Abstract
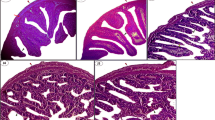
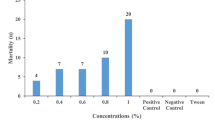
In addition to antibiotic properties, medicinal plants are important sources of chemicals with potential application as pesticides. The present study deals with antitermitic potential of seed extracts of Withania somnifera (Indian ginseng), Croton tiglium (jamalgoota) and Hygrophila auriculata (talimkhana). The seed extracts caused changes in tunneling behaviour, number of bacterial colonies in hindgut and activities of enzymes in midgut of Odontotermes obesus. C. tiglium showed the lowest LT50 (12.85 and 2.65 h) among the three seed extracts at concentrations of 50% (half dilution of the extract) and 100% (extract without dilution), respectively. There was no tunneling in soil treated with 100% concentration of seed extracts of W. somnifera and C. tiglium. Numbers of bacterial colonies in the gut of termites from soils treated with 50% and 100% concentrations of the three plants did not differ significantly, but they differed from those in termites from untreated soil. At 50% concentrations of seed extracts of the tested plants, the difference in hindgut enzyme activities was not obvious, however, at 100% concentrations the enzyme activities in the termites from soils treated with seed extracts significantly differed from controls and differences were also recorded between the plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams R.P., McDaniel C.A. & Carter F.I. 1988. Termiticidal activities in the heartwood, bark/sapwood and leaves of Juniperus species from the United States. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 16: 453–456.
Badshah H., Farmanullah Salihah Z., Aur Saljoqi & Shakur M. 2004. Toxic effects of ak (Calotripis procera) plant extracts against termites (Heterotermes indicola and Coptotermes heimi) (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Pakistan J. Biol. Sci. 7: 1603–1606.
Badshah H., Khan A.S., Farid A., Zeb A. & Khan A. 2005. Toxic effects of palpoluck Polygonum hydropepper L. and Bhang Cannabis sativa L. plants extracts against termites Heterotermes indicola (Wasmann) and Coptotermes heimi (Wasmann) (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 27: 705–710
Bignell D.E. & Eggleton P. 2000. Termites in ecosystems, pp. 363–387. In: Abe T.D., Bignell D.E. & Higashi M. (eds), Termites: Evolution, Sociality, Symbioses, Ecology, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Blaske V.U., Hertel H. & Forschler B.T. 2003. Repellent effect of isoborneol on subterranean termites (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae) in soils of different composition. J. Econ. Entomol. 96: 1267–1274.
Boue S.M. & Raina A.K. 2003. Effects of plant flavonoids on fecundity, survival and feeding of the Formosan subterranean termite. J. Chem. Ecol. 29: 2575–2584.
Chang S.T., Cheng S.S. & Wang S.Y. 2001. Antitermitic activity of essential oils and components from Taiwania (Taiwania cryptomerioides). J. Chem. Ecol. 27: 1267–1274.
Drapeau G. 1974. Protease from Staphylococcus aureus, p. 469. In: Lorand L. (ed.), Methods in Enzymology 45B, Acad. Press, NY.
Ijaz M. & Aslam M. 2003. Infestation trend of Odontotermes obesus (Rambur) on wheat crop (Triticum aestivum L.) in rainfed conditions. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2: 699–701.
Mahboob S., Shahid M., Iqbal T. & Jamil A. 2007. Screening leaves of medicinal plant extracts against gram negative bacterial strains, p. 105. In: 9th Int. Symp. Protein Structure Function Relationship, Workshop on Characterization of Proteins, Jan. 11–14, Univ. Karachi, Karachi, Pakistan.
Maistrello L., Henderson G. & Laine R.A. 2003. Comparative effects of vetiver oil, nootkatone and disodium octaborate tetrahydrate on Coptotermes formosanus and its symbiotic fauna. Pest Manage. Sci. 59: 58–68.
Mao L. & Henderson G. 2005. Antifeedant and toxic properties of plant alkaloids against Formosan subterranean termites, 0986. In: The ESA Annual Meeting and Exhibition, December, Ft. Lauderdale, FL.
Nihei K., Asaka Y., Mine Y. & Kubo I. 2005. Insect antifeedants from Croton jatrophoides: structures of zumketol, zumsenin, and zumsenol. J. Nat. Prod. 68: 244–247.
Ohkuma M., Noda S., Hongoh Y. & Kudo T. 2001. Coevolution of symbiotic systems of termites and their gut microorganisms. RIKEN Rev. 41: 73–77.
Richard W., Ibrahim S. & Henderson G. 2003. Effects of sesame seed extracts on the Formosan subterranean termite (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae), D0159. In: The 2003 ESA Annual Meeting and Exhibition, October, Cincinnati, OH.
Sbeghen A.C., Dalfovo V., Serafini L.A. & Monteiro de Barros N. 2002. Repellence and toxicity of basil, citronella, ho-sho and rosemary oils for the control of the termite, Cryptotermes brevis (Isoptera: Kalotermitidae). Sociobiology 40: 585–594.
Shields C.R., Orton T.J. & Stuber C.W. 1983. An outline of general resource needs and procedures for the electrophoretic separation of active enzymes from plant tissue, pp. 443–512. In: Tanksley S.D. & Orton T.J. (eds), Isozymes in Plant Genetics and Breeding, Elsevier Sci. Publish., B.V., Amsterdam.
Singh G., Singh O.P., Prasad Y.R., De-Lampasona M.P. & Catalan C. 2003. Chemical and biocidal investigations on rhizome volatile oil of Curcuma zedoaria Rosc—Part 32. Indian J. Chem. Technol. 10: 462–465.
Singh G., Singh O.P., Prasad Y.R., De-Lampasona M.P. & Catalan C. 2004. Chemical and insecticidal investigation in leaf oil of Coleus amboinicus Lour. J. Flavour Fragrance 17: 440–442.
Terras F.R.G., Schoofs H.M.E., de Bolle M.F.C., van Leuven F., Rees S.B., Vanderleyden J., Cammue B.P.A. & Broekaert W.F. 1992. Analysis of two novel classes of plant antifungal proteins from radish (Raphanus sativus) seeds. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 15301–15309.
Vidya M., Seeta R., Mishra C. & Deshpande L. 1984. A rapid and simplified procedure for purification of a cellulose from Fusarium lini. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 26: 41–45.
Waller D.A. 1996. Ampicillin, tetracycline and urea as protozocides for symbionts of Reticulitermes flavipes and R. virginicus (Isoptera: Rhinotermitidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 86: 77–81.
Zhu B.C., Henderson G., Chen E., Fei H. & Laine R.A. 2001. Evaluation of vetiver oil and seven insect-active essential oils against the Formosan subterranean termite. J. Chem. Ecol. 27: 1617–1625.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, S., Riaz, M.A., Malik, A.H. et al. Effect of seed extracts of Withania somnifera, Croton tiglium and Hygrophila auriculata on behavior and physiology of Odontotermes obesus (Isoptera, Termitidae). Biologia 62, 770–773 (2007). https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-007-0134-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2478/s11756-007-0134-0