Abstract
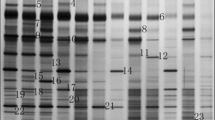
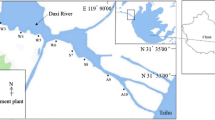
To compare the effect of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209) on microbial community from the Pearl River estuary, the microbial community at three in situ sites and the responses of microbial community to BDE-209 stressor were investigated. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of 16S rRNA gene showed that microbial community at site A2 has less diversity than sites A1 and A3. Physicochemical parameters (NH4-N, salinity and SiO3-Si) could significantly impact the microbial community composition in this estuary. In laboratory-incubated experiments, results indicated high concentration of BDE 209 (100 mg/kg) could increase the microbial diversity at sites A1 and A2, whereas reduced the microbial diversity at site A3. The unweighted pair group method with arithmetic means cluster analysis and principal component analysis demonstrated that the community structure changes at sites A1 and A2 were driven by the BDE 209 concentration, whereas at site A3 they depended on the incubation time. Thirty-five days after the addition of 100 mg/kg BDE 209, Firmicutes were found to be the dominant bacteria at sites A1 and A2. These data suggest the BDE 209 may have different effects on the microbial community in the Pearl River estuary.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BDE 209:
-
decabromodiphenyl ether
- CCA:
-
canonical correspondence analysis
- DCA:
-
detrended correspondence analysis
- DGGE:
-
denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis
- log Kow :
-
octanol-water partition coefficient
- MSM:
-
mineral salt medium
- PAHs:
-
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
- PBDEs:
-
polybrominated diphenyl ethers
- PCA:
-
principal component analysis
- PRD:
-
the Pearl River Delta
- UPGMA:
-
unweighted pair group method with arithmetic means
References
Altschul S.F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E.W. & Lipman D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410.
Amann R.I., Ludwig W. & Schleifer K.H. 1995. Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbialcells without cultication. Microbiol. Res. 59: 143–169.
An T., Chen J., Li G., Ding X., Sheng G., Fu J., Mai B. & O’Shea K.E. 2008. Characterization and the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 immobilized hydrophobic montmorillonite photocatalysts degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209). Catal. Today 139: 69–76.
Benson D.A., Cavanaugh M., Clark K., Karsch-Mizrachi I., Lipman D.J., Ostell J. & Sayers E.W. 2013. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Database issue): D36–D42.
Cao H., Hong Y., Li M. & Gu J.D. 2012. Community shift of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria along an anthropogenic pollution gradient from the Pearl River Delta to the South China Sea. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 94: 247–259.
Castle D.M., Montgomery M.T. & Kirchman D.L. 2006. Effects of naphthalene on microbial community composition in the Delaware estuary. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 56: 55–63.
de Wit C. 2002. An overview of brominated flame retardants in the environment. Chemosphere 46: 583–624.
Deng D., Guo J., Sun G., Chen X., Qiu M. & Xu M 2011. Aerobic debromination of deca-BDE: isolation and characterization of an indigenous isolate from a PBDE contaminated sediment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 65: 465–469.
Flocco C.G., Gomes N.C.M., Mac Cormack W. & Smalla K. 2009. Occurrence and diversity of naphthalene dioxygenase genes in soil microbial communities from the Maritime Antarctic. Environ. Microbiol. 11: 700–714.
Gerecke A.C., Hartmann P.C., Heeb N.V., Kohler H.P.E., Giger W., Schmid P., Zennegg M. & Kohler M. 2005. Anaerobic degradation of decabromodiphenyl ether. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39: 1078–1083.
Guan Y.F., Sojinu O.S.S., Li S.M & Zeng E.Y. 2009. Fate of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in the environment of the Pearl River estuary, South China. Environ. Pollut. 157: 2166–2172.
He J., Robrock K.R. & Alvarez-Cohen L. 2006. Microbial reductive debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs). Environ. Sci. Technol. 40: 4429–4434.
Hill T.C.J., Walsh K.A., Harris J.A. & Moffett B.F. 2003. Using ecological diversity measures with bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 43: 1–11.
Hong Y.G., Yin B. & Zheng T.L. 2011. Diversity and abundance of anammox bacterial community in the deep-ocean surface sediment from equatorial Pacific. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 89: 1233–1241.
Horner-Devine M.C., Lage M., Hughes J.B. & Bohannan B.J.M. 2004. A taxa-area relationship for bacteria. Nature 432: 750–753.
Huang H.W., Chang B.V. & Cheng C.H. 2012. Biodegradation of dibromodiphenyl ether in river sediment. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 68: 1–6.
Iwamoto T., Tani K., Nakamura K., Suzuki Y., Kitagawa M., Eguchi M. & Nasu M. 2000. Monitoring impact of in situ biostimulation treatment on groundwater bacterial community by DGGE. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 32: 129–141.
Liu G., Yu L., Li J., Liu X. & Zhang G. 2011a. PAHs in soils and estimated air soil exchange in the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Monit. Assess 173: 861–870.
Liu L., Zhu W., Xiao L. & Yang L. 2011b. Effect of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209) and dibromodiphenyl ether (BDE 15) on soil microbial activity and bacterial community composition. J. Hazard. Mater. 186: 883–890.
Mai B.X., Fu J.M., Zhang G., Lin Z., Min Y.S., Sheng G.Y. & Wang X.M. 2001. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from the Pearl river and estuary, China: spatial and temporal distribution and sources. Appl. Geochem. 16: 1429–1445.
Mai B.X., Chen S.J., Luo X.J., Chen L.G., Yang Q.S., Sheng G.Y., Peng P.G., Fu J.M. & Zeng E.Y. 2005. Distribution of polybrominated diphenyl ethers in sediments of the Pearl River Delta and adjacent South China Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39: 3521–3527.
Moon H.B., Kannan K., Lee S.J. & Choi M. 2007. Polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) in sediment and bivalves from Korean coastal waters. Chemosphere 66: 243–251.
Muyzer G. & Ramsing N.B. 1995. Molecular methods to study the organization of microbial communities. Water Sci. Technol. 32: 1–9.
Peng J.J., Cai C., Qiao M., Li H. & Zhu Y.G. 2010. Dynamic changes in functional gene copy numbers and microbial communities during degradation of pyrene in soils. Environ. Pollut. 158: 2872–2879.
Robrock K.R., Coelhan M., Sedlak D.L. & Alvarez-Cohen L. 2009. Aerobic biotransformation of polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) by bacterial isolates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43: 5705–5711.
Robrock K.R., Korytar P. & Alvarez-Cohen L. 2008. Pathways for the anaerobic microbial debromination of polybrominated diphenyl ethers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 42: 2845–2852.
Sun F.L., Wang Y.S., Wu M.L., Wang Y.T. & Li Q.P. 2011. Spatial heterogeneity of bacterial community structure in the sediments of the Pearl River estuary. Biologia 66: 574–584.
Suzuki M.T. & Giovannoni S.J. 1996. Bias caused by template annealing in the amplification of mixtures of 16S rRNA genes by PCR. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 625–630.
Tabor S. & Richardson C.C. 1987. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84: 4767–4771.
Tamura K., Peterson D., Peterson N., Stecher G., Nei M. & Kumar S. 2011. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28: 2731–2739.
ter Braak C.J.F. & Smilauer P. 2002. CANOCO Reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide: software for canonical community ordination (Version 4.5). Microcomputer Power. Ithaca, NY, USA.
Wang Y.S., Huang Y.J., Chen W.C. & Yen J.H. 2009. Effect of carbendazim and pencycuron on soil bacterial community. J. Hazard. Mater. 172: 84–91.
Wang Y.S., Lou Z.P., Sun C.C. & Sun S. 2008. Ecological environment changes in Daya Bay, China, from 1982 to 2004. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 56: 1871–1879.
Wu Y., He T., Zhong M., Zhang Y., Li E., Huang T. & Hu Z. 2009. Isolation of marine benzo[a]pyrene-degrading Ochrobactrum sp. BAP5 and proteins characterization. J. Environ. Sci. 21: 1446–1451.
Yao Y., Guan J., Tang P., Jiao H., Lin C., Wang J., Lu Z., Min H. & Gao H. 2010. Assessment of toxicity of tetrahydrofuran on the microbial community in activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 5213–5221.
Yogui G.T. & Sericano J.L. 2009. Polybrominated diphenyl ether flame retardants in the U.S. marine environment: a review. Environ. Int. 35: 655–666.
Zhang Y., Dong J., Yang Z., Zhang S. & Wang Y. 2008. Phylogenetic diversity of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in mangrove sediments assessed by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Arch. Microbiol. 190: 19–28.
Zhou H.W., Wong A.H.Y., Yu R.M.K., Park Y.D., Wong Y.S. & Tam N.F.Y. 2008. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-induced structural shift of bacterial communities in mangrove sediment. Microbiol. Ecol. 58: 153–160.
Zhu W., Liu L., Zou P., Xiao L. & Yang L. 2010. Effect of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209) on soil microbial activity and bacterial community composition. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 26: 1891–1899.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Electronic supplementary material. The online version of this article (DOI: 10.2478/s11756-013-0227-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, P., Wang, YS., Sun, CC. et al. Microbial community shift with decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE 209) in sediments of the Pearl River estuary, China. Biologia 68, 788–796 (2013). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0227-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-013-0227-x