Abstract
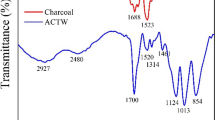
Herein we present spent black tea as an adsorbent for the removal of Congo red dye from aqueous solutions. The effects of various parameters such as pH, time, temperature, adsorbent dosage and adsorbate dosage on dye adsorption were investigated. Batch experiments were conducted using different amount of adsorbent material (2.5–1000 mg) at varying amounts of adsorbate (5–500 mg/L) at 35°C and different pH (1–13). A maximum dye removal of >80% was achieved with an adsorbent dose of 100 mg, adsorbate concentration of 5 mg/L under pH range of 6 within 5 min at room temperature. The experimental data were modeled by Langmuir, Freundlich and Temkin isotherms and conforms to both Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms but not to Temkin isotherm. The proposed spent black tea can be effectively used as a low cost adsorbent for the removal of Congo red dye.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma, J., and Janveja, B., Rasayan J. Chem., 2008, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 936–942.
Tan, I.A.W., Hameed, B.H., and Ahmad, A.L., Chem. Eng. J., 2007, vol. 127, no. 1, pp. 111–119.
Ayandal, O. S., Adeyi, O., Durojaiye, B., and Olafisoye O., Pol. J. Environ. Stud., 2012, vol. 21, no. 5, pp. 1147–1152.
Yao, Z., Wang, L., and Qi, J., Clean., 2009, vol. 37, pp. 642–648.
Abd EI–Latif, M.M., Ibrahim, A.M., and EI–Kady, M.F., J. Amer. Sci., 2010, vol. 6, pp. 267–283.
Ghaedi, M., Tashkhourian, J., Pebdani, A.A., et al., Korean. J. Chem. Eng., 2011, vol. 28, pp. 2255–2261.
Sen, T.K., Afroze, S., and Ang, H.M., Water, Air and Soil Pollut., 2011, vol. 218, pp. 499–515.
Sharma, Y.C. and Uma, S., J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2010, vol. 55, pp. 435–439.
Wang, S., Zhu, Z.H., Coomes, A., et al., J. Colloid. Interface Sci., 2005, vol. 284, pp. 440–446.
Mokgalaka, N.S., McCrindle, R.I., and Botha, B.M., J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom., 2004, vol. 19, pp. 1375–1378.
Hameed, B.H., J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, vol. 161, pp. 753–759.
Murugesan, G.S., Sathishkumar, M., and Swaminathan, K., Biores. Technol., 2006, vol. 97, pp. 483–487.
Wasewar, K.L., Atif, M., Prasad, B., and Mishra, I.M., Desalination, 2009, vol. 244, pp. 66–71.
Lavecchia, R., Pugliese, A., and Zuorro, A., Chem. Eng. Trans., 2010, vol. 19, pp. 73–78.
Sheku, A.K., Moyoa, M., Khamlichb, S., and Okonkwoa, J.O., Toxicol. Environ. Chem., 2014, vol. 96, pp. 1452–1462.
Saqib, A.N.S., Waseem, A., Khan, A.F., et al., Ecol. Eng., 2013, vol. 51, pp. 88–94.
Sarwar, A., Mahmood, Q., Bilal, M., et al., Desalin. Water. Treat., 2013, vol. 6, pp. 1–9.
Sarah, S., Shah, A. N. S., Mujahid, A., et al., Ibid., 2014, vol. 52, pp. 40–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The text was submitted by the authors in English.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, R.J., Saqib, A.N.S., Farooq, R. et al. Removal of Congo Red from Aqueous Solutions by Spent Black Tea as Adsorbent. J. Water Chem. Technol. 40, 206–212 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X18040057
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X18040057