Abstract
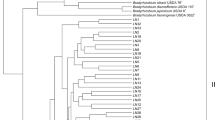
Strains of Azotobacter mediate in the nitrogen fixation process by reducing of N2 to ammonia. In this study, 50 strains were isolated from different rhizospheric soil in central Iran, by using soil paste-plate method. These strains were biochemically identified and characterized on differential LG medium based on morphological and physiological properties. Results obtained showed that identified strains were belonging to three species, namely A. chroococcum, A. vinelandii and A. beijernckii. In order to molecular analysis, the 16S rRNA gene was amplified using 27f and 1495r primers and PCR products were subsequently restricted with RsaI, HpaII and HhaI. Cluster analysis based on amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis were revealed intraspecific polymorphism and differentiated strains into two mains clusters, clusters A and B. Cluster A strains were related to the A. vinelandii, whereas cluster B strains were related to the A. chroococcum and A. beijerinckii. The results show that amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis is a powerful and discriminatory tool for the identification of members of the genus Azotobacter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becking, J.H., The family Azotobacteraceae, in The Procaryotes: A Handbook on Habitats, Isolation, and Identification of Bacteria, Heidelberg: Springer, 1981, p. 2440.
Tchan, Y.T., Azotobacteraceae, in Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Kreig, N.R. and Holt, J.G., Eds., Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Press, 1984, pp. 220–229.
Tejera, N., Lluch, C., Martinez-Toledo, M.V., and Gonzalez-Lopez, M.V., Isolation and characterization of Azotobacter and Azospirillum strains from the sugarcane rhizosphere, Plant Soil, 2005, vol. 270, no. 1, pp. 223–232.
Holt, J.G., Krieg, N.R., Sneath, P.H.A., et al., Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology, Philadelphia: Williams and Wilkins Press, 1994.
De Smedth, J., Bauwens, M., Tytgat, R., and De Ley, J., Intraand intergeneric similarities of ribosomal ribonucleic acid cistrons of free-living, nitrogenfixing bacteria, Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol., 1980, vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 106–122.
Jensen, V. and Petersen, E.J., Taxonomic studies on Azotobacter chroococcum Bejjerinck and Azotobacter beijerinckii Lipman, J. R. Vet. Agric. Coll., 1995, vol. 84, no. 4, pp. 107–126.
Clementi, F., Alginate production by Azotobacter vinelandii, Biotechnology, 1997, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 327–361.
Spinosa-Victoria, D., Lopez-Reyes, L., and Cruz-Benitez, A.D.L., Use of 16S rRNA gene for characterization of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria associated with corn, Articulo Cientiffico, Rev. Fitotec. Mex., 2009, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 31–37.
Bahri, S., Wahyudi, A.T., and Mubarik, N.R., Genetic diversity of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria of Bacillus sp. based on 16S rRNA sequence and amplified rDNA restriction analysis, Microbiology, 2009, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 12–16.
Turner, G.L. and Gibson, A.H., Measurement of nitrogen fixation by indirect means, in Methods for Evaluating Biological Nitrogen Fixation, Bergersen, F.J., Ed., Chichester: Wiley, 1980, pp. 111–158.
Rademaker, J.L. and W. de Bruijn, F.J., Characterization and classification of microbes by rep-PCR genomic finger printing and computer-assisted pattern analyses, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 1997, vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 665–667.
Weisburg, W.G., Barns, S.M., Pelletier, D.A., and Lane, D.J., 16S Ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study, J. Bacteriol., 1991, vol. 173, no. 2, pp. 697–703.
Aqquilanti, L., Cavalca, L., Clementi, F., et al., Amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis for the characterization of Azotobacteraceae: a contribution to the study of these free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria, Microbiol. Meth., 2004, vol. 57, no. 1, pp. 197–206.
Sokal, R.R. and Sneath, P.H.A., Principle of Numerical taxonomy, San Francisco: W.H. Freeman, 1963.
Rohlf, F.J., NTSYS-pc. Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System, version 1.8 Applied Biostatistics, New York: Setauket Press, 1998.
Shannon, C.E. and Weaver, W., The Mathematical Theory of Communication, Urbana: Univ. Illinois Press, 1949.
González-Lypez, J., Microorganismos Diazotrofos Asociados a Rances De Plantas No Leguminosas, Madris: Rueda Press, 1992.
Esquivel, G., Calva-Calva, G., Ferrera-Cerrato, R., et al., Encystment of Azotobacter nigricans grown diazotrophically on kerosene as sole carbon source, Arch. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 191, no. 3, pp. 275–281.
Ahmad, F., Ahmad, I., and Khan, M.S., Screening of freeliving rhizospheric bacteria for their multiple plant growth promoting activities, Microbiol. Res., 2006, vol. 163, no. 1, pp. 173–181.
Aquilanti, L., Favilli, F., and Clementi, F., Comparison of different strategies for isolation and preliminary identification of Azotobacter from soil samples, Soil Biol. Biochem., 2004, vol. 36, no. 1, pp. 1475–1483.
Amos, W. and Harwoud, J., Factors affecting levels of genetic diversity in natural population, Biol. Sci., 1998, vol. 353, no. 1366, pp. 177–186.
Baere, T.D., Mendoca, R., Claeys, G., et al., Evaluation of amplified rDNA restriction analysis (ARDRA) for the identification of cultured mycobacteria in diagnostic laboratory, BMC Microbiol., 2002, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 1–22.
Jayarao, B.M., Dorer, J.R., and Oliver, S.P., Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA of streptococcus and Enterococcus species of bovine origin, J. Clin. Microbiol., 1992, no. 9, pp. 2235–2240.
Sasaki, E., Osawa, R., Nishitani, Y., and Whiley, R.A., ARDRA and RAPD analysis of human and animal isolates of Streptococcus gallolyticus, J. Vet. Med. Sci., 2004, vol. 66, no. 11, pp. 1467–1470.
Tiedje, J.M., Asuming-Brempong, S., Nusslein, K., et al., Opening the black box of soil microbial diversity, Appl. Soil. Ecol., 1999, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 109–122.
Moyer, C.L., Tiedje, J.M., Dobbs, F.C., and Karl, D.M., A computer-simulated restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of bacterial smallsubunit rRNA genes: efficacy of selected tetrameric restriction enzymes for studies of microbial diversity in nature, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1996, vol. 62, no. 7, pp. 2501–2507.
Vaneechoutte, M., Rossau, R., and De Vos, P., Rapid identification of the Comamonadaceae with amplified ribosomal restriction analysis (ARDRA), FEMS Microbiol. Letts., 1992, vol. 93, no. 3, pp. 227–234.
Chéneby, D., Philippot, L., Hartmann, A., et al., 16s rRNA gene analysis for characterization of denitrifying bacteria isolated from three agricultural soils, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2000, vol. 34, no. 2, pp. 121–128.
Jang, J., Bongjoon, K., Jongho, L., et al., Identification of Weissella species by the genus-specific amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis, FEMS Microbiol. Letts., 2002, vol. 212, no. 1, pp. 29–34.
Ventura, M., Elli, M., Reniero, R., and Zink, R., Molecular microbial analysis of bifidobacterium isolates from different environments by the species-specific amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis (ARDRA), FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2001, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 113–121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
About this article
Cite this article
Mazinani, Z., Asgharzadeh, A. Genetic diversity of Azotobacter strains isolated from soils by amplified ribosomal DNA restriction analysis. Cytol. Genet. 48, 293–301 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452714050041
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3103/S0095452714050041