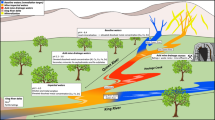
Abstract
Sediment cores were collected from the Tilbury Tidal Basin in the Thames Estuary to determine the depositional history of metals in the estuary. Profiles of metals in sediments deposited in the lower Thames Estuary show a 30–50% decrease in concentration for Ag, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn, and a 70% decrease for Hg in recent decades. Historic depth soundings data showed the decreases in metal concentrations occurred between 1944 and 1966. The decline in sediment metal concentrations has been attributed to reduced inputs to the estuary, following updating of the major sewage treatment works in 1959 and 1963. This is indicated by the through-core distribution of Mn which implies that prior to 1960 the sediments were deposited in anoxic conditions, which subsequently improved. An increase in Mn concentrations observed in one of the cores has been attributed to increases in the dissolved oxygen of the estuarine waters resulting from the increased efficiency of the sewage treatment works.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Anglian Sea Defence Management Study. 1991. Stage 3. Study Task Report—Tidal Circulation. Sir W. Halcrow and Partners and UK AEA, p. 32–42. Harwell, United Kingdom.
Attrill, M. J. andThomas, M. 1995. Heavy metal concentrations in sediment from the Thames Estuary, UK.Marine Pollution Bulletin 30:742–744.
Bourg, A. C. M. 1988. Physico-chemical speciation of trace elements in oxygenated estuarine water, p. 289–321.In T. S. West and H. W. Nurnberg (eds.), The Determination of Trace Metals in Natural Waters. Blackwell Publishers, Oxford, England.
Brown, M. J. andJ. N. Lester. 1979. Metal removal in activated sludge, the role of bacterial extracellular polymers.Water Research 13:817–837.
Bruland, K. W., K. Bertine, M. Koide, andE. D. Goldberg. 1974. History of Metal pollution in Southern California coastal zone.Environmental Science and Technology 8:425–432.
Bryan, G. W. and P. E. Gibbs. 1983. Heavy metals in the Fal estuary, Cornwall: A study of long-term contamination by mining waste and its effects on estuarine organisms.Marine Biology Association UK, Occidental Publishing., No 2.
Bryan, G. W. andW. J. Langston. 1992. Bioavailability, accumulation and effects of heavy metals in sediments with special reference to United Kingdom estuaries: A review.Environmental Pollution 76:89–131.
Calvert, S. E. andT. F. Pedresen. 1993. Geochemistry of recent oxic and anoxic marine sediment: Implications for the geological record.Marine Geology 113:67–88.
Chiffoleau, J. F., D. Cossa, D. Auger, andI. Truquet. 1994. Trace metal distribution, partition and fluxes in the Seine estuary (France) in low discharge regime.Marine Chemistry 47:145–158.
Cockburn, A. G. 1979. Beckton's part in the great Thames clean-up.Surveyor 15, March 1979.
De Groot, A. J. andE. Allersma. 1973. Field observations on the transport of heavy metals in sediments, p. 85–94.In P. A. Krendel (ed.), Heavy metals in the Aquatic Environment, Proceedings of the International Conference, Nashville, 1973, Pergamon Press Ltd., Oxford, England.
Edmond, J. M., A. Spivack, B. C. Grant, M. H. Hu, Z. X. Chen, S. Chen, andX. S. Zong. 1985. Chemical dynamics of the Changjiang estuary.Continental Shelf Research 4:17–36.
Fletcher, C. A., J. M. Bubb, andJ.N. Lester. 1994a. Magnitude and distribution of anthropogenic contaminants in salt marsh sediments of the Essex coast, UK. II. Selected metals and metalloids.Science of the Total Environment 155:47–59.
Fletcher, C. A., J. M. Bubb, andJ. N. Lester. 1994b. Magnitude and distribution of anthropogenic contaminants in salt marsh sediments of the Essex coast, UK. I. Topographical, and chemical characteristics.Science of the Total Environment 155:31–45.
Fletcher, C. A., N. C. Meakins, J. M. Bubb, andJ. N. Lester 1994. Magnitude and distribution of contaminants in salt marsh sediments of the Essex coast, UK. III. Chlorophenoxy acid ands-triazine herbicides.Science of the Total Environment 155:61–72.
Förstner, U. andG. T. W. Wittmann. 1979. Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Gaudette, H. E. andW. R. Flight. 1974. An inexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediments.Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 44(1):249–253.
Gobeil, C., N. Silverberg, andN. Silverberg 1981. Factors influencing particulate organic matter geochemistry in the St. Lawrence estuary turbidity maximum.Marine Chemistry 10: 123–140.
Goldstone, M. E., P. P. W. Kirk, andJ. N. Lester. 1990. The behaviour of heavy metals during wastewater treatment. I. Cadmium, chromium and copper.Science of the Total Environment 95:233–252.
Grant, A. andR. Middleton. 1990. An assessment of metal contamination of sediment in the Humber Estuary, U.K.Estuarine and Coastal Shelf Science 31:71–85.
Greeves, I. S. 1980. London Docks 1800–1980. A Civil Engineering History. Thomas Telford Ltd., London, England.
Inglis, C. C. andF. H. Allen. 1957. The regimen of the Thames Estuary as affected by currents, saliinities and river flows.Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers 7:827–878.
Jacobs, L. andS. Emerson. 1985. Partitioning and transport of metals across the O2/H2O interface in a permanently anoxic basin: Framvaren Fjord, Norway.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 49:1433–1444.
Kersten, M. 1988. Geobiological effects on the mobility of contaminants in marine sediments. p. XXX-XXX.In W. Salomons, B. L. Bayne, E. K. Duursma, and U. Förstner (eds.), Pollution of the North Sea Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany.
Kersten, M. andU. Förstner. 1987. Cadmium associations in freshwater and marine sediment, p. 51–88.In J. O. Nriagu and J. B. Sprague (eds.), Cadmium in the Aquatic Environment, Wiley Series in Advances in Environmental Science and Technology, Vol. 19, John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Kramer, K. J. M., R. Misdorp, G. Berger, andR. Duijts. 1991. Maximum pollutant concentrations at the wrong depth: A misleading pollution history in a sediment core.Marine Chemistry 36:183–198.
Lester, J. N. 1983. Significance and behaviour of heavy metals in waste water treatment processes. 1. Sewage treatment and effluent discharge.Science of the Total Environment 30:1–44.
Lester, J. N., R. M. Harrison, andR. Perry. 1979. The balance of heavy metals through a sewage treatment works 1. Lead, Cadmium and Copper.Science of the Total Environment 12:13–23.
Letzsch, W. S. andR. W. Frey. 1980. Deposition and erosion in a Holocene salt marsh, Sapelo Island, Georgia.Journal of Sedimentary petrology 50:529–542.
Lo, C. K. andY. S. Fung. 1992. Heavy metal pollution profiles of dated sediment cores from Hebe Haven, Hong Kong.Water Research 26:1605–1619.
Loring, D. H. 1991. Normalisation of heavy-metal data from estuarine and coastal sediments. ICESJournal of Marine Science 48:101–115.
Mitchell, J. K. 1976. Fundamentals of Soil Behaviour. Wiley, New York.
North Sea Task Force. 1993a. North Sea Quality Status Report 1993. ‘Report on sub-region 3b’, p. 40–51, Oslo and Paris Commissions, London.
North Sea Task Force. 1993b. North Sea Quality Status Report 1993. p. 24–25. Oslo and Paris Commissions, London.
O'Reilly Wiese, S., J. M. Bubb, andJ. N. Lester. 1995. The significance of sediment metal concentrations in two eroding Essex salt marshes.Marine Pollution Bulletin 30:190–199.
Paetzel, M. andH. Schrader. 1994. Do decreased trace metal concentrations in surficial Skagerrak sediments over the last 15–30 years indicate decreased pollution?.Environmental Pollution 84:213–226.
Pethick, J. S. 1981. Long-term accretion rates on tidal salt marshes.Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 51:571–577.
Pye, K. andP. W. French. 1993. Erosion and Accretion Processes on British Salt Marshes. Vol. 2, Database of British Salt Marshes. p. 215–237, and Vol. 3, National Survey of Accretion and Erosion Trends. p. 33-47. Cambridge Environmental Research Consultants Ltd, Cambridge, United Kingdom.
Rossin, A. C., R. M. Sterritt, andJ. N. Lester. 1981. The influence of process parameters on the removal of heavy metals in activated sludge.Water, Air and Soil Pollution 19:105–121.
Schmidt, H. andC. E. Reimers. 1991. The Recent History of Trace Metal Accumulation in the Santa Barbara Basin, Southern California Borderland.Estuarine and Coastal Shelf Science 33:485–500.
Scrimshaw, M. D., J. M. Bubb, andJ. N. Lester. 1994. Magnitude and distribution of contaminants in salt marsh sediments of the Essex coast. IV. Organochlorine insecticides and polychlorinated biphenyls.Science of the Total Environment 155:73–81.
Scrimshaw, M. D. andJ. N. Lester. 1995. Organochlorine contamination in sediments of the Inner Thames Estuary.Journal of the Institution of Water and Environmental Management 9:519–525.
Skowronek, F., J. Sagemann, F. Stenzel, andH. D. Schulz, 1994. Evolution of heavy-metal profiles in River Wester Estuary sediments, Germany.Environmental Geology 24:223–232.
Standing Committee of Analysis. 1980. Methods for the determination of waters: Suspended, settleable and total dissolved solids in waters and effluents. HMSO, London, United Kingdom.
Standing Committee of Analysis. 1981. The determination of alkalinity and acidity in water, 1981. HMSO, London, England.
Standing Committee of Analysits. 1987. Lithium, magnesium, calcium, strontium and barium in waters and sewage effluent by AAS, HMSO, London, England.
Tanner, C. B. andM. L. Jackson. 1947. Nomograph of sedimentation times for soil particles under gravity or centrifugal acceleration.Soil Science Society of America Proceedings 12:60–65.
Tessier, A., F. Rapin, andR. Carignan. 1985. Trace metals in oxic lake sediments: Possible adsorption onto iron oxyhydroxides.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 49:183–194.
Valette-Silver, N. J.. 1993. The use of sediment cores to reconstruct historical trends in contamination of estuarine and coastal sediments.Estuaries 16:577–588.
Windom, H., J. Byrd, R. Smith, Jr.,M. Hungspreugs, S. Dharmvanij, W. Thumtrakul, andP. Yeats. 1991. Trace metal—nutrient relationships in estuaries.Marine Chemistry 32:177–194.
Wood, L. B. 1982. The Restoration of the Tidal Thames, Adam Hilger Ltd., Bristol, England.
Zar, J. H., 1984. Biostatistical Analysis, Prentice-Hall Inc., New Jersey.
Zwolsman, J. G., G. W. Berger, andG. T. M. Van Eck. 1993. Sediment accumulation rates, historical input, postdepositional mobility and retention of major elements and trace metals in salt marsh sediments of the Scheldt estuary, SW Netherlands.Marine Chemistry 44:73–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Reilly Wiese, S.B., MacLeod, C.L. & Lester, J.N. A recent history of metal accumulation in the sediments of the Thames Estuary, United Kingdom. Estuaries 20, 483–493 (1997). https://doi.org/10.2307/1352608
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2307/1352608