Park HK. Endobronchial mass and ipsilateral pleural effusion as presenting features of sarcoidosis. J Formos Med Assoc. (2014) 113:974–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2014.01.020
76. Emel C, Serdar S, Adil C, Ibrahim M, Nimet D, Orhan Ç. Gastric involvement of sarcoidosis in a patient with multiple lung nodules. J Res Med Sci. (2015) 20:525–8. doi: 10.4103/1735-1995.163981
77. Paone G, Steffanina A, De Rose G, Leonardo G, Colombo D, Ricci P, et al. A life-threatening small bowel obstruction as onset of an unknown sarcoidosis: a case report. Respir Med Case Rep. (2021) 33:101379. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2021.101379
78. Hiroaki S, Masayasu O, Masaya I, Takehiro T, Nozomu W, Tetsuya Y, et al. Hepatic and gastric involvement in a case of systemic sarcoidosis presenting with rupture of esophageal varices. Intern Med. (2017) 56:2583–8. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8768-16
79. Jha O, Nair V, Talwar D. Hemorrhagic sarcoid pleural effusion: a rare entity. Lung India. (2016) 33:532–6. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.188975
80. Daniel S. Sarcoidosis pleural effusion: a not so common feature of a well-known pulmonary disease. Respir Care. (2010) 55:478–80.
81. Sahin A, Artaş H, Artaş G. An unusual cause of ascites and pleural effusion in an elderly woman: Sarcoidosis presenting with parailiac lymph node involvement. Turk J Gastroenterol. (2020) 31:731–3. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2020.19416
Keywords: splenomegaly, pancytopenia, sarcoidosis, glucocorticoid, case report
Citation: Qiao X, He S, Altawil A, Wang Q-y, Kang J, Li W-y and Yin Y (2022) Multisystemic Sarcoidosis Presenting With Leg Ulcers, Pancytopenia, and Polyserositis Was Successfully Treated With Glucocorticoids: A Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Med. 8:803852. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.803852
Received: 28 October 2021; Accepted: 21 December 2021;
Published: 15 February 2022.
Edited by:
Mohammed Munavvar, Lancashire Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, United KingdomReviewed by:
Gonçalo Boleto, Hôpital Cochin, FranceSebastian Majewski, Medical University of Lodz, Poland
Copyright © 2022 Qiao, He, Altawil, Wang, Kang, Li and Yin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wen-yang Li, sisy_@126.com; Yan Yin, yinyan1b@126.com
 Xin Qiao
Xin Qiao Shan He
Shan He  Qiu-yue Wang
Qiu-yue Wang Jian Kang
Jian Kang Wen-yang Li
Wen-yang Li Yan Yin
Yan Yin