Abstract
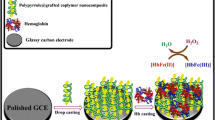
The purpose of the present study was to introduce a new voltammetric sensor of MXene/La3+-doped ZnO/hemoglobin (Hb) nanocomposite-modified glassy carbon electrode (MXene/La3+-doped ZnO/Hb/GCE) with a potential electro-conductivity and catalytic activity to detect the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). To this end, the method of cyclic voltammetry was used to analyze the electrochemical behavior of H2O2. The cathodic potential scanning showed the reduction peak at the potential of –0.2 V. The results revealed higher cathodic peak currents (Ipc) for the MXene/La3+-doped ZnO/Hb/GCE sensor when compared with a GCE alone. Moreover, using a differential pulse voltammetry, the range of linear concentration was obtained to be between 2.0 × 10–7 and 4.0 × 10–4 M, presenting the detection limit of 8.0 × 10–8 M. Additionally, acceptable recoveries were observed for the proposed approach in water samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Jing, Z., Yan, Y., Li, Z., X, Li., et al., An amperometric biosensor for the detection of hydrogen peroxide released from human breast cancer cells, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2013, vol. 41, p. 815.
Maji, S.K., Sreejith, S., Mandal, A.K., Ma, X., et al., Immobilizing gold nanoparticles in mesoporous silica covered reduced graphene oxide: A hybrid material for cancer cell detection through hydrogen peroxide sensing, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, vol. 6, p. 13648.
Xi, J., Xie, C., Yan, Z., Lu, W., et al., Pd nanoparticles decorated n-doped graphene quantum dotsn-doped carbon hollow nanospheres with high electrochemical sensing performance in cancer detection, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, vol. 8, p. 22563.
Ciriminna, R., Albanese, L., Meneguzzo, F., and Pagliaro, M., Hydrogen peroxide: A key chemical for today’s sustainable development, ChemSusChem, 2016, vol. 9, p. 3374.
Pennemann, H. and Kolb, G., Microstructured reactors as efficient tool for the operation of selective oxidation reactions, Catal. Today, 2016, vol. 278, p. 3.
Vishnu, N. and Kumar, A.S., Intrinsic iron-containing multiwalled carbon nanotubes as electro-Fenton catalyst for the conversion of benzene to redox-active surface-confined quinones, Chem. Electroanal. Chem., 2016, vol. 3, p. 986.
Amreen, K. and Kumar, A.S., A human whole blood chemically modified electrode for the hydrogen peroxide reduction and sensing: Real-time interaction studies of hemoglobin in the red blood cell with hydrogen peroxide, Electroanal. Chem., 2018, vol. 815, p. 189.
Nasir, M., Rauf, S., Muhammad, N., Nawaz, et al., Biomimetic nitrogen doped titania nanoparticles as a colorimetric platform for hydrogen peroxide detection, Colloid Interface Sci., 2017, vol. 505, p. 1147.
Qi, Z., Wang, L., You, Q., and Chen, Y., PA-Tb-Cu MOF as luminescent nanoenzyme for catalytic assay of hydrogen peroxide, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2017, vol. 96, p. 227.
Bhatia, P., Yadav, P., and Gupta, B.D., Surface plasmon resonance based fiber optic hydrogen peroxide sensor using polymer embedded nanoparticles, Sens. Actuators, B, 2013, vol. 182, p. 330.
Kafi, A.K.M., Wali, Q., Jose, R., Biswas, T.K., et al., A glassy carbon electrode modified with SnO2 nanofibers, polyaniline and hemoglobin for improved amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide, Microchim. Acta, 2017, vol. 184, p. 4443.
Tajik, S., Mahmoudi-Moghaddam, H., and Beito-llahi, H., Screen-printed electrode modified with La3+-doped Co3O4 nanocubes for electrochemical determination of hydroxylamine, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, vol. 166, p. B402.
Karimi-Maleh, H., Karimi, F., Alizadeh, M., and Sanati, A.L., Electrochemical sensors, a bright future in the fabrication of portable kits in analytical systems, Chem. Rec., 2020, vol. 20, p. 682.
Mahanthesha, K.R. and Swamy, B.K., Selective determination of norepinephrine at SAOS/MWCNT/MCPE: A voltammetric study, Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem., 2018, vol. 10, p. 321.
Karimi-Maleh, H., Karimi, F., Orooji, Y., Mansouri, G., et al., A new nickel-based co-crystal complex electrocatalyst amplified by NiO dope Pt nanostructure hybrid; a highly sensitive approach for determination of cysteamine in the presence of serotonin, Sci. Rep., 2020, vol. 10, p. 11699.
Xu, G., Huo, D., Hou, C., Zhao, Y., et al., A regenerative and selective electrochemical aptasensor based on copper oxide nanoflowers-single walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite for chlorpyrifos detection, Talanta, 2018, vol. 178, p. 1046.
Mahmoudi-Moghaddam, H., Tajik, S., and Beitollahi, H., A new electrochemical DNA biosensor based on modified carbon paste electrode using graphene quantum dots and ionic liquid for determination of topotecan, Microchem. J., 2019, vol. 150, p. 104085.
Sabour, B., One-step electrochemical preparation of oleic acid capped superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in ethanol medium and its characterization, Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem., 2018, vol. 10, p. 310.
Karimi-Maleh, H., Karimi, F., Malekmohammadi, S., Zakariae, N., et al., An amplified voltammetric sensor based on platinum nanoparticle/polyoxometalate/two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets composite and ionic liquid for determination of N-hydroxysuccinimide in water samples, J. Mol. Liq., 2020, vol. 310, p. 113185.
Tajik, S., Beitollahi, H., Garkani-Nejad, F., Kirlikovali, K.O., et al., Recent electrochemical applications of metal-organic framework-based materials, Cryst. Growth Des., 2020, vol. 20, p. 7034.
Tahernejade, R. and Sheikhshoaie, I., Kojic acid analysis in foodstuff using a reduced graphene oxide/NiO nanocomposite modified electrode, Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem., 2017, vol. 9, p. 784.
Beitollahi, H., Safaei, M., and Tajik, S., Different electrochemical sensors for determination of dopamine as neurotransmitter in mixed and clinical samples: A review, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res., 2019, vol. 6, p. 81.
Karimi-Maleh, H., Cellat, K., Arıkan, K., Savk, A., et al., Palladium–nickel nanoparticles decorated on functionalized-MWCNT for high precision non-enzymatic glucose sensing, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2020, vol. 250, p. 123042.
Suraniti, E., Abintou, M., Durand, F., and Mano, N., Heat and drying time modulate the O2 reduction current of modified glassy carbon electrodes with bilirubin oxidases, Bioelectrochemistry, 2012, vol. 88, p. 65.
Miraki, M., Karimi-Maleh, H., Taher, M.A., Cheraghi, S., et al., Voltammetric amplified platform based on ionic liquid/NiO nanocomposite for determination of benserazide and levodopa, J. Mol. Liq., 2019, vol. 278, p. 672.
Beitollahi, H., Tajik, S., Garkani-Nejad, F., and Safaei, M., Recent advances in ZnO nanostruture based electrochemical sensors and biosensors, J. Mater. Chem. B, 2020, vol. 8, p. 5826.
Shetti, N.P., Nayak, D.S., Malode, S.J., and Kulkarni, R.M., An electrochemical sensor for clozapine at ruthenium doped TiO2 nanoparticles modified electrode, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, vol. 247, p. 858.
Karimi-Maleh, H., Sheikhshoaie, M., Sheikhshoaie, I., Ranjbar, M., et al., A novel electrochemical epinine sensor using amplified CuO nanoparticles and an-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate electrode, New J. Chem., 2019, vol. 43, p. 2362.
Tahernejad-Javazmi, F., Shabani-Nooshabadi, M., and Karimi-Maleh, H., Analysis of glutathione in the presence of acetaminophen and tyrosine via an amplified electrode with MgO/SWCNTs as a sensor in the hemolyzed erythrocyte, Talanta, 2018, vol. 176, p. 208.
Bao, J., Qi, Y., Huo, D., Hou, J., et al., A sensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on AuNPs/CuO NWs-MoS2 modified electrode, J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, vol. 166, p. B1179.
Alavi-Tabari, S.A.R., Khalilzadeh, M.A., and Karimi-Maleh, H., Simultaneous determination of doxorubicin and dasatinib as two breast anticancer drugs uses an amplified sensor with ionic liquid and ZnO nanoparticle, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2018, vol. 811, p. 84.
Beitollahi, H., Mahmoudi-Moghaddam, H., and Tajik, S., Voltammetric determination of bisphenol a in water and juice using a lanthanum(III)-doped cobalt(II, III) nanocube modified carbon screen-printed electrode, Anal. Lett., 2019, vol. 52, p. 1432.
Zhu, Y., Pan, D., Hu, X., Han, H., et al., An electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide/gold nano-particles modified electrode for determination of iron in coastal waters, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, vol. 243, p. 1.
Baghizadeh, A., Karimi-Maleh, H., Khoshnama, Z., Hassankhani, A., et al., A Voltammetric sensor for simultaneous determination of vitamin c and vitamin B6 in food samples using ZrO2 nanoparticle/ionic liquids carbon paste electrode, Food Anal. Methods, 2015, vol. 8, p. 549.
Ren, Q., Shen, X., Sun, Y., Fan, R., et al., A highly sensitive competitive immunosensor based on branched polyethyleneimine functionalized reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles modified electrode for detection of melamine, Food Chem., 2020, vol. 304, p. 125397.
Zhang, C.J., Pinilla, S., McEvoy, N., Cullen, et al., Oxidation stability of colloidal two-dimensional titanium carbides (MXenes), Chem. Mater., 2017, vol. 29, p. 4848.
Zhang, C., Beidaghi, M., Naguib, M., Lukatskaya, M.R., et al., Synthesis and charge storage properties of hierarchical niobium pentoxide/carbon/niobium carbide (MXene) hybrid materials, Chem. Mater., 2016, vol. 28, p. 3937.
Li, H., Hou, Y., Wang, F., Lohe, M.R., et al., Flexible all-solid-state supercapacitors with high volumetric capacitances boosted by solution processable MXene and electrochemically exfoliated graphene, Adv. Energy Mater., 2017, vol. 7, p. 1601847.
Wang, H., Wu, Y., Yuan, X., Zeng, G., et al., Clay-inspired MXene-based electrochemical devices and photo-electrocatalyst: State-of-the-art progresses and challenges, Adv. Mater., 2018, vol. 30, p. 1704561.
Yukird, J., Kongsittikul, P., Qin, J., Chailapakul, O., et al., Zn@graphene nanocomposite modified electrode for sensitive and simultaneous detection of Cd(II) and Pb (II), Synth. Met., 2018, vol. 245, p. 251.
Ahmad, R., Tripathy, N., Jang, N.K., Khang, G., et al., Fabrication of highly sensitive uric acid biosensor based on directly grown ZnO nanosheets on electrode surface, Sens. Actuators, B, 2015, vol. 206, p. 146.
Ridhuan, N.S., Razak, K.A., and Lockman, Z., Fabrication and characterization of glucose biosensors by using hydrothermally grown ZnO nanorods, Sci. Rep., 2018, vol. 8, p. 13722.
Guo, W., Li, X., Qin, H., and Wang, Z., PEG-20000 assisted hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical ZnO flowers: structure, growth and gas sensor properties, Phys. E (Amsterdam), 2015, vol. 73, p. 163.
Bijad, M., Karimi-Maleh, H., and Khalilzadeh, M.A., Application of ZnO/CNTs nanocomposite ionic liquid paste electrode as a sensitive voltammetric sensor for determination of ascorbic acid in food samples, Food Anal. Methods, 2013, vol. 6, p. 1639.
Chen, W., Weng, W., Niu, X., Li, X., et al., Boron-doped graphene quantum dots modified electrode for electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of hemoglobin, J. Electroanal. Chem., 2018, vol. 823, p. 137.
Alhabeb, M., Maleski, K., Anasori, B., Lelyukh, P., et al., Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2TxMXene), Chem. Mater., 2017, vol. 29, p. 7633.
Bard, A.J. and Faulkner, L.R., Fundamentals and applications, Electrochem. Methods, 2001, vol. 2, p. 580.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
About this article
Cite this article
Fariba Beigmoradi, Hadi Beitollahi MXene/La3+ Doped ZnO/Hb Nanocomposite Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode as Novel Voltammetric Sensor for Determination of Hydrogen Peroxide. Surf. Engin. Appl.Electrochem. 57, 708–714 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3103/S106837552106003X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S106837552106003X