Abstract
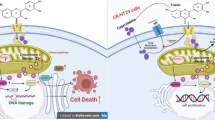
Nanoparticle-mediated combination therapies have significant impact on improving the therapeutic efficacy of cancer. The aim of the current work was to investigate the apoptotic efficacy of Zinc Oxid nanoparticles (ZnONPs) in combination with Cytochalasin H (CytoH) in human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. The anti cancer activity of combined treatment of CytoH and ZnONPs was performed using MTT assay, Annexin V-propidium iodide staining, Caspase assay, and Hoechst 33342 staining. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction was conducted to detect of p53 as a tumor suppressor gene expression in cancerous cells. Also, measurement of ROS generation was performed using flow cytometry. According to the MTT assay results, the combination of CytoH and ZnONPs significantly decreased the viability of cancer MCF-7 cells than either CytoH or ZnONPs alone as compared with normal HEK293 cells. The experiments, such as caspase 8 and 9 assay and Hoechst 33342 staining, showed that the combined treatment of CytoH and ZnONPs significantly increased the level of cell apoptosis pathway as compared with breast cancer cells treated with CytoH or ZnONPs alone. As demonstrated by annexin V/PI detection assay, the percentage of apoptotic MCF-7 cells was significantly increased, following combined treatment with CytoH and ZnONPs as compared with CytoH or ZnONPs alone. Moreover, by comparing the combination of CytoH and ZnONPs to CytoH and ZnONPs alone the ability of combined treatment to up-regulate p53 gene expression was observed. The results of the present study showed that combination of CytoH and ZnONPs could have a powerful synergistic cytotoxic effect on breast cancer cell line. Moreover, this is the first report indicating a new insight into how CytoH and ZnONPs can enhance apoptosis and cell growth in breast cancer cells.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
One-way analysis of variance
- CytoH:
-
Cytochalasin H
- DCF-DA:
-
2′,7′–dichlorofluorescein diacetate
- DCF:
-
2′, 7′ –dichlorofluorescin
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HEK293:
-
Human embryonic kidney 293
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- ZnONPs:
-
Zinc Oxid nanoparticles
References
Akhtar MJ, Ahamed M, Kumar S, Khan MM, Ahmad J, Alrokayan SA (2012) Zinc oxide nanoparticles selectively induce apoptosis in human cancer cells through reactive oxygen species. Int J Nanomedicine 7:845–857. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S29129
Ann LC, Mahmud S, Bakhori SK, Sirelkhatim A, Mohamad D, Hasan H, Seeni A, Rahman RA (2014) Antibacterial responses of zinc oxide structures against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Streptococcus pyogenes. Ceram Int 40:2993–3001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.10.008
Freeman JA, Espinosa JM (2012) The impact of post transcriptional regulation in the p53 network. Brief Funct Genom 12:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1093/bfgp/els058
Guo D, Wu C, Jiang H, Li Q, Wang X, Chen B (2008) Synergistic cytotoxic effect of different sized ZnO nanoparticles and daunorubicin against leukemia cancer cells under UV irradiation. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 93:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2008.07.009
Hackenberg S, Scherzed A, Harnisch W, Froelich K, Ginzkey C, Koehler C, Hagen R, Kleinsasser N (2012) Antitumor activity of photo-stimulated zinc oxide nanoparticles combined with paclitaxel or cisplatin in HNSCC cell lines. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 114:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2012.05.014
Hassan HFH, Mansour AM, Abo-Youssef AMH, Elsadek BEM, Messiha BAS (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticles as a novel anticancer approach; in vitro and in vivo evidence. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 44:235–243. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.12681
Hayat K, Gondal MA, Khaled MM, Ahmed S, Shemsi AM (2011) Nano ZnO synthesis by modified sol gel method and its application in heterogeneous photocatalytic removal of phenol from water. Appl Catal A Gen 393:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2010.11.032
Hu CMJ, Aryal S, Zhang L (2010) Nanoparticle-assisted combination therapies for effective cancer treatment. Therap Deliv 2:323–334. https://doi.org/10.4155/tde.10.13
Jain TK, Morales MA, Sahoo SK, Leslie-Pelecky DL, Labhasetwar V (2005) Iron oxide nanoparticles for sustained delivery of anticancer agents. Mol Pharm 2:194–205. https://doi.org/10.1021/mp0500014
Khalili H, Shandiz SAS, Baghbani-Arani F (2017) Anticancer properties of Phyto-synthesized silver nanoparticles from medicinal plant Artemisia tschernieviana Besser aerial parts extract toward HT29 human Colon adenocarcinoma cells. J Clust Sci 28:1617–1636. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-017-1172-6
Kitazumi I, Tsukahara M (2011) Regulation of DNA fragmentation: the role of caspases and phosphorylation. FEBS J 278:427–441. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07975.x
Kominami K, Nakabayashi J, Nagai T, Tsujimura Y, Chiba K, Kimura H, Miyawaki A, Sawasaki T, Yokota H, Manabe N, Sakamaki K (2012) The molecular mechanism of apoptosis upon caspase-8 activation: quantitative experimental validation of a mathematical model. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Mol Cell Res 1823:1825–1840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.07.003
Kutanzi KR, Yurchenko OV, Beland FA, Checkhun VF, Pogribny IP (2011) MicroRNA-mediated drug resistance in breast cancer. Clin Epigenetics 2:171–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13148-011-0040-8
Lee J, Yi JM, Kim H, Lee YJ, Park JS, Bang OS, Kim NS (2014) Cytochalasin H, an active anti-angiogenic constituent of the ethanol extract of Gleditsia sinensis. Thorns Biol Pharm Bull 37:6–12. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b13-00318
Lee JJ, Yazan LS, Abdullah CAC (2017) A review on current nanomaterials and their drug conjugate for targeted breast cancer treatment. Int J Nanomedicine 12:2373–2384. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S127329
Ma C, Song M, Zhang Y, Yan M, Zhang M, Bi H (2014) Nickel nanowires induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by generation of reactive oxygen species in HeLa cells. Toxicol Rep 1:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2014.04.008
Mignani S, Bryszewska M, Klajnert-Maculewicz B, Zablocka M, Majoral JP (2015) Advances in combination therapies based on nanoparticles for efficacious cancer treatment: an analytical report. Biomacromolecules 16:1–27. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm501285t
Namvar F, Rahman HS, Mohamad R, Azizi S, Mohd Tahir P, Chartrand MS, Yeap SK (2015) Cytotoxic Effects of Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Murine Cell Lines. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/593014
Natarajan P, May JA, Sanderson HM, Zabe M, Spangenberg P, Heptinstall S (2000) Effects of cytochalasin H, a potent inhibitor of cytoskeletal reorganisation, on platelet function. Platelets 11:467–476. https://doi.org/10.1080/09537100020027842
Powell D, Chandra S, Dodson K, Shaheen F, Wilt K, Ireland S, Syed M, Dash S, Wiese T, Mandal T, Kundu A (2017) Aptamer-functionalized hybrid nanoparticle for the treatment of breast cancer. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 114:108–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.01.011
Rasmussen JW, Martinez E, Louka P, Wingett DG (2010) Zinc oxide nanoparticles for selective destruction of tumor cells and potential for drug delivery applications. Expert Opin Drug Del 7:1063–1077. https://doi.org/10.1517/17425247.2010.502560
Salehi S, Shandiz SAS, Ghanbar F, Darvish MR, Ardestani MS, Mirzaie A, Jafari M (2016) Phyto-synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Artemisia marschalliana Sprengel aerial parts extract and assessment of their antioxidant, anticancer, and antibacterial properties. Int J Nanomedicine 11:1835–1846. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S99882
Sharon M, Choudhary AK, Kumar R (2010) Nanotechnology in agricultural diseases and food safety. J Phytol 2:83–92
Sonvico F, Mornet S, Vasseur S, Dubernet C, Jaillard D, Degrouard J, Hoebeke J, Duguet E, Colombo P, Couvreur P (2005) Folate-conjugated iron oxide nanoparticles for solid tumor targeting as potential specific magnetic hyperthermia mediators: synthesis, physicochemical characterization, and in vitro experiments. Bioconjug Chem 16:1181–1188. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc050050z
Su J, Lai H, Chen J, Li L, Wong YS, Chen T et al (2013) Natural Borneol, a Monoterpenoid compound, potentiates Selenocystine-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by enhancement of cellular uptake and activation of ROS-mediated DNA damage. PLoS ONE 8e63502. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063502
Sullivan KD, Galbraith MD, Andrysik Z, Espinosa JM (2018) Mechanisms of transcriptional regulation by p53. Cell Death Differ 25:133–143. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.174
Vafaee M, Ghamsari MS (2007) Preparation and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles by a novel sol–gel route. Mater Lett 61:3265–3268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2006.11.089
Wang W, Zhang L, Chen T, Guo W, Bao X, Wang D, Ren B, Wang H, Li Y, Wang Y, Chen S, Tang B, Yang Q, Chen C (2017) Anticancer effects of resveratrol-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles on human breast Cancer cells. Molecules 22:1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22111814
Wells JM, Cutler HG, Cole RJ (1976) Toxicity and plant growth regulator effects of cytochalasin H isolated from Phomopsis sp. Can J Microbiol 22:1137–1143. https://doi.org/10.1139/m76-165
Yi JM, Jinhee K, Jong-Shik P, Jun L, You Jin L, Jin Tae H, Ok-Sun B, No Soo K (2015) In Vivo anti-tumor effects of the ethanol extract of Gleditsia sinensis thorns and its active constituent, Cytochalasin H. Biol Pharm Bull 38:909–912. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b14-00647
Yuan L, Wang Y, Wang J, Xiao H, Liu X (2014) Additive effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles and isoorientin on apoptosis in human hepatoma cell line. Toxicol Lett 225:294–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.12.015
Yuan Y, Cai T, Xia X, Zhang R, Chiba P, Cai Y (2016) Nanoparticle delivery of anticancer drugs overcomes multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Drug Deliv 23:3350–3357. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2016.1178825
Zak AK, Majid WHA, Darroudi M, Yousefi R (2011) Synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles prepared in gelatin media. Mater Lett 65:70–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2010.09.029
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baghbani-Arani, F., Sadat Shandiz, S. Combination of Cytochalasin H and zinc oxide nanoparticles in human breast cancer: an insight into apoptosis study. Biologia 76, 763–772 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00611-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-020-00611-x