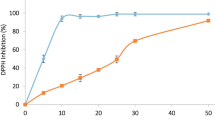
Abstract
The research has shown that exposure to ionizing radiation at the dose of 30 cGy leads to the activation of NO-synthase way of nitrogen oxide synthesis, as well as to the accumulation of its stable metabolites and 3'-nitrotyrosine modified proteins in rat peripheral blood leucocytes and the renal cortical layer. NO-synthase activity was preserved at the control value through the consumption of red wine naturalpolyphenolic complex concentrates by the irradiated animals. The content of proteins modified by tyrosine nitration decreased in the early period of post-radiation exposure due to the influence of the investigated concentrate. Thus the ability of red wine natural polyphenolic complex concentrates to prevent adverse changes in L-arginine/NO system and, therefore, inhibit the development of nitrative stress induced by low doses of ionizing radiation has been proved experimentally.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mughal, S.K., Myazin, A.E., Zhavoronkov, L.P., Rubanovich, A.V., and Dubrova, Y.E., The dose and dose-rate effects of paternal irradiation on transgenerational instability in mice: a radiotherapy connection, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 7, p. e41300.
Snijders, A.M., Marchetti, F., Bhatnagar, S., Duru, N., Han, J., Hu, Z., Mao, J., Gray, J.W., and Wyrobek, A.J., Genetic differences in transcript responses to low-dose ionizing radiation identify tissue functions associated with breast cancer susceptibility, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 10, p. e45394.
Lee, J., Giordano, S., and Zhang, J., Autophagy, mitochondria and oxidative stress: cross-talk and redox signaling, Biochem. J., 2012, vol. 441, no. 2, pp. 523–540.
Alderton, W.K., Cooper, C.E., and Knowles, R.G., Nitric oxide synthases: structure, function and inhibition, Biochem. J., 2001, vol. 357, pt. 3, pp. 593–615.
Pacher, P., Beckman, J.S., and Liaudet, L., Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease, Physiol. Rev., 2007, vol. 87, no. 1, pp. 315–424.
Dede, S., Deger, Y., Kahraman, T., and Kiliçalp, D., Effects of X-ray radiation on oxidation products of nitric oxide in rabbits treated with antioxidant compounds, Turk. J. Biochem., 2009, vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 15–18.
Forstermann, U. and Li, H., Therapeutic effect of enhancing endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression and preventing eNOS uncoupling, Br. J. Pharmacol., 2011, vol. 164, no. 2, pp. 213–223.
Tschudi, M.R., Mesaros, S., Luscher, T.F., and Malinski, T., Direct in situ measurement of nitric oxide in mesenteric resistance arteries. Increased decomposition by superoxide in hypertension, Hypertension, 1996, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 32–35.
Swei, A., Lacy, F., DeLano, F.A., and Schmid-Shonbein, G.W., Oxidative stress in the Dahl hypertensive rats, Hypertension, 1997, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 1628–1633.
Kerr, S., Brosman, M.J., McIntyre, M., Reid, J.L., Dominiczak, A.F., and Hamilton, C.A., Superoxide anion production is increased in a model of genetic hypertension: role of the endothelium, Hypertension, 1999, vol. 33, no. 6, pp. 1353–1358.
Pandey, K.B. and Rizvi, S.I., Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease, Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev., 2009, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 270–278.
Van Golde, P.H., van der Westelaken, M., Bouma, B.N., and van de Wiel, A., Characteristics of piraltin, a polyphenol concentrate, produced by freeze-drying of red wine, Life Sci., 2004, vol. 74, no. 9, pp. 1159–1166.
Das, S., Santani, D.D., and Dhalla, N.S., Experimental evidence for the cardioprotective effects of red wine, Exp. Clin. Cardiol., 2007, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 5–10.
Zabbarova, I. and Kanai, A., Targeted delivery of radioprotective agents to mitochondria, Mol. Interv., 2008, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 294–302.
Dohadwala, M.M. and Vita, J.A., Grapes and cardiovascular disease, J. Nutr., 2009, vol. 139, no. 9, pp. 1788S–1793s.
Basli, A., Soulet, St., Chaher, N., Merillon, J.-M., Chibane, M., Monti, J.-P., and Richard, T., Wine polyphenols: potential agents in neuroprotection, Oxid. Med. Cell Longev., 2012, vol. 2012, pp. 2–14.
Svobodova, A., Psotova, J., and Walterova, D., Natural phenolics in the prevention of UV-induced skin damage. A review, Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc Czech. Repub., 2003, vol. 147, no. 2, pp. 137–145.
Londhe, J.S., Devasagayam, T.P.A., Foo, L.Y., and Ghaskadbi, S.S., Radioprotective properties of polyphenols from Phyllanthus amarus Linn, J. Radiat. Res., 2009, vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 303–309.
Greenrod, W. and Fenech, M., The principal phenolic and alcoholic components of wine protect human lymphocytes against hydrogen peroxide- and ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage in vitro, Mutagenesis, 2003, vol. 18, no. 2, pp. 119–126.
Barnes, S., D’Alessandro, T., Kirk, M.C., Patel, R.P., Boersma, B.J., and Darley-Usmar, V.M., The importance of in vivo metabolism of polyphenols and their biological actions, in Phytochemicals: Mechanisms of Action, Meskin, M.S., et al., Eds., Florida: CRC Press, 2004, ch. 4, pp. 51–59.
Drel, V.R. and Sybirna, N., Protective effects of polyphenolics in red wine on diabetes associated oxidative/ nitrative stress in streptozotocin-diabetic rats, Cell Biol. Int., 2010, vol. 34, no. 12, pp. 1147–1153.
Nichols, J.A. and Katiyar, S.K., Skin photoprotection by natural polyphenols: Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and DNA repair mechanisms, Arch. Dermatol. Res., 2010, vol. 302, no. 2, pp. 71–83.
Singleton V.L., Orthofer, R., and Lamuela-Raventos, R.M., Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent, Methods Enzymol., 1999, vol. 299, pp. 152–178.
Miranda, K.M., Espey, M.G., and Wink, D.A., A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite, Nitric Oxide, 2001, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 62–71.
Dawson, J. and Knowles, R.G., A microtiter-plate assay of human NOS isoforms, Methods Mol. Biol., 1998, vol. 100, pp. 237–242.
Lowri, O.H., Rosebrough, N.J., Farr, A.L., and Randall, R.J., Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent, Biol. Chem., 1951, vol. 193, no. 1, pp. 265–275.
Laemmli, U.K., Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4, Nature, 1970, vol. 227, no. 5259, pp. 680–685.
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T., and Gordon, J., Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1979, vol. 76, no. 9, pp. 4350–4354.
Molla, M. and Panes, J., Radiation-induced intestinal inflammation, World J. Gastroenterol., 2007, vol. 13, no. 22, pp. 3043–3046.
McFarland, H.I., Puig, M., Grajkowska, L.T., Tsuji, K., Lee, J.P., Mason, K.P., Verthelyi, D., and Rosenberg, A.S., Regulatory T cells in γ irradiation-induced immune suppression, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 6, p. e39092.
Gisone, P., Dubner, D., Perez, M.D.R., Michelin, S., and Puntarulo, S., The role of nitric oxide in the radiation-induced effects in the developing brain, In Vivo, 2004, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 281–292.
Jelkmann, W., Regulation of erythropoietin production, J. Physiol., 2011, vol. 589, pt 6, pp. 1251–1258.
Liu, S.Z., Nonlinear dose-response relationship in the immune system following exposure to ionizing radiation: mechanisms and implications, Nonlinearity Biol. Toxicol. Med., 2003, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 71–92.
Prasad, K.N., Cole, W.C., and Hasse, G.M., Health risks of low dose ionizing radiation in humans: a review, Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood), 2004, vol. 229, no. 5, pp. 378–382.
Matsumoto, H., Takahashi, A., and Ohnishi, T., Nitric oxide radicals choreograph a radioadaptive response, Cancer Res., 2007, vol. 67, no. 18, pp. 8574–8579.
Roberts, R.A., Laskin, D.L., Smith, C.V., Robertson, F.M., Allen, E.M.G., Doorn, J.A., and Slikker, W., Nitrative and oxidative stress in toxicology and disease, Toxicol. Sci., 2009, vol. 112, no. 1, pp. 4–16.
Wink, D.A., Hines, H.B., Cheng, R.Y.S., Switzer, C.H., Flores-Santana, W., Vitek, M.P., Ridnour, L.A., and Colton, C.A., Nitric oxide and redox mechanisms in the immune response, J. Leukoc. Biol., 2011, vol. 89, no. 6, pp. 873–891.
Beckman, J.S., Beckman, J.W., Chen, J., Marshall, P.A., and Freeman, B.A., Apparent hydroxyl radical production by peroxinitrite: implications for endotherlial injury from nitric oxide and superoxide, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1990, vol. 87, no. 4, pp. 1620–1624.
Lee, C.I., Liu, X., and Zweier, J.L., Regulation of xanthine oxidase by nitric oxide and peroxynitrite, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, vol. 275, no. 13, pp. 9369–9376.
Sutherland, B.A., Rahman, R.M., Appleton, I., Mechanisms of action of green tea catechins, with a focus on ischemia-induced neurodegeneration, J. Nutr. Biochem., 2006, vol. 17, no. 5, pp. 291–306.
Wallace, T.C., Anthocyanins in cardiovascular disease, Adv. Nutr., 2011, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1–7.
Knowles, R.G. and Moncada, S., Nitric oxide synthases in mammals, Biochem. J., 1994, vol. 298, pt. 2, pp. 249–258.
Foster, M.W., Hess, D.T., and Stamler, J.S, Protein S-nitrosylation in health and disease: a current perspective, Trends Mol. Med., 2009, vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 391–404.
Wu, C., Parrott, A.M., Fu, C., Liu, T., Marino, S.M., Gladyshev, V.N., Jain, M.R., Baykal, A.T., Li, Q., Oka, S., Sadoshima, J., Beuve, A., Simmons, W.J., and Li, H., Thioredoxin 1-mediated post-translational modifications: reduction, transnitrosylation, denitrosylation, and related proteomics methodologies, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 2011, vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 2565–2604.
Anand, P. and Stamler, J.S., Enzymatic mechanisms regulating protein S-nitrosylation: implications in health and disease, J. Mol. Med. (Berl.), 2012, vol. 90, no. 3, pp. 233–244.
Hernansanz-Agustin, P., Izquierdo-Alvarez, A., Garcia-Ortiz, A., Ibiza, S., Serrador, J.M., and Martinez-Ruiz, A., Nitrosothiols in the immune system: signaling and protection, Antioxid. Redox. Signal., 2013, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 288–308.
Lu, C., Kavalier, A., Lukyanov, E., and Gross, S.S., S-sulfhydration/desulfhydration and S-nitrosylation/denitrosylation: a common paradigm for gasotransmitter signaling by H2S and NO, Methods, 2013, vol. 62, no. 2, pp. 177–181.
D’Alessandro, T., Prasain, J., Benton, M.R., Botting, N., Moore, R., Darley-Usmar, V., Patel, R., and Barnes, S., Polyphenols, inflammatory response, and cancer prevention: chlorination of isoflavones by human neutrophils, J. Nutr., 2003, vol. 133, no. 11, Suppl. 1, pp. 3773S–3777S.
Kamisaki, Y., Wada, K., Bian, K., Balabanli, B., Davis, K., Martin, E., Behbod, F., Lee, Y.-C., and Murad, F., An activity in rat tissues that modifies nitrotyrosine-containing proteins, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1998, vol. 95, no. 20, pp. 11584–11589.
Koeck, T., Fu, X., Hazen, S.L., Crabb, J.W., Stuehr, D.J., and Aulak, K.S., Rapid and selective oxygen-regulated protein tyrosine denitration and nitration in mitochondria, J. Biol. Chem., 2004, vol. 279, no. 26, pp. 27257–27262.
Monteiro, H.P., Arai, R.J., and Travassos, L.R., Protein tyrosine phosphorylation and protein tyrosine nitration in redox signaling, Antioxid. Redox Signal., 2008, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 843–889.
Kelly, G.S., Quercetin. Monograph, Altern. Med. Rev., 2011, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 172–194.
Leopoldini, M., Russo, N., and Toscano, M., The molecular basis of working mechanism of natural polyphenolic antioxidants, Food Chem., 2011, vol. 125, no. 2, pp. 288–306.
Ishimoto, H., Tai, A., Yoshimura, M., Amakura, Y., Yoshida, T., Hatano, T., and Ito, H., Antioxidative properties of functional polyphenols and their metabolites assessed by an ORAC assay, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 2012, vol. 76, no, 2, pp. 395–399.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Sabadashka, M., Sybirna, N. Reduction of radiation-induced nitrative stress in leucocytes and kidney cells of rats upon administration of polyphenolic complex concentrates from red wine. Cytol. Genet. 50, 187–195 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452716030099
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452716030099